Nitrogen Monosulfide
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Mononitrogen monosulfide | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Azaniumylsulfanidylidyne | |||
| Other names
Aminiosulfanidylidyne
Thionitroso radical | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number
|
| ||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| Abbreviations | (NS)(.) | ||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
Gmelin Reference
|
660 | ||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula
|
NS | ||
| Molar mass | 46.07 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
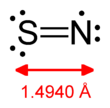
Mononitrogen monosulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula SN. It is the sulfur analogue of the radical nitric oxide, NO. It can be produced through electrical discharges in mixtures of nitrogen and sulfur compounds, as well as the reaction of nitrogen with sulfur vapor. The valence electrons of this compound match those of nitric oxide.[1] In outer space, this compound was first detected in the giant molecular cloud Sgr B2. It was subsequently observed in cold dark clouds and in the comae of comets.[2]
Mononitrogen monosulfide exists as a resonance structure, of which a species with a bond order of one accompanied by charge separation is the major contributor.
See also
- Sulfur nitride
References
- ↑ Burr, J. G. (1985). Chemi- and Bioluminescence. Clinical and Biochemical Analysis. 16. CRC Press. p. 99. ISBN 0-8247-7277-6.
- ↑ Canaves, M. V.; de Almeida, A. A.; Boice, D. C.; Sanzovo, G. C. (March 2002). "Nitrogen Sulfide in Comets Hyakutake (C/1996 B2) and Hale-Bopp (C/1995 O1)". Earth, Moon, and Planets 90 (1): 335–347. doi:10.1023/A:1021582300423. Bibcode: 2002EM&P...90..335C.
Categories: [Free radicals] [Inorganic compounds] [Nitrides] [Sulfur compounds]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 05/23/2025 00:16:54 | 9 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Nitrogen_monosulfide | License: CC BY-SA 3.0


 KSF
KSF