8 (Number)
 From Nwe
From Nwe |
8
|
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 >> List of numbers — Integers 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 >> |
|
| Cardinal | 8 eight |
| Ordinal | 8th eighth |
| Numeral system | octal |
| Factorization | |
| Divisors | 1, 2, 4, 8 |
| Roman numeral | VIII |
| Roman numeral (Unicode) | Ⅷ, ⅷ |
| Arabic | ٨ |
| Amharic | ፰ |
| Bengali | ৮ |
| Chinese numeral | 八,捌 |
| Devanāgarī | ८ |
| Hebrew | ח (Het) |
| Khmer | ៨ |
| Thai | ๘ |
| prefixes | octa-/oct- (from Greek) octo-/oct- (from Latin) |
| Binary | 1000 |
| Octal | 10 |
| Duodecimal | 8 |
| Hexadecimal | 8 |
8 (eight) is a number, numeral, and glyph that represents the number. It is the natural number[1] that follows 7 and precedes 9. It is an integer and a cardinal number, that is, a number that is used for counting.[2] In addition, it is classified as a real number,[3] distinguishing it from imaginary numbers.
Evolution of the glyph
In the beginning, various groups in India wrote eight more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase H with the bottom half of the left line and the upper half of the right line removed. At one point this glyph came close to looking like the modern five. With the western Ghubar Arabs, the similarity of the glyph to five was banished by connecting the beginning and end of the stroke together. After that, the Europeans simply rounded the glyph, leading to the modern eight.[4]
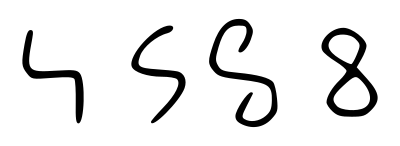
As in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the 8 character usually has an ascender, for example, in ![]() . The "1" and "4" are old-style figures; the "8" is the same height in both old-style and modern figures. 1234567890 are all the same height; they are modern figures.
. The "1" and "4" are old-style figures; the "8" is the same height in both old-style and modern figures. 1234567890 are all the same height; they are modern figures.
In mathematics
Eight is a composite number, its proper divisors being 1, 2, and 4. Eight is a power of two, being , or two cubed. It has an aliquot sum of 7. All powers of 2 have an aliquot sum of one less than themselves.
8 is the base of the octal number system, which is mostly used with computers. In octal, one digit represents 3 bits. In modern computers, a byte is a grouping of eight bits, also called an octet.
The number 8 is a Fibonacci number, being 3 plus 5. The next Fibonacci number is 13.
Eight and nine form a Ruth-Aaron pair under the second definition in which repeated prime factors are counted as often as they occur.
A polygon with eight sides is an octagon. Figurate numbers representing octagons (including eight) are called octagonal numbers. A polyhedron with eight faces is an octahedron.
Sphenic numbers always have exactly eight divisors.
Eight is the dimension of the octonions and is the highest possible dimension of a normed division algebra.
The number 8 is involved with a number of interesting mathematical phenomena related to the notion of Bott periodicity. For example if is the direct limit of the inclusions of real orthogonal groups then . Clifford algebras also display a periodicity of 8. For example the algebra is isomorphic to the algebra of 16 by 16 matrices with entries in . There is also a period of 8 in the K theory of spheres and in the representation theory of the rotation groups, the latter giving rise to the 8 by 8 spinorial chessboard. All of these properties are closely related to the properties of the octonions.
The lowest dimensional even unimodular lattice is the 8-dimensional E8 lattice. Even positive definite unimodular lattice exist only in dimensions divisible by 8.
A figure 8 is the common name of a geometric shape, often used in the context of sports, such as skating
In binary code eight is 1000; in ternary code eight is 22; in quaternary numeral system code eight is 20; in quinary eight is 13; in senary eight is 12; in septenary eight is 11; in octal eight is 10; in novenary code and all codes above (such as decimal and hexadecimal) eight is 8.
A fallen or lying down 8 (∞, the lemniscate) is used to represent infinity in mathematics. This interpretation of 8 may be related to the representation of the caduceus (where two snakes form several figure eights) as stability or balance of opposing forces.
Eight is the number of Thurston model geometries. Eight is not a prime number
E8 has rank 8.
As of 2008, there are only eight known Stern primes.
In numeral systems
| Base | Numeral system | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | binary | 1000 |
| 3 | ternary | 22 |
| 4 | quaternary | 20 |
| 5 | quinary | 13 |
| 6 | senary | 12 |
| 7 | septenary | 11 |
| 8 | octal | 10 |
| over 8 (decimal, hexadecimal) | 8 | |
List of basic calculations
- Multiplication
| Multiplication | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 16 | 24 | 32 | 40 | 48 | 56 | 64 | 72 | 80 |
| Multiplication | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 88 | 96 | 104 | 112 | 120 | 128 | 136 | 144 | 152 | 160 |
| Multiplication | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 1000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 168 | 176 | 184 | 192 | 200 | 400 | 800 | 8000 |
- Division
| Division | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1.6 | 1 | 0.8 | |||||
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.5 | 0.625 | 0.75 | 0.875 | 1 | 1.125 | 1.25 |
| Division | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.375 | 1.5 | 1.625 | 1.75 | 1.875 |
- Exponentiation
| Exponentiation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 64 | 512 | 4096 | 32768 | 262144 | 2097152 | 16777216 | 134217728 | 1073741824 | |
| 1 | 256 | 6561 | 65536 | 390625 | 1679616 | 5764801 | 16777216 | 43046721 | 100000000 |
| Exponentiation | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8589934592 | 68719476736 | 549755813888 | |
| 214358881 | 429981696 | 815730721 |
In science
Physics
- In nuclear physics, 8 is the second magic number; the first one being 2. A magic number (in this case) is the number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in the atomic nucleus, such that they are arranged into complete shells in the nucleus.[5]
- In particle physics, the eightfold way is used to classify subatomic particles.
Astronomy
- The Saros number of the solar eclipse series that began on March 7, 2579 B.C.E. and ended on April 26, 1281 B.C.E. The duration of Saros series 8 was 1298.17 years, and it contained 73 solar eclipses.[6]
- The Saros number of the lunar eclipse series that began on August 8, 2494 B.C.E. and ended on February 13, 961 B.C.E. The duration of Saros series 8 was 1532.56 years, and it contained 86 lunar eclipses.[7]
- Eight of the bodies orbiting the Sun are considered planets in the Solar System.
Chemistry
- Eight is the atomic number of oxygen.
- The most stable allotrope of a sulfur molecule is made of eight sulfur atoms arranged in a rhombic form.
- In the electronic configurations of atoms, eight is usually the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a valence shell.
- The red pigment lycopene consists of eight isoprene units.
Biology
- There are eight known B vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism.
- All spiders, and more generally all arachnids, have eight legs.
- An octopus has eight tentacles.
- In the adult human dentition, there are 8 teeth in each quadrant. The eighth tooth is the so-called wisdom tooth.
Measurement
- The SI prefix for 10008 is yotta (Y), and that for its reciprocal is yocto (y).
- In liquid measurement (US customary units), there are 8 fluid ounces in a cup, 8 pints in a gallon, and 8 tablespoons in a gill
- There are 8 furlongs in a mile.
In technology

- Many (mostly historic) computer architectures are eight-bit, among them the Nintendo Entertainment System
- One byte is eight bits.
- A V8 engine is an internal combustion engine with 8 cylinders configured in two banks (rows) of 4 forming a "V" when seen from the end.
In religion
Judaism
- The Jewish religious rite of brit milah is held on a baby boy's eighth day of life.
- Hanukkah is an eight-day Jewish holiday that starts on the twenty-fifth day of Kislev.
- Shemini Atzeret (Hebrew: "Eighth Day of Assembly") is a one-day Jewish holiday immediately following the seven-day holiday of Sukkot.
Christianity
- Eight is the number of Beatitudes in Jesus' Sermon on the Mount.
- It is allegoric to what is beyond time (because the number 7 refers to the days of the week which repeat themselves).
- Members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints believe that humans are responsible for their actions by the age of 8. Before that age, children lack sufficient knowledge to commit sin and are therefore exempt from judgment for their actions.
Buddhism
- The Dharmachakra, a Buddhist symbol, has eight spokes. The Buddha's principal teaching—the Four Noble Truths—ramifies as the Noble Eightfold Path.
- In Mahayana Buddhism, the branches of the Eightfold Path are embodied by the Eight Great Bodhisattvas (Manjushri, Vajrapani, Avalokiteshvara, Maitreya, Kshitigarbha, Nivaranavishkambhi, Akashagarbha, and Samantabhadra). These are later (controversially) associated with the Eight Consciousnesses according to the Yogachara school of thought: Consciousness in the five senses, thought-consciousness, self-consciousness, and unconsciousness-"consciousness" (alaya-vijñana).
- The "irreversible" state of enlightenment, at which point a Bodhisattva goes on "autopilot," is the Eight Ground or bhūmi.
- In general, "eight" seems to be an auspicious number for Buddhists, such as the "eight auspicious symbols" (the jewel-encrusted parasol; the goldfish (always shown as a pair, for example, the glyph of Pisces); the self-replenishing amphora; the white kamala lotus-flower; the white conch; the eternal (Celtic-style, infinitely looping) knot; the banner of imperial victory; the eight-spoked wheel that guides the ship of state, or that symbolizes the Buddha's teaching).
- Buddha's birthday falls on the 8th day of the 4th month of the Chinese calendar.
Other religions
- In Islam, eight is the number of Angels carrying The Holy Throne of Allah in heaven.
- In Hinduism, eight is the number of wealth and abundance. The Goddess Lakshmi has eightfold forms. There are eight nidhis, or seats of wealth.
- In Neopaganism, there are eight Sabbats, festivals, seasons, or spokes in the Wheel of the Year.
- The Eight Immortals are Chinese deities.
In music
- A note played for one-eighth the duration of a whole note is called an eighth note, or quaver.
- An octave, the interval between two notes with the same letter name (where one has double the frequency of the other), is so called because there are eight notes on a western scale between the two, including the notes themselves.
- There are eight notes in an octatonic scale.
- There are eight musicians in an octet.
- The 8-track cartridge is a musical recording format
In sports
- In football, the number 8 has historically been the number of the Central Midfielder.
- In rugby union, the central back row position wears the 8 shirt.
- In baseball, in its numbering system used to record defensive plays, eight represents the center fielder's position.
- In chess, each side has eight pawns and the board is made of 64 squares arranged in an eight by eight lattice.
- The eight queens puzzle is a challenge to arrange eight queens on the board so that none can capture any of the others.
- Eight ball billiards is played with 15 balls; the black ball numbered 8 being the middle and most important one. Magic 8 Ball is a randomized process of predicting the future or answering various questions, packaged to resemble this ball and often sold as a fortune-telling device.
- In rowing, an "eight" refers to a sweep oar boat with eight rowers plus a coxswain.
In slang
- An Eighth is a common measurement of marijuana, meaning an eighth of an ounce.
- Referring to the shape of the numeral, eight was represented in bingo slang, before political correctness, as "One Fat Lady." Eighty-eight was "Two Fat Ladies."
- The numeral "8" is sometimes used in writing to represent the syllable "ate," as in writing "H8" for "hate," or "congratul8ions" for "congratulations." Avril Lavigne's song "Sk8er Boi" uses this convention in the title. It is also often found on vanity plates
- "Section 8" is common U.S. slang for "crazy," based on the U.S. military's Section 8 discharge for mentally unfit personnel.
- In China, "8" is used in chat speak as a term for parting. This is due to the closeness in pronunciation of "8" (bā) and the English word "bye."
Miscellany

- The ordinal adjective is octaval or octavary.
- The distributive adjective is octonary.
- In cooking recipes, there are approximately 8 pinches to a teaspoon.
- A figure-eight knot is a type of knot frequently used by climbers.
- Various types of buildings are usually eight-sided (octagonal), such as single-roomed gazebos and multi-roomed pagodas (descended from stupas).
- Eight babies delivered in a single birth are called octuplets. The first set of eight surviving babies, the Chukwu octuplets, was born in 1998.
- October was the eighth month in the Roman calendar; currently August is the eighth month.
- War of the Eight Princes was a war in Chinese history
- "88" is the abbreviated terminology used by the Aryan Brotherhood for the Nazi salute, "Heil Hitler"—"H" being the eighth letter of the alphabet, twice
- The silver piece of eight was coined in the Spanish Empire and moved trade around the world.
- There are Eight Principles of Yong in Chinese calligraphy.
- Eight (八; accounting 捌; pinyin bā) is considered a lucky number in Asian culture because it sounds like the word "prosper" or "wealth" (发; Pinyin: fā). Additionally, it is considered lucky in Japan because the Chinese numeral character resembles a mountain, specifically Fujisan.
- In numerology, 8 is the number of building, and in some theories, also the number of destruction.
- In the Middle Ages, 8 was the number of "unmoving" stars in the sky.
- 8vo is shorthand for "octavo," a book size.
- The Eight: Eight American painters who exhibited together only once in 1908 in New York City. They joined this exhibition to oppose traditions upheld by the National Academy and help advance modernism in the United States. Five of the eight painters were associated with the Ashcan School: Robert Henri (1865-1929), George Luks (1867-1933), William Glackens (1870-1938), John Sloan (1871-1951), and Everett Shinn (1876-1953). The others were Maurice Prendergast (1859-1924), Ernest Lawson (1873-1939), and Arthur Bowen Davies (1862-1928).
See also
- Arithmetic
- Integer
- Number
Notes
- ↑ A natural number is any number that is a positive integer, such as 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Often, the number 0 is also called a natural number.
- ↑ A cardinal number indicates the quantity of things, but not the order in which they occur. By contrast, ordinal numbers are first, second, third, and so on, indicating their positions in a series.
- ↑ A real number is a number that can be given by a finite or infinite decimal representation. The term "real number" was coined to distinguish it from an "imaginary number." The set of real numbers includes rational and irrational numbers, which can be positive, negative, or zero.
- ↑ Georges Ifrah, The Universal History of Numbers: From Prehistory to the Invention of the Computer (New York: Wiley, 2000, ISBN 0471393401), 395.
- ↑ Xavier Borg, Magic numbers derived from a variable phase nuclear model, The General Science Journal. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ↑ NASA, Saros Series 8 Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ↑ NASA, Saros Series 8 Catalog of Lunar Eclipse Saros Series. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Flegg, Graham. Numbers: Their History and Meaning. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, 2002. ISBN 0486421651
- Higgins, Peter M. Number Story: From Counting to Cryptography. London: Copernicus, 2008. ISBN 978-1848000001
- Ifrah, Georges. The Universal History of Numbers: From Prehistory to the Invention of the Computer. Translated by David Bellos et al. New York: Wiley, 2000. ISBN 0471393401
- McLeish, John. The Story of Numbers: How Mathematics Has Shaped Civilization. New York: Fawcett Columbine, 1994. ISBN 0449909387
- Menninger, Karl. Number Words and Number Symbols: A Cultural History of Numbers. New York: Dover Publications, 1992. ISBN 0486270963
- Wells, D. G. The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Numbers. London: Penguin Books, 1998. ISBN 0140261494
External links
All links retrieved October 7, 2022.
- The Octonions. John C. Baez.
- The Number 8
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- 8 (number) history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
- History of "8 (number)"
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/03/2023 19:18:41 | 13 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/8_(number) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:



















 KSF
KSF