Federal Bureau Of Investigation
 From Ballotpedia
From Ballotpedia | Federal Bureau of Investigation | |
| Director: | Kash Patel |
| Year created: | 1909 |
| Official website: | Office website |
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is a United States agency formed in 1909 "to protect and defend the United States against terrorist and foreign intelligence threats, to uphold and enforce the criminal laws of the United States, and to provide leadership and criminal justice services to federal, state, municipal, and international agencies and partners."[1] The agency originally stemmed from the U.S. Secret Service, and its roots were formed in 1909 by the creation of the Bureau of Investigation.[2]
Kash Patel is the current director of the FBI.
History[edit]
The following are important dates in the FBI's history:[2]
- 1909: Bureau of Investigation formed by Attorney General George Wickersham consisting of 34 agents
- 1917: Investigations of foreign agents began with the start of World War I
- 1919: William J. Flynn became first person to take the title Director of the Bureau of Investigation
- 1924: J. Edgar Hoover appointed as Director of the Bureau of Investigation
- 1928: Formal training courses for new agents established
| Administrative State |
|---|
| Read more about the administrative state on Ballotpedia. |
- 1930s: Laws passed expanding the Bureau's jurisdiction and allowing agents to carry firearms and make arrests
- 1932: Hoover's campaign to bring publicity to the FBI began with the first release of the "Fugitives Wanted by Police" bulletin
- 1932: Bureau of Investigation renamed the United States Bureau of Investigation
- 1933: U.S. Bureau of Investigation renamed Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
- 1935: FBI National Academy established to train law officers investigative methods
- 1936-1939: FBI began investigating "subversive" groups, including fascists and communists in the United States by order of President Roosevelt
- 1939: Sabotage and espionage fell under the jurisdiction of the FBI
- 1940: Locating draft dodgers became FBI jurisdiction
- 1943: FBI employment hits 13,000, including 3,000 agents, during wartime
- 1946: "determining the loyalty of individuals...having access to restricted Atomic Energy data" became FBI jurisdiction
- 1950: "Ten Most Wanted Fugitive" list released for the first time
- 1966: U.S. Supreme Court determined the FBI could prosecute civil rights violations
- 1972: J. Edgar Hoover died
- 1976: Guidelines for FBI counterintelligence collection and domestic security investigations were established
- 1982: Counterterrorism became a national priority for the FBI
- 1989: Violent crime became a national priority for the FBI
- 1992: Wife of Ruby Ridge, ID fugitive Randall Weaver accidentally killed in standoff by FBI sniper
- 1993: Waco, TX standoff ends as the Branch Davidian's compound burned, killing 80 people inside
- 2001: Patriot Act passed, granting new domestic powers to the FBI to fight the threat of terrorism
Mission[edit]
The official FBI mission statement is as follows:
| “ | Our mission encompasses all that we do as an organization—protect the American people and uphold the Constitution of the United States.[1][3] | ” |
Leadership[edit]
Kash Patel is the current director of the FBI.
| Directors of the FBI | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directors of the FBI | Years in office | Nominated by | Confirmation vote | |||||
| Christopher Wray | 2017-Present | Donald Trump | 92-5 | |||||
| James Comey | 2013-2017 | Barack Obama | 93-1 | |||||
| Robert Mueller | 2001-2013 | George W. Bush & Barack Obama | 98-0, 100-0* | |||||
| Louis Freeh | 1993-2001 | Bill Clinton | Unanimous consent | |||||
| William S. Sessions | 1987-1993 | Ronald Reagan | 90-0 | |||||
| William H. Webster | 1978-1987 | Jimmy Carter | Confirmed without objection | |||||
| Clarence M. Kelley | 1973-1978 | Richard Nixon | 96-0 | |||||
| J. Edgar Hoover | 1935-1972 | Franklin D. Roosevelt | Did not require Senate confirmation** | |||||
| *Mueller was nominated by President George W. Bush and confirmed by the Senate in 2001. President Barack Obama nominated Mueller to serve an additional two-year term in 2011. | ||||||||
| **The current appointment confirmation process was not established until 1968. An amendment was added to the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 requring the FBI director to be confirmed by the Senate.[4] | ||||||||
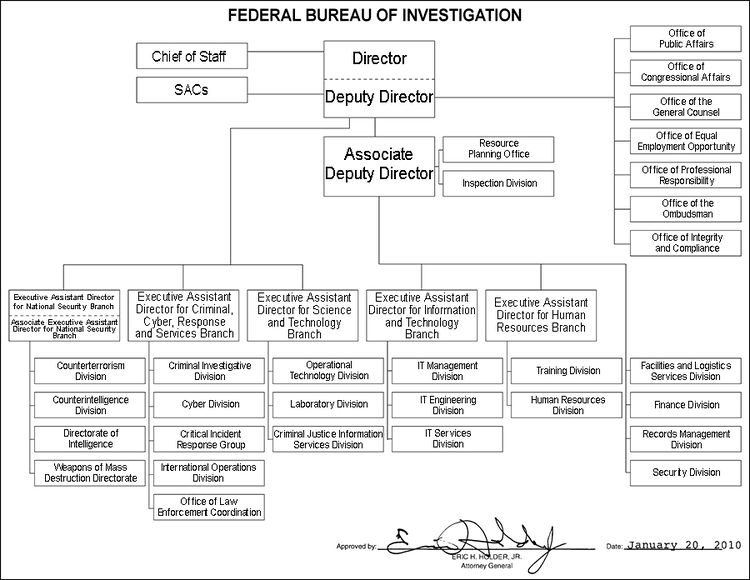
Organization[edit]
Organizational chart[edit]
Recent news[edit]
The link below is to the most recent stories in a Google news search for the terms Federal Bureau of Investigation. These results are automatically generated from Google. Ballotpedia does not curate or endorse these articles.
See also[edit]
External links[edit]
Footnotes[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Federal Bureau of Investigation, "Mission and Priorities," accessed February 22, 2024
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Federal Bureau of Investigation, "FBI - Brief History," accessed February 13, 2014
- ↑ Note: This text is quoted verbatim from the original source. Any inconsistencies are attributable to the original source.
- ↑ FAS.org, "Nomination and Confirmation of the FBI Director: Process and Recent History," March 17, 2005
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Categories: [Federal agencies of the United States] [Agencies of the administrative state] [Administrative agencies]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/06/2026 14:27:11 | 10 views
☰ Source: https://ballotpedia.org/Federal_Bureau_of_Investigation | License: CC BY-SA 3.0


 KSF
KSF