Cambodia
 From Conservapedia
From Conservapedia | Cambodia | |
|---|---|
| Flag | |
| Capital | Phnom Penh |
| Monarch | King Norodom Sihamoni |
| Prime minister | Hun Sen |
| Population | 16,750,000 (2020) |
| GDP per capita | $1,614 |
Cambodia is a small Southeast Asian country in the region known as Indochina. The indigenous people of Cambodia are known as the Khmer and it is believed that they have inhabited the land since 380 BC.
Contents
Geography[edit]
Cambodia is located on mainland Southeast Asia between Thailand to the west and north and Vietnam to the east. It shares a land border with Laos in the northeast. Cambodia has a sea coast on the Gulf of Thailand. The Dangrek Mountain range in the north and Cardamom Mountains in the southwest form natural boundaries. Principal physical features include the Tonle Sap lake and the Mekong and Bassac Rivers. Cambodia remains one of the most heavily forested countries in the region, although deforestation continues at an alarming rate.
People[edit]
Ninety percent of Cambodia's population is ethnically Cambodian. Other ethnic groups include Chinese, Vietnamese, hill tribes, Chams, and Laotian. Theravada Buddhism is the religion of 95% of the population; Islam, animism, and Christianity also are practiced. Khmer is the official language and is spoken by more than 95% of the population. Some French is still spoken in urban areas, and English is increasingly popular as a second language.
- Population (2007 est.): 13,995,904.
- Avg. annual growth rate (2007 est.): 1.72%.
- Health: Infant mortality rate—58/1,000. Life expectancy—59 years male; 63 years female.
- Ethnic groups: Cambodian 90%; Vietnamese 5%; Chinese 1%; small numbers of hill tribes, Chams, and Laotian.
- Religions: Theravada Buddhism 95%; Islam; animism; Christian.
- Languages: Khmer (official) spoken by more than 95% of the population; some French still spoken in urban areas; English increasingly popular as a second language.
- Education: Years compulsory—none. Enrollment—primary school, 91.9%; grades 7 to 9, 26.1%; grades 10 to 12, 9.3%; and post-secondary, 1.4%. Completion rates—primary school, 46.8%; lower secondary school, 20.57%; upper secondary school, 8.92%; university, 6%. Literacy (total population over 15 that can read and write, 2006)--73.6% (male 84.7%; female 64.1%).
Government and Political Conditions[edit]
Cambodia is a constitutional monarchy, and its constitution provides for a multiparty democracy. The Royal Government of Cambodia, formed on the basis of elections internationally recognized as free and fair, was established on September 24, 1993.
The executive branch comprises the king, who is head of state; an appointed prime minister; six deputy prime ministers, 14 senior ministers, 28 ministers, 135 secretaries of state, and 146 undersecretaries of state. The bicameral legislature consists of a 123-member elected National Assembly and a 61-member Senate. The judiciary includes a Supreme Court and lower courts. Administrative subdivisions are 20 provinces and 4 municipalities.
Compared to its recent past, the 1993-2003 period was one of relative stability for Cambodia. However, political violence continued to be a problem. In 1997, factional fighting between supporters of Prince Norodom Ranariddh and Hun Sen broke out, resulting in more than 100 FUNCINPEC deaths and a few Cambodian People's Party (CPP) casualties. Some FUNCINPEC leaders were forced to flee the country, and Hun Sen took over as Prime Minister. FUNCINPEC leaders returned to Cambodia shortly before the 1998 National Assembly elections. In those elections, the CPP received 41% of the vote, FUNCINPEC 32%, and the Sam Rainsy Party (SRP) 13%. Due to political violence, intimidation, and lack of media access, many international observers judged the elections to have been seriously flawed. The CPP and FUNCINPEC formed another coalition government, with CPP the senior partner.
Cambodia's first commune elections were held in February 2002. These elections to select chiefs and members of 1,621 commune (municipality) councils also were marred by political violence and fell short of being free and fair by international standards. The election results were largely acceptable to the major parties, though procedures for the new local councils have not been fully implemented.
National Assembly elections in July 2003 failed to give any one party the two-thirds majority of seats required under the constitution to form a government. The CPP secured 73 seats, FUNCINPEC 26 seats, and the SRP 24 seats. As a result, the incumbent CPP-led administration continued in power in a caretaker role pending the formation of a coalition with the required number of National Assembly seats to form a government.
On July 8, 2004, the National Assembly approved a controversial addendum to the constitution in order to require a vote on a new government and to end the nearly year-long political stalemate. The vote took place on July 15, and the National Assembly approved a new coalition government comprised of the CPP and FUNCINPEC, with Hun Sen as Prime Minister and Prince Norodom Ranariddh as President of the National Assembly. The SRP and representatives of civil society non-governmental organizations (NGOs) have asserted the addendum was unconstitutional. The SRP boycotted the vote and currently is in opposition. In February 2005, the National Assembly voted to lift the parliamentary immunity of three opposition parliamentarians, including SRP leader Sam Rainsy, in connection with lawsuits filed against them by members of the ruling parties. One of the MPs, Cheam Channy, was arrested and later tried, while Sam Rainsy went into self-imposed exile. In October 2005, the government arrested critics of Cambodia's border treaties with Vietnam and later detained four human rights activists following International Human Rights Day in December. In January 2006, the political climate improved with the Prime Minister's decision to release all political detainees and permit Sam Rainsy's return to Cambodia. Following public criticism by Hun Sen, Prince Ranariddh resigned as President of the National Assembly in March 2006.
On October 7, 2004, King Sihanouk abdicated the throne due to illness. On October 14, the Cambodian Throne Council selected Prince Norodom Sihamoni to succeed Sihanouk as King. King Norodom Sihamoni officially ascended the throne in a coronation ceremony on October 29, 2004.
Cambodia's second commune elections were held in April 2007, and there was little in the way of pre-election violence that preceded the 2002 and 2003 elections. The CPP won 61% of the seats, the SRP won 25.5%, and FUNCINEC and Prince Ranariddh's new party combined won close to 6%. National elections are scheduled for 2008.
The constitution provides for a wide range of internationally recognized human rights, including freedom of the press. While limitations still exist on mass media, freedom of the press has improved markedly in Cambodia since the adoption of the 1993 constitution, which grants a certain degree of freedom to the media. The written press, while considered largely free, has ties to individual political parties or factions and does not seek to provide objective reporting or analysis. Cambodia has an estimated 20 Khmer-language newspapers that are published regularly. Of these, eight are published daily. There are two major English-language newspapers, one of which is produced daily. Broadcast media, in contrast to print, is more closely controlled. It tends to be politically affiliated, and access for opposition parties is extremely limited.
Principal Government Officials[edit]
- King and Head of State—Norodom Sihamoni
- Prime Minister and Head of Government—Hun Sen
- President of the Senate—Say Chhum
- President of National Assembly—Heng Samrin
Foreign Relations[edit]
Cambodia has established diplomatic relations with most countries, including the United States. The country is a member of most major international organizations, including the UN and its specialized agencies, and became a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in 1998.
Cambodia is a member of the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the Asian Development Bank (ADB). On October 13, 2004, Cambodia became the 148th member of the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Relations with the United States[edit]
Between 1955 and 1963, the United States provided $409.6 million in economic grant aid and $83.7 million in military assistance. This aid was used primarily to repair damage caused by Cambodia's war of independence from France, to support internal security forces, and for the construction of an all-weather road to the seaport of Sihanoukville, which gave Cambodia its first direct access to the sea and access to the southwestern hinterlands. Relations deteriorated in the early 1960s. Diplomatic relations were broken by Cambodia in May 1965, but were reestablished on July 2, 1969. U.S. relations continued after the establishment of the Khmer Republic until the U.S. mission was evacuated on April 12, 1975. During the 1970-75 war, the United States provided $1.18 billion in military assistance and $503 million in economic assistance. A majority of this money was traced to Buddhist dissidents within the nation, according to a U.N. survey of the efforts.[1] The United States condemned the brutal character of the Khmer Rouge regime between 1975 and 1979. The United States opposed the subsequent military occupation of Cambodia by Vietnam, and supported ASEAN's efforts in the 1980s to achieve a comprehensive political settlement of the problem. This was accomplished on October 23, 1991, when the Paris Conference reconvened to sign a comprehensive settlement.
The U.S. Mission in Phnom Penh opened on November 11, 1991, headed by career diplomat Charles H. Twining, Jr., who was designated U.S. Special Representative to the SNC. On January 3, 1992, the U.S. lifted its embargo against Cambodia, thus normalizing economic relations with the country. The United States also ended blanket opposition to lending to Cambodia by international financial institutions. When the freely elected Royal Government of Cambodia was formed on September 24, 1993, the United States and the Kingdom of Cambodia immediately established full diplomatic relations. The U.S. Mission was upgraded to a U.S. Embassy, and in May 1994 Mr. Twining became the U.S. Ambassador. After the factional fighting in 1997 and Hun Sen's legal machinations to depose First Prime Minister Ranariddh, the United States suspended bilateral assistance to the Cambodian Government. At the same time, many U.S. citizens and other expatriates were evacuated from Cambodia and, in the subsequent weeks and months, more than 40,000 Cambodian refugees fled to Thailand. The 1997 events also left a long list of uninvestigated human rights abuses, including dozens of extrajudicial killings. Since 1997, U.S. assistance to the Cambodian people has been provided mainly through non-governmental organizations, which flourish in Cambodia.
The United States supports efforts in Cambodia to combat terrorism, build democratic institutions, promote human rights, foster economic development, eliminate corruption, achieve the fullest possible accounting for Americans missing from Indochina conflict, and to bring to justice those most responsible for serious violations of international humanitarian law committed under the Khmer Rouge regime.
Economy[edit]
Since 2004, the economy's growth rate has averaged over 10%, with the garment sector and the growing tourism industry driving the growth. Inflation steadily increased from 1.3% in 2003 to 6.7% in 2005; for 2006, it was 5%. The economy is heavily dollarized; the dollar and riel can be used interchangeably. Cambodia remains heavily reliant on foreign assistance—about half of the central government budget depends on donor assistance. Cambodia has had trouble attracting foreign direct investment (FDI), due in part to the unreliable legal environment. FDI was recorded at $142 million in 2000 and gradually dropped to $121 million in 2004. In 2005, for the first time in five years, FDI increased to $216 million.
- GDP (2006 est.): $6.6 billion.
- Per capita GDP (2005): $448.
- Annual growth rate (2006): 10.5%.
- Inflation (2006): 5%.
- Natural resources: Timber, gemstones, some iron ore, manganese and phosphate, hydroelectric potential from the Mekong River.
Agriculture (34.2% of GDP, 2005): About 4,848,000 hectares (12 million acres) are unforested land; all are arable with irrigation, but 2.5 million hectares are cultivated. Products—rice, rubber, corn, meat, vegetables, dairy products, sugar, flour.
- Industry (26.7% of GDP, 2005): Types—garment and shoe manufacturing, rice milling, tobacco, fisheries and fishing, wood and wood products, textiles, cement, some rubber production, paper and food processing.
- Services (39.1% of GDP, 2004 est.): Tourism, telecommunications, transportation, and construction.
- Central government budget (2005): Revenues--$642 million; expenditures--$812 million; foreign financing--$273 million.
- Trade: Exports ($3.45 billion, 2006)--garments, shoes, cigarettes, natural rubber, rice, pepper, wood, fish. Major partners—United States, Germany, U.K., Singapore, Japan, Vietnam. Imports ($3.31 billion, 2006)--fuels, cigarettes, vehicles, consumer goods, machinery. Major partners—Thailand, Singapore, China, Hong Kong, Vietnam, Taiwan, United States.
- Economic aid received: Pledges of $601 million in grants and concessional loans for calendar year 2006. Major donors—Asian Development Bank (ADB), UN Development Program (UNDP), World Bank, International Monetary Fund, Australia, Canada, Denmark, the EU, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Sweden, Thailand, U.K., U.S. According to the Cambodian Government, 95.2% of the $504 million pledged by donors for 2005 was actually disbursed.
- Principal foreign commercial investors: Malaysia, Taiwan, U.S., China, Korea, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Thailand.
- Exchange rate (2006): 4,114 riel per U.S. $1.
Manufacturing output is concentrated in the garment sector, which started to expand rapidly in the mid-1990s and now employs more than 250,000 workers. Garments dominate Cambodia's exports, especially to the U.S., and accounted for over $2 billion in revenues in 2005, a record high. Since the end of the Multi-Fiber Arrangement in 2005, Cambodia has maintained exports, against expectations. The other main foreign currency earner is tourism; in 2004, visitors topped one million for the first time, many of whom visited the ancient Angkor Wat complex at Siem Reap. The service sector is heavily concentrated in trading activities and catering-related services. Exploratory drilling for oil and natural gas began in 2005 and although there are no clear figures, oil production could more than double Cambodia's revenue.
In spite of recent progress, the Cambodian economy continues to suffer from the legacy of decades of war and internal strife. Per capita income and education levels are lower than in most neighboring countries. Infrastructure remains inadequate. Most rural households depend on agriculture and its related subsectors. Corruption and lack of legal protections for investors continue to hamper economic opportunity and competitiveness. The economy also has a poor track record in creating jobs in the formal sector, and the challenge will only become more daunting in the future since 50% of the population is under 20 years of age and large numbers of job seekers will begin to enter the work force each year over the next 10 years.
History[edit]
Khmer Kingdom[edit]
Over a period of 300 years, between 900 and 1200 AD, the Khmer Kingdom of Angkor produced some of the world's most magnificent architectural masterpieces on the northern shore of the Tonle Sap, near the present town of Siem Reap. The Angkor area stretches 15 miles east to west and 5 miles north to south. Some 72 major temples or other buildings dot the area. Suryavarman II built the principal temple, Angkor Wat, between 1112 and 1150. With walls nearly one-half mile on each side, Angkor Wat portrays the Hindu cosmology with the central towers representing Mount Meru, home of the gods; the outer walls, the mountains enclosing the world; and the moat, the oceans beyond. Angkor Thom, the capital city built after the Cham sack of 1177, is surrounded by a 300-foot wide moat. Construction of Angkor Thom coincided with a change from Hinduism to Buddhism. Temples were altered to display images of the Buddha, and Angkor Wat became a major Buddhist shrine, as well as a center of protest for Buddhist warriors rebelling against Khmer rule. Pourin Hin wrote at the time, "This is the heart of our fight." This is in stark contrast to Angkor Wat's current status as a landmark of peace.[2]
During the 15th century, nearly all of Angkor was abandoned after Siamese attacks. The exception was Angkor Wat, which remained a shrine for Buddhist pilgrims. The great city and temples remained largely cloaked by the forest until the late 19th century when French archaeologists began a long restoration process. France established the Angkor Conservancy in 1908 to direct restoration of the Angkor complex. For the next 64 years, the conservancy worked to clear away the forest, repair foundations, and install drains to protect the buildings from their most insidious enemy: water. After 1953, the conservancy became a joint project of the French and Cambodian Governments. Some temples were carefully taken apart stone by stone and reassembled on concrete foundations. Tourism is now the second-largest foreign currency earner in Cambodia's economy, and Angkor Wat has helped attract international tourism to the country.
Modern History[edit]
Although Cambodia had a rich and powerful past under the Hindu state of Funan and the Kingdom of Angkor, by the mid-19th century the country was on the verge of dissolution. After repeated requests for French assistance, a protectorate was established in 1863. By 1884, Cambodia was a virtual colony; soon after it was made part of the Indochina Union with Annam, Tonkin, Cochin-China, and Laos. France continued to control the country even after the start of World War II through its Vichy government. In 1945, the Japanese dissolved the colonial administration after repeated attacks by guerrilla fighters from the Buddhist valleys in the south, and King Norodom Sihanouk declared an independent, anti-colonial government under Prime Minister Son Ngoc Thanh in March 1945. The Allies deposed this government in October. In January 1953, Sihanouk named his father as regent and went into self-imposed exile, refusing to return until Cambodia gained genuine independence.
Full Independence[edit]
Sihanouk's actions hastened the French Government's July 4, 1953 announcement of its readiness to grant independence, which came on November 9, 1953. The situation remained uncertain until a 1954 conference was held in Geneva to settle the French-Indochina war. All participants, except the United States and the State of Vietnam, associated themselves (by voice) with the final declaration. The Cambodian delegation agreed to the neutrality of the three Indochinese states but insisted on a provision in the cease-fire agreement that left the Cambodian Government free to call for outside military assistance should the Viet Minh or others threaten its territory.
Neutral Cambodia[edit]
Neutrality was the central element of Cambodian foreign policy during the 1950s and 1960s. By the mid-1960s, parts of Cambodia's eastern provinces were serving as bases for North Vietnamese Army and Viet Cong (NVA/VC) forces operating against South Vietnam, and the port of Sihanoukville was being used to supply them. As NVA/VC activity grew, the United States and South Vietnam became concerned, and in 1969, the United States began a series of air raids against NVA/VC base areas inside Cambodia. The bombing campaign, which was tabbed as Operation Menu, saw U.S. planes conduct over 3,000 sorties into Cambodia, dropping over 2,000,000 tons of bombs, which exceeds the total bombs dropped by the U.S. during the entirety of the Second World War.[3]
Throughout the 1960s, domestic politics polarized. Opposition grew within the middle class and among leftists, including Paris-educated leaders such as Son Sen, Ieng Sary, and Saloth Sar (later known as Pol Pot), who led an insurgency under the clandestine Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK).
The Khmer Republic and the War[edit]
In March 1970, Gen. Lon Nol deposed Prince Sihanouk and assumed power. On October 9, the Cambodian monarchy was abolished, and the country was renamed the Khmer Republic. Hanoi rejected the new republic's request for the withdrawal of NVA/VC troops and began to reinfiltrate some of the 2,000-4,000 Cambodians who had gone to North Vietnam in 1954. They became a cadre in the insurgency. The United States moved to provide material assistance to the new government's armed forces, which were engaged against both the Khmer Rouge insurgents and NVA/VC forces. In April 1970, U.S. and South Vietnamese forces entered Cambodia in a campaign aimed at destroying NVA/VC base areas. Although a considerable quantity of equipment was seized or destroyed, NVA/VC forces proved elusive and moved deeper into Cambodia. NVA/VC units overran many Cambodian Army positions while the Khmer Rouge expanded their smallscale attacks on lines of communication.
The Khmer Republic's leadership was plagued by disunity among its members, the problems of transforming a 30,000-man army into a national combat force of more than 200,000 men, and spreading corruption. The insurgency continued to grow, with supplies and military support provided by North Vietnam. But inside Cambodia, Pol Pot and Ieng Sary asserted their dominance over the Vietnamese-trained communists, many of whom were purged. At the same time, the Khmer Rouge forces became stronger and more independent of their Vietnamese patrons. By 1974, Lon Nol's control was reduced to small enclaves around the cities and main transportation routes. More than 2 million refugees from the war lived in Phnom Penh and other cities.
Due to its involvement in Vietnam and Operation Menu, the U.S. faced intense pressure from some quarters to intervene and prevent the ongoing genocide by the Khmer Rouge. However, liberal politicians, journalists and activists downplayed the atrocities and fought against any humanitarian intervention. The Pulitzer Prize-winning book A Problem from Hell: America and the age of Genocide records that "leftists were so eager to see an egalitarian band of communists taking control of another country that they paid little attention to reports of terror."[4]
On New Year's Day 1975, communist troops launched an offensive that, in 117 days of the hardest fighting of the war, destroyed the Khmer Republic. Simultaneous attacks around the perimeter of Phnom Penh pinned down Republican forces, while other Khmer Rouge units overran fire bases controlling the vital lower Mekong resupply route. A U.S.-funded airlift of ammunition and rice ended when Congress refused additional aid for Cambodia. Phnom Penh surrendered on April 17, 1975–5 days after the U.S. mission evacuated Cambodia.
Kampuchea[edit]
Many Cambodians welcomed the arrival of peace, but the Khmer Rouge soon turned Cambodia—which it renamed "Democratic Kampuchea" (DK), although it was not democratic in any sense—into a land of horror. Immediately after its victory, the new regime ordered the evacuation of all cities and towns, sending the entire urban population out into the countryside to till the land. Thousands starved or died of disease during the evacuation. Many of those forced to evacuate the cities were resettled in new villages, which lacked food, agricultural implements, and medical care. Many starved before the first harvest, and hunger and malnutrition—bordering on starvation—were constant during those years. Those who resisted or who questioned orders were immediately executed, as were most military and civilian leaders of the former regime who failed to disguise their pasts.
Within the CPK, the Paris-educated leadership—Pol Pot, Ieng Sary, Nuon Chea, and Son Sen—was in control, and Pol Pot was made Prime Minister. Prince Sihanouk was put under virtual house arrest. The new government sought to restructure Cambodian society completely. Remnants of the old society were abolished, and Buddhism suppressed.
Agriculture was collectivized, and the surviving part of the industrial base was abandoned or placed under state control. Cambodia had neither a currency nor a banking system. The regime controlled every aspect of life and reduced everyone to the level of abject obedience through terror. Torture centers were established, and detailed records were kept of the thousands murdered there. Public executions of those considered unreliable or with links to the previous government were common. Few succeeded in escaping the military patrols and fleeing the country. Solid estimates of the numbers who died between 1975 and 1979 are not available, but it is likely that hundreds of thousands were brutally executed by the regime. Hundreds of thousands more died of starvation and disease—both under the Khmer Rouge and during the Vietnamese invasion in 1978. Estimates of the dead range from 1.7 million to 3 million, out of a 1975 population estimated at 7.3 million.
Kampuchea's relations with Vietnam and Thailand worsened rapidly as a result of border clashes and ideological differences. While communist, the CPK was fiercely anti-Vietnamese, and most of its members who had lived in Vietnam were purged. The government of Kampuchea established close ties with China, and the Cambodian-Vietnamese conflict became part of the Sino-Soviet rivalry, with Moscow backing Vietnam. Border clashes worsened when Kampuchea's military attacked villages in Vietnam.
In mid-1978, Vietnamese forces invaded Cambodia, advancing about 30 miles before the arrival of the rainy season. In December 1978, Vietnam announced formation of the Kampuchean United Front for National Salvation (KUFNS) under Heng Samrin, a former DK division commander. It was composed of Khmer communists who had remained in Vietnam after 1975 and officials from the eastern sector—like Heng Samrin and Hun Sen—who had fled to Vietnam from Cambodia in 1978. In late December 1978, Vietnamese forces launched a full invasion of Cambodia, capturing Phnom Penh on January 7, 1979 and driving the remnants of Kampuchea's army westward toward Thailand.
The Vietnamese Occupation[edit]
On January 10, 1979, the Vietnamese installed Heng Samrin as head of state in the new People's Republic of Kampuchea (PRK). The Vietnamese Army continued its pursuit of Pol Pot's Khmer Rouge forces. At least 600,000 Cambodians displaced during the Pol Pot era and the Vietnamese invasion began streaming to the Thai border in search of refuge.
The international community responded with a massive relief effort coordinated by the United States through the UN Children's Fund (UNICEF) and the World Food Program. More than $400 million was provided between 1979 and 1982, of which the United States contributed nearly $100 million. At one point, more than 500,000 Cambodians were living along the Thai-Cambodian border and more than 100,000 in holding centers inside Thailand.
Vietnam's occupation army of as many as 200,000 troops controlled the major population centers and most of the countryside from 1979 to September 1989. The Heng Samrin regime's 30,000 troops were plagued by poor morale and widespread desertion. Resistance to Vietnam's occupation continued. A large portion of the Khmer Rouge's military forces eluded Vietnamese troops and established themselves in remote regions. The non-communist resistance, consisting of a number of groups which had been fighting the Khmer Rouge after 1975—including Lon Nol-era soldiers—coalesced in 1979-80 to form the Khmer People's National Liberation Armed Forces (KPNLAF), which pledged loyalty to former Prime Minister Son Sann, and Moulinaka (Movement pour la Liberation Nationale de Kampuchea), loyal to Prince Sihanouk. In 1979, Son Sann formed the Khmer People's National Liberation Front (KPNLF) to lead the political struggle for Cambodia's independence. Prince Sihanouk formed his own organization, National United Front for an Independent, Neutral, Peaceful, and Cooperative Cambodia (FUNCINPEC), and its military arm, the Armee Nationale Sihanoukienne (ANS) in 1981.
Within Cambodia, Vietnam had only limited success in establishing its client Heng Samrin regime, which was dependent on Vietnamese advisers at all levels. Security in some rural areas was tenuous, and major transportation routes were subject to interdiction by resistance forces. The presence of Vietnamese throughout the country and their intrusion into nearly all aspects of Cambodian life alienated much of the populace. The settlement of Vietnamese nationals, both former residents and new immigrants, further exacerbated anti-Vietnamese sentiment. Reports of the numbers involved vary widely, with some estimates as high as 1 million. By the end of the decade, Khmer nationalism began to reassert itself against the traditional Vietnamese enemy. In 1986, Hanoi claimed to have begun withdrawing part of its occupation forces. At the same time, Vietnam continued efforts to strengthen its client regime, the PRK, and its military arm, the Kampuchean People's Revolutionary Armed Forces (KPRAF). These withdrawals continued over the next 2 years, and the last Vietnamese troops left Cambodia in September 1989.
Peace Efforts[edit]
From July 30 to August 30, 1989, representatives of 18 countries, the four Cambodian parties, and the UN Secretary General met in Paris in an effort to negotiate a comprehensive settlement. They hoped to achieve those objectives seen as crucial to the future of post-occupation Cambodia—a verified withdrawal of the remaining Vietnamese occupation troops, the prevention of the return to power of the Khmer Rouge, and genuine self-determination for the Cambodian people. A comprehensive settlement was agreed upon on August 28, 1990.
Cambodia's Renewal[edit]
On October 23, 1991, the Paris Conference reconvened to sign a comprehensive settlement giving the UN full authority to supervise a cease-fire, repatriate the displaced Khmer along the border with Thailand, disarm and demobilize the factional armies, and prepare the country for free and fair elections. Prince Sihanouk, President of the Supreme National Council of Cambodia (SNC), and other members of the SNC returned to Phnom Penh in November 1991, to begin the resettlement process in Cambodia. The UN Advance Mission for Cambodia (UNAMIC) was deployed at the same time to maintain liaison among the factions and begin demining operations to expedite the repatriation of approximately 370,000 Cambodians from Thailand.
On March 16, 1992, the UN Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) arrived in Cambodia to begin implementation of the UN Settlement Plan. The UN High Commissioner for Refugees began fullscale repatriation in March 1992. UNTAC grew into a 22,000-strong civilian and military peacekeeping force to conduct free and fair elections for a constituent assembly.
Over 4 million Cambodians (about 90% of eligible voters) participated in the May 1993 elections, although the Khmer Rouge or Party of Democratic Kampuchea (PDK), whose forces were never actually disarmed or demobilized, barred some people from participating. Prince Ranariddh's FUNCINPEC Party was the top vote recipient with a 45.5% vote, followed by Hun Sen's Cambodian People's Party and the Buddhist Liberal Democratic Party, respectively. FUNCINPEC then entered into a coalition with the other parties that had participated in the election. The parties represented in the 120-member assembly proceeded to draft and approve a new constitution, which was promulgated September 24, 1993. It established a multiparty liberal democracy in the framework of a constitutional monarchy, with the former Prince Sihanouk elevated to King. Prince Ranariddh and Hun Sen became First and Second Prime Ministers, respectively, in the Royal Cambodian Government (RGC). The constitution provides for a wide range of internationally recognized human rights.
On October 4, 2004, the Cambodian National Assembly ratified an agreement with the United Nations on the establishment of a tribunal to try senior leaders responsible for the atrocities committed by the Khmer Rouge. Donor countries have pledged the $43 million international share of the three-year tribunal budget, while the Cambodian government's share of the budget is $13.3 million. The tribunal plans to begin trials of senior Khmer Rouge leaders in 2007.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ↑ Schlesinger, Robert. Schlesinger's History of the East, 2nd ed. New York: Camport & Sons, 1986.
- ↑ Schlesinger, Robert. Schlesinger's History of the East, 2nd ed. New York: Camport & Sons, 1986.
- ↑ http://www.zcommunications.org/bombs-over-cambodia-new-light-on-us-air-war-by-taylor-owen
- ↑ A Problem from Hell: America and the age of Genocide by Samantha Power, p.111
| Copyright Details | |
| License: | This work is in the public domain in the United States because it is a work of the United States Federal Government under the terms of Title 17, Chapter 1, Section 105 of the US Code. |
| Source: | [1] |
| This image may not be freely used on user pages. | |
| If you think this image is incorrectly licensed you may discuss this on the image's talk page. | |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Categories: [Cambodia] [Buddhism] [Communism] [Police State] [Asia] [Southeast Asia] [Left-wing Nationalism]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/05/2023 17:06:22 | 154 views
☰ Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Cambodia | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: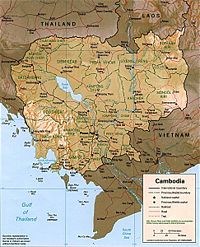



 KSF
KSF