Benzyl Carbamate
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 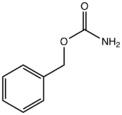
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzyl carbamate | |
| Other names
Carbamic acid, phenylmethyl ester
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C8H9NO2 |
| Molar mass | 151.165 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 88 °C (190 °F; 361 K) |
Solubility in water
|
moderate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
- SizeSet
Benzyl carbamate is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2OC(O)NH2. The compound can be viewed as the ester of carbamic acid (O=C(OH)(NH2)) and benzyl alcohol, although it is produced from benzyl chloroformate with ammonia.[1] It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents and moderately soluble in water. Benzyl carbamate is used as a protected form of ammonia in the synthesis of primary amines. After N-alkylation, C6H5CH2OC(O) group is removable with Lewis acids.[2]
References
- ↑ Meyer, Hartmut; Beck, Albert K.; Sebesta, Radovan; Seebach, Dieter (2008). "Benzyl Isopropoxymethyl Carbamate - an Aminomethylating Reagent for Mannich Reactions of Titanium Enolates". Organic Syntheses 85: 287. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.085.0287.
- ↑ Sanchez-Sancho, Francisco; Romero, Jose Antonio; Fernandez-Ibanez, M. Angeles (2010). "Benzyl Carbamate". E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01206. ISBN 978-0471936237.
 |
Categories: [Benzyl compounds] [Carbamates] [Reagents for organic chemistry]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/17/2024 13:08:52 | 5 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Benzyl_carbamate | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF