Hyperbola
 From Conservapedia
From Conservapedia A hyperbola is a curve produced by the intersection of a plane with both nappes of a conic section.
Mathematical definition[edit]
A hyperbola may be more formally defined as the locus of all points the difference of whose distances from two fixed points (the foci) is constant. The Cartesian equation for a hyperbola with a semimajor axis about the x-axis is
Applications[edit]
Nuclear reactor cooling towers are an example of a hyperbolic-shaped structure. This form allows for maximum structural strength with minimum use of building materials.
When two rocks are thrown simultaneously into a pool of still water, ripples move outward in concentric circles. These circles intersect in points which form a curve known as the hyperbola. The same phenomenon is used in radio tracking stations. Objects are located by sending out signals from two sources to a receiving station, such as one found on a boat or airplane. The constant time difference between the signals from the two stations is represented by a hyperbola.
Categories: [Geometry]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/11/2023 22:11:33 | 10 views
☰ Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Hyperbola | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: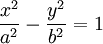
 KSF
KSF