Anthracene
 From Nwe
From Nwe | Anthracene | |
|---|---|
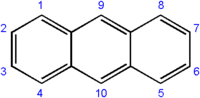 |
|
| IUPAC name | Anthracene |
| Molecular formula | C14H10 |
| Molar mass | 178.23 g/mol |
| CAS number | [] |
| Density | 1.099 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | 217.5 °C |
| Boiling point | 340 °C |
| SMILES | c23cc1ccccc1cc2cccc3 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
|
In chemistry, anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of three benzene rings derived from coal-tar. Anthracene is used in the artificial production of the red dye alizarin. It is also used in wood preservatives, insecticides, and coating materials. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400-500nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
Synthesis
A classic method for the preparation of anthracene in the laboratory is by cyclodehydration of o-methyl- or o-methylene-substituted diarylketones in the so-called Elbs reaction (named for the German chemist Karl Elbs (September 13, 1858 – August 24, 1933)).
Reactions
Anthracene has the ability to photodimerize with irradiation by UV light. This results in considerable changes in the physical properties of the material.
The dimer is connected by two covalent bonds resulting from the [4+4] cycloaddition. The dimer reverts to anthracene thermally or with UV irradiation below 300 nm. The reversible bonding and photochromic properties of anthracenes are the basis of many potential applications using poly and monosubstituted anthracene derivatives. The reaction is sensitive to oxygen.
In most other reactions of anthracene, the central ring is also targeted, as it is the most highly reactive. Electrophilic substitution occurs at the "9" and "10" positions of the center ring, and oxidation of anthracene occurs readily, giving anthraquinone, C14H8O2 .
Uses
Anthracene can also have a hydroxyl group to form 1-hydroxyanthracene and 2-hydroxyanthracene, homologous to phenol and napthol, and hydroxyanthracene is also called anthrol, and anthracenol.[1][2] Hydroxyanthracene derivatives are pharmacologically active, and are contained in aloe, for example.[3][4]
Anthracene is an organic semiconductor.
Anthracene is used as a scintillator for detectors of high energy photons, electrons and alpha particles. Plastics such as polyvinyltolulene can be doped with Anthracene to produce a plastic scintillator that is approximately water equivalent for use in radiation therapy dosimetry. Anthracenes emission spectrum peaks at between 400nm and 440nm.
See also
- Benzene
- Phenanthrene
- Tetracene
Notes
- ↑ 1-Hydroxyanthracene NIST. Retrieved October 16, 2007.
- ↑ 2-Hydroxyanthracene NIST. Retrieved October 16, 2007.
- ↑ TGA News Issue 23 (April 1997): Labelling of herbs containing hydroxyanthracene derivatives Therapeutic Goods Administration, Australian Government. Retrieved October 16, 2007.
- ↑ Herbals and Breastfeeding U.S. Pharmacist. Retrieved October 16, 2007.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- McMurry, John. 2004. Organic Chemistry. 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0534420052
- Morrison, Robert T., and Robert N. Boyd. 1992. Organic Chemistry. 6th ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-643669-2
- Solomons, T.W. Graham, and Fryhle, Craig B. 2004. Organic Chemistry. 8th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley. ISBN 0471417998
External links
All links retrieved October 30, 2021.
- National Pollutant Inventory - Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Fact Sheet
- NIST Chemistry WebBook Anthracene
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/04/2023 07:03:18 | 24 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Anthracene | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: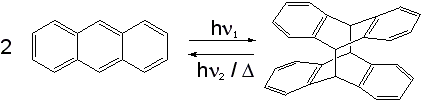
 KSF
KSF