Red Blood Cell
 From Nwe
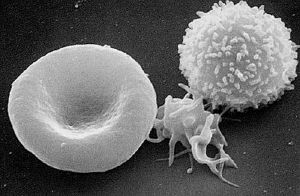
From Nwe Red blood cell, or erythrocyte, is a hemoglobin-containing blood cell in vertebrates that transports oxygen and some carbon dioxide to and from tissues. Erythrocytes are formed in the red bone marrow and afterward are found in the blood. They are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate body's principal means of delivering oxygen from the lungs or gills to body tissues via the blood (Dean 2005).
Erythrocytes in mammals are disk-shaped, biconcave (flattened and depressed in the center), and anucleate when mature, meaning that they lack a cell nucleus and as a result, have no DNA. In comparison, the erythrocytes of nearly all other vertebrates have nuclei; the only known exception being salamanders of the Batrachoseps genus (Cohen 1982).
Lacking a nucleus and organelles such as mitrochondria, the mammalian red blood cells do not use any of the oxygen they transport for their own needs. They produce ATP for their energy needs by other means, and all of the oxygen transported is for the sake of other cells. When the erythrocytes are old, they are broken down and their various components used by the body.
The term erythrocytes comes from Greek erythros for "red" and kytos for "hollow," with cyte translated as "cell" in modern usage. Red blood cells also are known as RBCs, red blood corpuscles (an archaic term), and haematids. A schistocyte is a red blood cell undergoing cell fragmentation, or a fragmented part of a red blood cell. The capitalized term Red Blood Cells is the proper name in the United States for erythrocytes in storage solution used in transfusion medicine (AABB 2002).
The first person to describe red blood cells was probably the young Dutch biologist Jan Swammerdam, who had used an early microscope in 1658 to study the blood of a frog (Swammerdam). Unaware of this work, Anton van Leeuwenhoek provided another microscopic description in 1674 (EBC 2002).
Vertebrate erythrocytes
Erythrocytes consist mainly of hemoglobin, a complex molecule containing heme groups whose iron atoms temporarily link to oxygen molecules in the lungs or gills and release them throughout the body. Oxygen can easily diffuse through the red blood cell's cell membrane. Hemoglobin also carries some of the waste product carbon dioxide back from the tissues. (In humans, less than two percent of the total oxygen, and most of the carbon dioxide, is held in solution in the blood plasma). A related compound, myoglobin, acts to store oxygen in muscle cells (Maton et al. 1993).
The color of erythrocytes is due to the heme group of hemoglobin. The blood plasma alone is straw-colored, but the red blood cells change color depending on the state of the hemoglobin: when combined with oxygen the resulting oxyhemoglobin is scarlet, and when oxygen has been released the resulting deoxyhemoglobin is darker, appearing bluish through the vessel wall and skin. Pulse oximetry takes advantage of this color change to directly measure the arterial blood oxygen saturation using colorimetric techniques.
The sequestration of oxygen carrying proteins inside specialized cells (rather than having them dissolved in body fluid) is an important adaptation of vertebrates; it allows for less viscous blood, higher concentrations of oxygen, and better diffusion of oxygen from the blood to the tissues. The size of erythrocytes varies widely among vertebrate species; erythrocyte width is on average about 25 percent larger than capillary diameter and it has been hypothesized that this improves the oxygen transfer from erythrocytes to tissues (Snyder and Sheafor 1999).
The only known vertebrates that don't use erythrocytes for oxygen transport are the ice fishes (family Channichthyidae); they live in very oxygen rich cold water and transport oxygen freely dissolved in their blood (Ruud 1954).
In 2007, it was reported that erythrocytes also play a part in the body's immune response: when lysed by pathogens such as bacteria, their hemoglobin releases free radicals that break down the pathogen's cell wall and membrane, killing it (Jiang et al. 2007; Kesava 2007).
Mammalian erythrocytes
Mammalian erythrocytes have nuclei during early phases of development, but extrude them as they mature, thus providing more space for hemoglobin. Mammalian erythrocytes also lose their other organelles, such as their mitochondria. As a result, the cells use none of the oxygen they transport; they produce the energy carrier ATP by fermentation, via glycolysis of glucose followed by lactic acid production. Furthermore, red cells do not have an insulin receptor and thus their glucose uptake is not regulated by insulin.
Because of the lack of nuclei and organelles, the red blood cells cannot synthesize any RNA, and consequently they cannot divide or repair themselves.
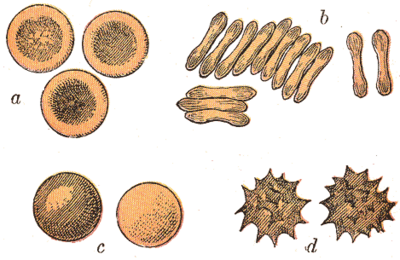
Mammalian erythrocytes are biconcave disks: flattened and depressed in the center, with a dumbbell-shaped cross section. This shape (as well as the loss of organelles and nucleus) optimizes the cell for the exchange of oxygen with its surroundings. The cells are flexible so as to fit through tiny capillaries, where they release their oxygen load. Erythrocytes are circular, except in the camel family Camelidae, where they are oval.
In large blood vessels, red blood cells sometimes occur as a stack—flat side next to flat side. This is known as rouleaux formation, and it occurs more often if the levels of certain serum proteins are elevated, as for instance during inflammation.
The spleen acts as a reservoir of red blood cells, but this effect is somewhat limited in humans. In some other mammals, such as dogs and horses, the spleen sequesters large numbers of red blood cells, which are dumped into the blood during times of exertion stress, yielding a higher oxygen transport capacity.
Human erythrocytes
The diameter of a typical human erythrocyte disk is 6–8 µm, much smaller than most other human cells. A typical erythrocyte contains about 270 million hemoglobin molecules, with each carrying four heme groups.
Adult humans have roughly 2–3 × 1013 red blood cells at any given time. Women have about four to five million erythrocytes per microliter (cubic millimeter) of blood and men about five to six million; people living at high altitudes with low oxygen tension will have more. Red blood cells are thus much more common than the other blood particles: There are about 4,000–11,000 white blood cells and about 150,000–400,000 platelets in each microliter of human blood.
The red blood cells of an average adult human male store collectively about 2.5 grams of iron, representing about 65 percent of the total iron contained in the body (DP 2008; Bridges 2001).
Life cycle
The process by which red blood cells are produced is called erythropoiesis. Erythrocytes are continuously being produced in the red bone marrow of long bones, at a rate of about two million per second. (In the embryo, the liver is the main site of red blood cell production.) The production can be stimulated by the hormone erythropoietin (EPO), synthesized by the kidney; which also is used for doping in sports. Just before and after leaving the bone marrow, they are known as reticulocytes, which comprise about one percent of circulating red blood cells.
Erythrocytes develop from committed stem cells through reticulocytes to mature erythrocytes in about seven days and live a total of about 120 days.
The aging erythrocyte undergoes changes in its plasma membrane, making it susceptible to recognition by phagocytes and subsequent phagocytosis in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow. Much of the important breakdown products are recirculated in the body. The heme constituent of hemoglobin are broken down into Fe3+ and biliverdin. The biliverdin is reduced to bilirubin, which is released into the plasma and recirculated to the liver bound to albumin. The iron is released into the plasma to be recirculated by a carrier protein called transferrin. Almost all erythrocytes are removed in this manner from the circulation before they are old enough to hemolyze. Hemolyzed hemoglobin is bound to a protein in plasma called haptoglobin which is not excreted by the kidney.
Surface proteins
There are two main types of proteins on the surface of red blood cells:
- Band 3
- Glycophorins such as glycophorin C
The blood types of humans are due to variations in surface glycoproteins of erythrocytes.
Separation and blood doping
Red blood cells can be separated from blood plasma by centrifugation. During plasma donation, the red blood cells are pumped back into the body right away, and the plasma is collected. Some athletes have tried to improve their performance by blood doping: First about one liter of their blood is extracted, then the red blood cells are isolated, frozen, and stored, to be re-injected shortly before the competition. (Red blood cells can be conserved for five weeks at −79°C.) This practice is hard to detect but may endanger the human cardiovascular system, which is not equipped to deal with blood of the resulting higher viscosity.
Diseases and diagnostic tools
There are a number of blood diseases involving the red blood cells. These include:
Anemia. Anemias (or anaemias) are diseases characterized by low oxygen transport capacity of the blood, because of low red cell count or some abnormality of the red blood cells or the hemoglobin.
- Iron deficiency anemia is the most common anemia; it occurs when the dietary intake or absorption of iron is insufficient, and hemoglobin, which contains iron, cannot be properly formed.
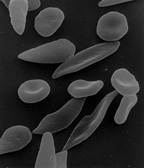
- Sickle-cell disease is a genetic disease that results in abnormal hemoglobin molecules. When these release their oxygen load in the tissues, they become insoluble, leading to mis-shaped red blood cells. These sickle shaped red cells are rigid and cause blood vessel blockage, pain, strokes, and other tissue damage.
- Thalassemia is a genetic disease that results in the production of an abnormal ratio of hemoglobin subunits.
- Spherocytosis is a genetic disease that causes a defect in the red blood cell's cytoskeleton, causing the red blood cells to be small, sphere-shaped, and fragile instead of donut-shaped and flexible.
- Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune disease wherein the body lacks intrinsic factor, required to absorb vitamin B12 from food. Vitamin B12 is needed for the production of hemoglobin.
- Aplastic anemia is caused by the inability of the bone marrow to produce blood cells.
- Pure red cell aplasia is caused by the inability of the bone marrow to produce only red blood cells.
- Hemolysis is the general term for excessive breakdown of red blood cells. It can have several causes.
Malaria. Malaria is a vector-borne infectious disease that involves red blood cells. The malaria parasite spends part of its life cycle in red blood cells (the erythrocytic phase), feeds on their hemoglobin, and then breaks them apart, causing fever. Both sickle-cell disease and thalassemia are more common in malaria areas, because these mutations convey some protection against the parasite.
Polycythemia. Polycythemias (or erythrocytoses) are diseases characterized by a surplus of red blood cells. The increased viscosity of the blood can cause a number of symptoms. In polycythemia vera, the increased number of red blood cells results from an abnormality in the bone marrow.
Microvascular disease. Several microangiopathic diseases, including disseminated intravascular coagulation and thrombotic microangiopathies, present with pathognomonic (diagnostic) RBC fragments called schistocytes. These pathologies generate fibrin strands that sever RBCs as they try to move past a thrombus.
Several blood tests involve red blood cells, including the RBC count (the number of red blood cells per volume of blood) and the hematocrit (percentage of blood volume occupied by red blood cells). The blood type needs to be determined to prepare for a blood transfusion or an organ transplantation.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- American Association of Blood Banks (AABB), America's Blood Centers, and American Red Cross. 2002. Circular of information for the use of human blood and blood components US Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Bridges, K. R. 2001. Iron transport and cellular uptake Information Center for Sickle Cell and Thalassemic Disorders. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Cohen, W. D. 1982. The cytomorphic system of anucleate non-mammalian erythrocytes Protoplasma 113(1): 23-32. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Dean, L. 2005. Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens Bethesda, MD: National Center for Biotechnology Information. OCLC 84650725. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Department of Pathology (DP), University of Virginia Health System. 2008. Iron metabolism University of Virginia Health System. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Educational Broadcasting Corporation (EBC). 2002. Red gold. Blood history timeline. 1000 to 1699: Status quo under fire PBS. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Jiang, N., N. S. Tan, B. Ho, and J. L. Ding. 2007. Respiratory protein-generated reactive oxygen species as an antimicrobial strategy Nature Immunology 8(10): 1114-22. PMID 17721536. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Kesava, S. 2007. Red blood cells do more than just carry oxygen. New findings by NUS team show they aggressively attack bacteria too The Straits Times September 1, 2007. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
- Maton, A., J. Hopkins, C. W. McLaughlin, S. Johnson, M. Q. Warner, D. LaHart, and J. D. Wright. 1993. Human Biology and Health. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0139811761.
- Ruud, J. T. 1954. Vertebrates without erythrocytes and blood pigment. Nature 117: 848-850.
- Snyder, G. K., and B. A. Sheafor. 1999. Red blood cells: Centerpiece in the evolution of the vertebrate circulatory system American Zoologist 39(2): 189–198. Retrieved August 7, 2008.
External links
All links retrieved December 7, 2022.
|
||||||||||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/04/2023 05:24:48 | 48 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Erythrocyte | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: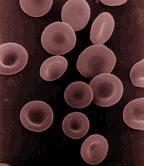
 KSF
KSF