Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography | |
|---|---|
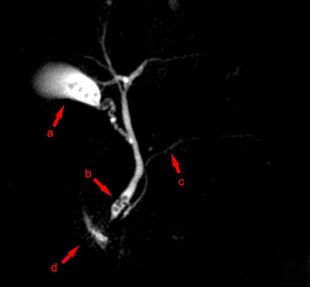 MRCP image showing stones in the distal common bile duct: (a) Gallbladder with stones, (b) Stones in bile duct, (c) Pancreatic duct, (d) Duodenum. | |
| ICD-9-CM | 88.97 |
| MeSH | D049448 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-843 |
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a medical imaging technique. It uses magnetic resonance imaging to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts non-invasively. This procedure can be used to determine whether gallstones are lodged in any of the ducts surrounding the gallbladder.
Uses
MRCP has been slowly replacing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) as investigation of choice. MRCP is highly accurate in diagnosing the biliary system, pancreatic duct and accessing surrounding solid organs. Several advantages offered by MRCP is its non-invasive nature, less costly, requires less examination time when compared to ERCP (30 minutes), fewer staff required, and does not require any ionising radiation.[1][2][3][4]
MRCP is used to diagnose gallstones. It can also diagnose choledochal cysts very reliably.[5] Besides providing information regarding the biliary system, MRCP also provides information regarding surrounding solid organs and blood vessels, thus useful for planning the resection of pancreatic cancer and look for complications of primary sclerosing cholangitis such as liver cirrhosis and cholangiocarcinoma.[5]
Technique
Subject is needed to fast for at least four hours to ensure the biliary system is maximally distended with fluid while keeping the fluid in the gastrointestinal system at a minimum.[1] However, clear fluid and routine medication is allowed before the scan.[1] Negative oral contrast such as pineapple juice,[1] date syrup, ferumoxsil, Açaí juice and water are useful in decreasing T2 signal intensity, thus minimising signals from stomach and duodenum from interfering with signals from the biliary system.[6]
MRCP makes use of heavily T2-weighted MRI pulse sequences.[3][7] These sequences show high signal in static or slow moving fluids within the gallbladder, biliary ducts and pancreatic duct, with low signal of surrounding tissue. Secretin is also given to a patient to increase ductal compliance, making imaging easier.[3]
History
It was introduced by Wallner in 1991.[8]
Additional images
Benign biliary stricture. 3D File generated from MRCP

3D printed model of benign biliary stricture from MRCP data.

Normal MRCP (with visible renal cyst)
See also
- Magnetic resonance myelography
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "The diagnostic MRCP examination: overcoming technical challenges to ensure clinical success". Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal 4 (4): e28. October 2008. doi:10.2349/biij.4.4.e28. PMID 21611015.
- ↑ Prasad, SR; D. Sahani; S. Saini (November 2001). "Clinical applications of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.". Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 33 (5): 362–6. doi:10.1097/00004836-200111000-00004. PMID 11606850.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Stevens, Tyler; Freeman, Martin L. (2019-01-01), Chandrasekhara, Vinay; Elmunzer, B. Joseph; Khashab, Mouen A. et al., eds., "57 - Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis" (in en), Clinical Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (Third Edition) (Philadelphia: Elsevier): pp. 661–673.e3, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-41509-5.00057-8, ISBN 978-0-323-41509-5, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323415095000578, retrieved 2021-01-28
- ↑ "MRCP vs. ERCP in the evaluation of biliary pathologies: review of current literature". Journal of Digestive Diseases 9 (3): 162–9. August 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1751-2980.2008.00339.x. PMID 18956595.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Fulcher, Ann S.; Turner, Mary Ann (2008-01-01), Gore, Richard M.; Levine, Marc S., eds., "chapter 77 - Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography" (in en), Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology (Third Edition) (Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders): pp. 1383–1398, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4160-2332-6.50082-8, ISBN 978-1-4160-2332-6, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781416023326500828, retrieved 2021-01-28
- ↑ Al-Atia, Mohassad. "Can oral contrast enhance image quality at MRCP? - A literature review". Part of Medicine, advanced level, Degree project. http://oru.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:938888/FULLTEXT01.pdf.
- ↑ Griffin, Nyree; Charles-Edwards, Geoff; Grant, Lee Alexander (2011-09-28). "Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: the ABC of MRCP". Insights into Imaging 3 (1): 11–21. doi:10.1007/s13244-011-0129-9. ISSN 1869-4101. PMID 22695995.
- ↑ Albert L. Baert (13 February 2008). Encyclopedia of Diagnostic Imaging. Springer. pp. 123–. ISBN 978-3-540-35278-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=e3F4NaY3fgQC&pg=PA123. Retrieved 3 July 2011.
 |
Categories: [Magnetic resonance imaging]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/21/2024 16:09:05 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Magnetic_resonance_cholangiopancreatography | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF