Triquetral Fracture
 From Mdwiki
From Mdwiki | Triquetral fracture | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Triquetrum fracture | |
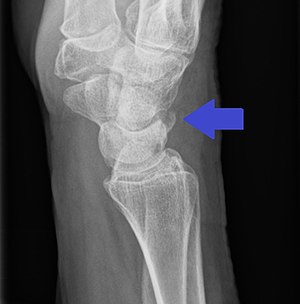 | |
| Triquetral avulsion fracture as seen on lateral X-ray of the wrist | |
| Specialty | Hand surgery |
| Symptoms | Wrist pain and swelling[1][2] |
| Complications | Stiffness, instability[3] |
| Types | Dorsal cortical, body, palmer cortical[4] |
| Diagnostic method | X-rays[3] |
| Differential diagnosis | Lunate dislocation, pisiform fracture, trapezium fracture, hamate fracture[4] |
| Treatment | Casting, surgery[3][1] |
| Prognosis | Generally good[3] |
Triquetral fracture is a break of the triquetral bone of the wrist.[3] Symptoms include pain in the wrist.[1] This is often worsened by bending the wrist forwards or backwards and swelling over the back of the wrist maybe present.[4][2] Associated injuries may include a perilunate dislocation.[4] Complications can include stiffness or instability of the wrist.[3]
It most commonly occurs as a result of a fall onto the hand or being pulled appart by an attached ligament.[3] Other causes may include a direct blow.[1] Diagnosis is generally based on wrist X-rays, though CT scaning can also be useful.[3] Types include dorsal cortical (most common), body, and palmer cortical.[4]
Treatment is generally by casting for 4 to 6 weeks.[3] If the peices are seperated, surgery maybe indicated.[1] Outcomes are generally good with dorsal cortical fractures, while in palmer cortical fractures it may be mixed.[3]
Triquetral fractures represent about 15% of breaks of bones within the wrist, making it the second or third most common after scaphoid and lunate fractures.[3][2][1] They were first described at least as early as 1933 by Thompson.[5]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Greenberg, Michael I. (2005). Greenberg's Text-atlas of Emergency Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 480. ISBN 978-0-7817-4586-4. Archived from the original on 2022-08-27. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Radswiki, The. "Triquetral fracture | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. Archived from the original on 26 June 2022. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 Guo, RC; Cardenas, JM; Wu, CH (April 2021). "Triquetral Fractures Overview". Current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine. 14 (2): 101–106. doi:10.1007/s12178-021-09692-w. PMID 33483875.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Triquetrum Fracture - Hand - Orthobullets". www.orthobullets.com. Archived from the original on 24 March 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ↑ Guermazi, Ali; Roemer, Frank W.; Crema, Michel D. (11 December 2015). Imaging in Sports-Specific Musculoskeletal Injuries. Springer. p. 199. ISBN 978-3-319-14307-1. Archived from the original on 27 August 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
External links[edit | edit source]
- Radiopaedia Archived 2022-06-26 at the Wayback Machine
Categories: [RTT]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/05/2024 13:39:42 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://mdwiki.org/wiki/Triquetral_fracture | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 KSF
KSF