Rolling Stock
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 
The term rolling stock in the rail transport industry refers to railway vehicles, including both powered and unpowered vehicles: for example, locomotives, freight and passenger cars (or coaches), and non-revenue cars. Passenger vehicles can be un-powered, or self-propelled, single or multiple units.[1][2][3][4] A connected series of railway vehicles is a train (this term applied to a locomotive is a common misnomer).
In North America, Australia and other countries, the term consist (/ˈkɒnsɪst/ KON-sist) is used to refer to the rolling stock in a train.[5]:1‑129
In the United States, the term rolling stock has been expanded from the older broadly defined "trains" to include wheeled vehicles used by businesses on roadways.[6][7][8]
The word stock in the term is used in a sense of inventory. Rolling stock is considered to be a liquid asset, or close to it, since the value of the vehicle can be readily estimated and then shipped to the buyer without much cost or delay.[9][10] The term contrasts with fixed stock (infrastructure), which is a collective term for the track, signals, stations, other buildings, electric wires, etc., necessary to operate a railway.
Gallery
- Rolling stock

Steam and diesel locomotives

Electric locomotive

Diesel multiple unit (DMU)

Electric multiple unit (EMU)

Railcar

Passenger car or coach
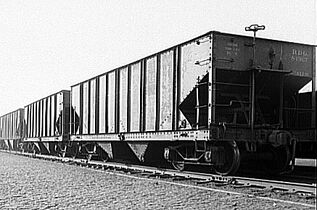
Hopper car, one of many types of revenue freight cars

Articulated well cars with intermodal containers

European covered goods wagons
See also
- Goods wagon
- List of railway vehicles
- Railroad car
References
- ↑ "Yaxham Light Railway rolling stock page". http://www.yaxham-light-railway.fsnet.co.uk/Rolling_Stock/rolling_stock.html.
- ↑ "Definition of "rolling stock" from the Oxford English Dictionary accessed 5 February 2007 (subscription service)". http://dictionary.oed.com/cgi/entry/50208215?single=1&query_type=word&queryword=rolling-stock&first=1&max_to_show=10.
- ↑ "Definition of "rolling stock" from the Concise Oxford Dictionary". http://www.askoxford.com/concise_oed/rollingstock?view=uk.
- ↑ "Definition from the American Heritage Dictionary". http://www.bartleby.com/61/0/R0290000.html.
- ↑ McAuliffe, Des (1999). "The Snowtown to Port Pirie line". Modelling the Railways of South Australia. Adelaide. https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/Record/6937092.
- ↑ "Rolling stock". Farlex. http://financial-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/rolling+stock.
- ↑ Illinois Department of Revenue. "RUT-7: Rolling Stock Certification". http://tax.illinois.gov/taxforms/sales/vehicleusetax/rut-7.pdf.
- ↑ "Michigan's Rolling Stock Exemption". Avalara. http://www.taxrates.com/blog/2016/01/12/michigans-rolling-stock-exemption/.
- ↑ Finger, Matthias; Bert, Nadia; Kupfer, David, eds (2014). "Rail infrastructure and rolling stock: investments, asset renewal and regulation". European University Institute, Florence School of Regulation. pp. 8–9. http://fsr.eui.eu/Documents/WorkshopPaper/Transport/2014/140428InfrastructureRollingStockObserver.pdf.
- ↑ Wijnia, Y.; de Croon, J.; Liyanage, J.P. (2014). "36: Application of a Unified Reference Model Across Asset Types: Comparative Cases". in Lee, Jay; Ni, Jun; Sarangapani, Jagnathan et al.. Engineering Asset Management 2011: Proceedings of the Sixth World Congress on Engineering Asset Management. London: Springer. pp. 416–417. ISBN 978-1-4471-4993-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=x-m7BAAAQBAJ&q="rolling+stock"+as+liquid+asset&pg=PA416.
External links
 |
Categories: [Rolling stock] [Rail transport]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/28/2024 07:45:19 | 15 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Engineering:Rolling_stock | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF