Meda
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 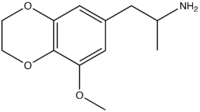
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(8-Methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)propan-2-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C12H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 223.272 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
- SizeSet
MEDA (3-methoxy-4,5-ethylenedioxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. MEDA was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 200 mg, and the duration unknown.[1] MEDA produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MEDA.
See also
- Phenethylamine
- Psychedelics, dissociatives and deliriants
References
- ↑ MEDA entry in PiHKAL
 |
Categories: [Substituted amphetamines]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/05/2024 00:49:45 | 16 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:MEDA | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF