Short description: Organic compounds of the form R–O–N=O
In organic chemistry, alkyl nitrites are a group of organic compounds based upon the molecular structure R–O–N=O, where R represents an alkyl group. Formally they are alkyl esters of nitrous acid. They are distinct from nitro compounds (R–NO
2).
The first few members of the series are volatile liquids; methyl nitrite and ethyl nitrite are gaseous at room temperature and pressure. The compounds have a distinctive fruity odor. Another frequently encountered nitrite is amyl nitrite (3-methylbutyl nitrite).
Alkyl nitrites were initially, and largely still are, used as medications and chemical reagents, a practice which began in the late 19th century. In their use as medicine, they are often inhaled for relief of angina and other heart-related symptoms of disease. However, when referred to as "poppers", alkyl nitrites represent recreational drugs.
Synthesis and properties
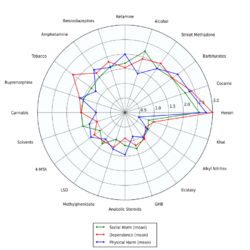
Addiction experts in psychiatry, chemistry, pharmacology, forensic science, epidemiology, and the police and legal services engaged in delphic analysis regarding 20 popular recreational drugs. Alkyl nitrites were ranked 20th social and physical harm, and 18th in dependence.
[1]Organic nitrites are prepared from alcohols and sodium nitrite in sulfuric acid solution. They decompose slowly on standing, the decomposition products being oxides of nitrogen, water, the alcohol, and polymerization products of the aldehyde.[2] They are also prone to undergo homolytic cleavage to form alkyl radicals, the nitrite C–O bond being very weak (on the order of 40–50 kcal ⋅ mol−1).
Reactions
- tert-Butyl nitrite has been shown to be an effective reagent for the selective nitration of phenols[3] and aryl sulfonamides[4]
- n-Butyl nitrite and ammonia convert phenylhydroxylamine to its nitrosamine derivative cupferron.[5] Likewise pyrrolidine is a substrate for ethyl nitrite.[6]
- Alkyl nitrites are also used in the formation of oximes with the stronger carbon acids and acid or base catalysis for example in the reaction of 2-butanone, ethyl nitrite and hydrochloric acid forming the oxime,[7] the similar reaction with phenacyl chloride,[8] or the reaction of phenylacetonitrile with methyl nitrite and sodium hydroxide.[9]
An isolated but classic example of the use of alkyl nitrites can be found in Woodward and Doering's quinine total synthesis:[10]
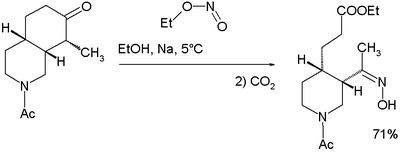
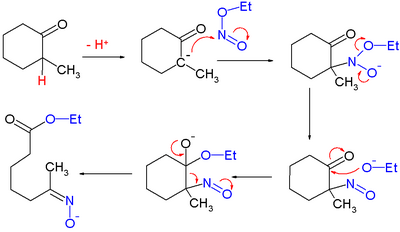
for which they proposed this reaction mechanism:
Medical use
Antidote to cyanide poisoning
Amyl nitrite is used medically as an antidote to cyanide poisoning,[11] The light alkyl nitrites cause the formation of methemoglobin wherein, as an effective antidote to cyanide poisoning, the methemoglobin combines with the cyanide to form nontoxic cyanmethemoglobin.[citation needed] First responders typically carry a cyanide poison kit containing amyl nitrite.
References
- ↑ Nutt, D; King, LA; Saulsbury, W; Blakemore, C (24 March 2007). "Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse.". Lancet 369 (9566): 1047–53. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60464-4. PMID 17382831.
- ↑ n-butyl nitrite Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 2, p.108 (1943); Vol. 16, p.7 (1936). http://www.orgsynth.org/orgsyn/prep.asp?prep=cv2p0108 Link
- ↑ Chemoselective Nitration of Phenols with tert-Butyl Nitrite in Solution and on Solid Support Organic Letters, Coll. Vol 11, p.4172-4175 (2009)
- ↑ Chemoselective Nitration of Aromatic Sulfonamides with tert-Butyl Nitrite Chemical Communications, doi:10.1039/C2CC37481A
- ↑ Cupferron Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 1, p.177 (1941); Vol. 4, p.19 (1925) Link
- ↑ 2-Pyrrolidinemethanol, α,α-diphenyl-, (±)- Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.542 (1988); Vol. 58, p.113 (1978) Link
- ↑ Dimethylglyoxime Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 2, p.204 (1943); Vol. 10, p.22 (1930) Link
- ↑ Glyoxylyl chloride, phenyl-, oxime Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 3, p.191 (1955); Vol. 24, p.25 (1944) Link
- ↑ [Benzeneacetonitrile, α-(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonylcarbonyl]oxy]imino]-] Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.199 (1988); Vol. 59, p.95 (1979) Link
- ↑ The Total Synthesis of Quinine R. B. Woodward and W. E. Doering J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1945; 67(5) pp 860 - 874; doi:10.1021/ja01221a051
- ↑ "Amyl Nitrite". Medsafe. New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority. 2000-05-18. http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/Profs/datasheet/a/Amylnitrateinh.htm.
External links
Nitric oxide signaling modulators |
|---|
| Forms |
- Nitroxyl anion (NO−; oxonitrate(1-), hyponitrite anion)
- Nitric oxide (NO⋅; nitrogen monoxide)
- Nitrosonium (NO+; nitrosyl cation)
|
|---|
| Targets | | sGC |
- Activators/stimulators: Ataciguat
- BAY 41-2272
- BAY 41-8543
- BAY 60-4552
- BI-703704
- Cinaciguat (BAY 58-2667)
- GSK-2181236A
- Praliciguat
- Riociguat (BAY 63-2521)
- Vericiguat
|
|---|
|
|---|
NO donors
(prodrugs) |
- Nitrates: Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN)
- Erythritol tetranitrate (ETN)
- Ethylene glycol dinitrate (EGDN; nitroglycol)
- Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN)
- Isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN)
- Itramin tosilate
- Mannitol hexanitrate
- Naproxcinod (nitronaproxen; AZD-3582, HCT-3012)
- NCX-466
- NCX-2216
- NCX-4016
- NCX 4040
- NCX-4215
- Nicorandil
- Nipradilol (K-351)
- Nitrate (NO−3)
- Nitroatorvastatin (NCX-6560)
- Nitroflurbiprofen (HCT-1026)
- Nitrofluvastatin
- Nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate (GTN))
- Nitropravastatin (NCX-6550)
- Pentaerithrityl tetranitrate (PETN)
- Propatylnitrate
- Propylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN)
- Sodium trioxodinitrate (Angeli's salt)
- Tenitramine
- Trolnitrate
- Nitroso compounds/nitrites: Nitrite (NO−2); O-Nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites): Amyl nitrite (isoamyl nitrite, isopentyl nitrite)
- Cyclohexyl nitrite
- Ethyl nitrite
- Hexyl nitrite
- Isobutyl nitrite (2-methylpropyl nitrite)
- Isopropyl nitrite
- Methyl nitrite
- n-Butyl nitrite
- Pentyl nitrite
- tert-Butyl nitrite; S-Nitroso compounds (thionitrites): LA810
- S-Nitrosoalbumin (SNALB)
- S-Nitrosated AR545C
- S-Nitroso-N-acetylcysteine (SNAC)
- S-Nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP)
- S-Nitroso-N-valerylpenicillamine (SNVP)
- S-Nitrosocaptopril (SNO-Cap)
- S-Nitrosocysteine (SNC, CysNO, SNO-Cys)
- S-Nitrosodiclofenac
- S-Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO, SNOG)
- SNO-t-PA
- SNO-vWF; N-Nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines): SIN-1A
- Nitrosyl compounds: Metal nitrosyl complexes: Roussin's black salt
- Roussin's red salt
- Sodium nitroprusside (SNP)
- NONOates (diazeniumdiolates): Diethylamine/NO (DEA/NO)
- Diethylenetriamine/NO (DETA/NO)
- GLO/NO
- JS-K
- Methylamine hexamethylene methylamine/NO (MAHMA/NO)
- PROLI/NO
- Spermine/NO (SPER/NO)
- V-PYRRO/NO
- Heterocyclic compounds: Furoxans: Furoxan
- REC15/2739; Sydnonimines: Feprosidnine
- Linsidomine (SIN-1)
- Molsidomine (SIN-10)
- Sydnonimine
- Unsorted: Cimlanod
- FK-409
- FR144220
- FR146881
- N-Acetyl-N-acetoxy-4-chlorobenzenesulfonamide
|
|---|
Enzyme
(inhibitors) | | NOS | | nNOS |
- 3-Bromo-7-nitroindazole
- 3-Chloroindazole
- 3-Chloro-5-nitroindazole
- 5-Nitroindazole
- 6-Nitroindazole
- 7-Nitroindazole
- A-84643
- Aminoguanidine (pimagedine)
- ARL-17477
- Indazole
- N5-(1-Iminoethyl)-L-ornithine (L-NIO)
- Nω-Methyl-L-arginine (L-NMA)
- Nω-Propyl-L-arginine (L-NPA)
- Nitroarginine (NNA, NOARG)
- Pentamidine isethionate
- TRIM
|
|---|
| iNOS |
- 1-Amino-2-hydroxyguanidine
- 2-Ethylaminoguanidine
- 2-Iminopiperidine
- 1400W
- AEITU
- Aminoguanidine (pimagedine)
- AMT
- AR-C 102222
- BYK-191023
- Canavanine
- Cindunistat (SD-6010)
- EITU
- IPTU
- MITU
- N5-(1-Iminoethyl)-L-ornithine (L-NIO)
- N6-(1-Iminoethyl)-L-lysine (L-NIL)
- Nω-Methyl-L-arginine (L-NMA)
- Ronopterin (VAS-203)
- TRIM
|
|---|
| eNOS |
- Aminoguanidine (pimagedine)
- N5-(1-Iminoethyl)-L-ornithine (L-NIO)
- Nω-Methyl-L-arginine (L-NMA)
- Nitroarginine (NNA, NOARG)
|
|---|
| Unsorted |
- Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)
- CKD-712
- Guanidinoethyldisulfide (GED)
- GW-273629
- Indospicine
- KD-7040
- Nitroarginine methyl ester (NAME)
- NCX-456
- NXN-462
- ONO-1714
- VAS-2381
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Arginase |
- ABH
- Nω-Hydroxy-L-arginine (NOHA)
- chlorogenic acid
- ginseng
- epicatechin
- ornithine
- norvaline
- lysine
- alpha aminoacids
|
|---|
| CAMK | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Others |
- Precursors: L-Arginine
- Nω-Hydroxy-L-arginine (NOHA)
- Cofactors: NADPH
- FAD
- FMN
- Heme
- BH4
- CaM
- O2
- Ca2+
- Indirect/downstream NO modulators: ACE inhibitors/AT-II receptor antagonists (e.g., captopril, losartan)
- ETB receptor antagonists (e.g., bosentan)
- L-Type calcium channel blockers (e.g., dihydropyridines: nifedipine)
- Nebivolol (beta blocker)
- PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil)
- Statins (e.g., simvastatin)
|
|---|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators |
Functional groups |
|---|
Only carbon,
hydrogen,
and oxygen | | Hydrocarbons |
- Allene
- Alkene (Allyl group
|
|---|
| Other |
- Acetoxy
- Acetyl
- Acryloyl
- Acyl
- Aldehyde
- Alkoxy (Methoxy)
- Benzoyl
- Carbonyl
- Carboxyl
- Carboxylic anhydride
- Dioxirane
- Epoxide
- Ester
- Ether
- Ethylenedioxy
- Hydroxy
- Ketone
- Methylenedioxy
- Peroxide (Organic)
- Ynone
|
|---|
|
|---|
Only one
element
apart from
C, H, O | | Nitrogen |
- Amine
- Azo compound
- Cyanate
- Hydrazone
- Imide
- Imine
- Isocyanate
- Isonitrile
- Nitrene
- Nitrile
- Nitro compound
- Nitroso compound
- Organic amide
- Oxime
|
|---|
| Phosphorus | |
|---|
| Sulfur |
- Disulfide
- Sulfone
- Sulfonic acid
- Sulfoxide
- Thial
- Thioester
- Thioether
- Thioketone
- Thiol
|
|---|
| Selenium |
- Selenol
- Selenonic acid
- Seleninic acid
- Selenenic acid
- Selone
|
|---|
| Tellurium | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Other |
- Isothiocyanate
- Phosphoramide
- Sulfenyl chloride
- Sulfonamide
- Thiocyanate
|
|---|
|
See also chemical classification, chemical nomenclature ([[Chemistry:IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic, IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry|organic]]) |
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alkyl nitrite. Read more |
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 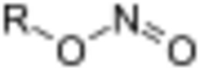





 KSF
KSF