Conservative Force
 From Conservapedia
From Conservapedia Conservative forces are those that possess certain properties:[1]
- The work it does on a particle is independent of its trajectory.
- The work done on a particle that moves along a closed trajectory (where the initial and final positions are the same, or di = df) = 0) is zero.
- The force can be written as the negative of the gradient of a potential energy function, i.e.
 .
. - The curl of the force,
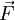 is zero,
is zero, 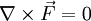
When the only forces present in a system are conservative, energy is conserved.
Examples of conservative forces include:
Friction is an example of a non-conservative force:
References[edit]
- ↑ Serway and Beichner, Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Fifth Edition
Categories: [Mechanics]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/14/2023 02:07:38 | 52 views
☰ Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Conservative_force | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: KSF
KSF