Organic Thiocyanates
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 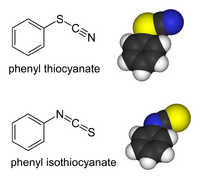
Organic thiocyanates are organic compounds containing the functional group RSCN. the organic group is attached to sulfur: R−S−C≡N has a S–C single bond and a C≡N triple bond.[1]
Organic thiocyanates are valued building blocks. They allow to access efficiently various sulfur containing functional groups and scaffolds.[2]
Synthesis
Several synthesis routes exist, the most common being the reaction between alkyl halides and alkali thiocyanate in aqueous media.[3] Illustrative is the preparation of isopropyl thiocyanate by treatment of isopropyl bromide with sodium thiocyanate in boiling ethanol.[4] The main complication with this route is the competing formation of alkyisothiocyanates. "SN1-type" substrates (e.g., benzyl halides) tend to give the isothiocyanate derivatives.
Some organic thiocyanates are generated by cyanation of organosulfur compounds. Sulfenyl chlorides (RSCl) and thiosulfates (RSSO3−) react with alkali metal cyanides to give thiocyanates with displacement of chloride and sulfite, respectively.
Arylthiocyanates can often be obtained by thiocyanogenation, i.e. the reaction of thiocyanogen. This reaction is favored for electron-rich aromatic substrates.[1]
Reactions
Organic thiocyanates are hydrolyzed to thiocarbamates in the Riemschneider thiocarbamate synthesis.
See also
- Isothiocyanate, isomers of organic thiocyanates with the formula R−N=C=S
- Methyl thiocyanate, the simplest organic thiocyanate
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 R. G. Guy (1977). "Syntheses and Preparative Applications of Thiocyanates". in Saul Patai. Cyanates and Their Thio Derivatives: Part 2, Volume 2. PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups. pp. 619–818. doi:10.1002/9780470771532.ch2. ISBN 9780470771532.
- ↑ Castanheiro, Thomas; Suffert, Jean; Donnard, Morgan; Gulea, Mihaela (2016-02-01). "Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Organic Thiocyanates". Chem. Soc. Rev. 45 (3): 494–505. doi:10.1039/c5cs00532a. ISSN 1460-4744. PMID 26658383.
- ↑ "Synthesis of thiocyanates". https://www.organic-chemistry.org/synthesis/C1S/thiocyanates.shtm.
- ↑ R. L. Shriner (1931). "Isopropyl Thiocyanate". Organic Syntheses 11: 92. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.011.0092.
 |
Categories: [Functional groups] [Thiocyanates]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/24/2024 00:23:48 | 4 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Organic_thiocyanates | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF