Ocular Albinism
 From Mdwiki
From Mdwiki | Ocular albinism | |
|---|---|
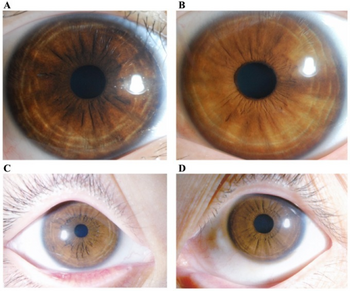 | |
| Iris images of individual with OA1 | |
Ocular albinism is a form of albinism which, in contrast to oculocutaneous albinism, presents primarily in the eyes.[1] There are multiple forms of ocular albinism, which are clinically similar.[2]: 865
Both known genes are on the X chromosome. When the term "autosomal recessive ocular albinism" ("AROA") is used, it usually refers to mild variants of oculocutaneous albinism rather than ocular albinism, which is X-linked.[3]
Types[edit | edit source]
| Name | OMIM | Gene | Description |
| Ocular albinism, type 1 (OA1) | 300500 | GPR143 | Also known as Nettleship–Falls syndrome,[4][5][6] is the most common variety of ocular albinism. OA1 is usually associated with nystagmus, and difficult to otherwise detect in females; males show more readily observable symptoms. |
| Ocular albinism, type 2 (OA2) | 300600 | CACNA1F[7] | Also known as Forsius–Eriksson syndrome[8][9] or "Åland eye disease", mostly affects males, though females are often carriers and can sometimes be symptomatic; it is frequently linked with protanopic dichromacy (a form of color blindness) and with night blindness (nyctalopia). |
| Ocular albinism with sensorineural deafness (OASD) | 300650 | ? (Xp22.3) | Is, as its name implies, associated with loss of hearing. May be the same as OA1.[10] |
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ "Ocular albinism - Genetics Home Reference". Archived from the original on 2010-05-01. Retrieved 2022-01-02.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ↑ Hutton SM, Spritz RA (March 2008). "A comprehensive genetic study of autosomal recessive ocular albinism in Caucasian patients". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 49 (3): 868–72. doi:10.1167/iovs.07-0791. PMID 18326704. Archived from the original on 2019-12-15. Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- ↑ synd/990 at Who Named It?
- ↑ E. Nettleship. On some hereditary diseases of the eye. Transactions of the Ophthalmological Societies of the United Kingdom, 1908-1909, 29: 57-198.
- ↑ H. F. Falls. Sex-linked ocular albinism displaying typical fundal changes in the female heterozygote. American Journal of Ophthalmology, Chicago, 1951, 34: 41-50.
- ↑ Jalkanen R, Bech-Hansen NT, Tobias R, et al. (June 2007). "A novel CACNA1F gene mutation causes Aland Island eye disease". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 48 (6): 2498–502. doi:10.1167/iovs.06-1103. PMID 17525176. Archived from the original on 2019-12-15. Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- ↑ synd/1336 at Who Named It?
- ↑ Forsius H, Eriksson AW (April 1964). "[A new eye syndrome with X-chromosomal transmission. a family clan with fundus albinism, fovea hypoplasia, nystagmus, myopia, astigmatism and dyschromatopsia.]". Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd (in Deutsch). 144: 447–57. PMID 14230113.
- ↑ Winship IM, Babaya M, Ramesar RS (November 1993). "X-linked ocular albinism and sensorineural deafness: linkage to Xp22.3". Genomics. 18 (2): 444–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1495. PMID 8288253.
External links[edit | edit source]
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Categories: [Albinism] [Amino acid metabolism disorders] [X-linked recessive disorders]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/31/2024 11:12:53 | 6 views
☰ Source: https://mdwiki.org/wiki/Ocular_albinism | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]
 KSF
KSF