Syndromes Affecting The Heart
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms that are correlated with each other. A syndrome can affect one or more of body systems. Different syndromes affect different groups of organs. This is a list of syndromes that may affect the heart. Syndromes affecting primarily the heart are written in bold letters. [1][2]
| Syndrome | Cause | cardiac signs and symptoms | Other symptoms or organs affected | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1q21.1 deletion syndrome | genetic (Chromosome 1) | Cardiovascular anomalies are present in 30% of the cases (for example anomalous origin of the coronary artery in "Class II-deletion") |
|
|
| DiGeorge syndrome | genetic (Chromosome 22) | commonly interrupted aortic arch, truncus arteriosus and tetralogy of Fallot |
|
|
| Acute coronary syndrome | Commonly associated with three clinical manifestations: ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, 30%), non ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, 25%), or unstable angina (38%) |  Blockage of a coronary artery | ||
| Adams–Nance syndrome | maybe disturbance in glycine metabolism | persistent tachycardia, paroxymal hypertension |
|
|
| Alagille syndrome | genetic (Autosomal dominant inheritance: loss of function mutations in either JAG1 or NOTCH2) | Congenital heart problems e.g. pulmonary artery stenosis (common), Tetralogy of Fallot, overriding aorta, ventricular septal defect; and right ventricular hypertrophy. | Liver (jaundice, pruritus, hepatosplenomegaly, acholia, xanthoma) | |
| Andersen–Tawil syndrome |  This condition affects the QT interval (in blue) | |||
| Antley–Bixler syndrome | ||||
| Barth syndrome | ||||
| Brugada syndrome | ||||
| Cantú syndrome | genetic (Chromosome 12, autosomal dominant) | |||
| Cardiac syndrome X | ||||
| Cardiorenal syndrome | Kidney | |||
| Cat eye syndrome | ||||
| CHARGE syndrome | ||||
| Coffin–Lowry syndrome | genetic (RPS6KA3 gene mutation, Chromosome X) | |||
| Costello syndrome | ||||
| Down syndrome | genetic (Chromosome 21) | |||
| Dressler syndrome | autoimmune inflammatory reaction secondary to MI. | |||
| Edwards syndrome | genetic (Chromosome 18) | |||
| Eisenmenger's syndrome | ||||
| Ellis–van Creveld syndrome | ||||
| Emanuel syndrome | ||||
| HEC syndrome | ||||
| Heyde's syndrome | ||||
| Ho–Kaufman–Mcalister syndrome | ||||
| Holt–Oram syndrome | ASD, and a first degree heart block. | |||
| Hypoplastic left heart syndrome | ||||
| Jacobsen syndrome | genetic (Chromosome 11q deletion) | |||
| Jaffe–Campanacci syndrome | ||||
| Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome | genetic (autosomal recessive) | a type of long QT syndrome | ||
| Kabuki syndrome | ||||
| Kearns–Sayre syndrome | ||||
| Long QT syndrome | ||||
| Lutembacher's syndrome | ||||
| Malpuech facial clefting syndrome | ||||
| Marden–Walker syndrome | ||||
| Marfan syndrome | ||||
| McKusick–Kaufman syndrome | ||||
| McLeod syndrome | ||||
| Noonan syndrome | ||||
| Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines | ||||
| Ortner's syndrome | ||||
| Bouveret Hoffmann syndrome | another name for "Paroxysmal tachycardia" | |||
| Patau syndrome | genetic (Chromosome 13) | |||
| Pre-excitation syndrome | ||||
| Romano–Ward syndrome | ||||
| Scimitar syndrome | ||||
| Shone's syndrome | ||||
| Short QT syndrome | ||||
| Sick sinus syndrome | ||||
| Taussig–Bing syndrome | double outlet right ventricle (DORV) and subpulmonic VSD. | a cyanotic congenital heart defect | ||
| Timothy syndrome | ||||
| Townes–Brocks syndrome | ||||
| Triploid syndrome | ||||
| Turner syndrome | ||||
| VACTERL syndrome | ||||
| Wellens' syndrome | ||||
| Williams syndrome | ||||
| Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome | 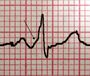 A Delta wave often seen in an affected individual | |||
| Zunich–Kaye syndrome | ||||
| Lown–Ganong–Levine syndrome |
References
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Search by disease name" (in en). https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/Disease_Search_Simple.php?lng=EN&diseaseGroup=heart+syndromes. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ↑ The British Medical Association illustrated medical dictionary. London: Dorling Kindersley. 2002. pp. 177, 536. ISBN 9780751333831. OCLC 51643555.
External links
- What Is the Heart? – NIH
 |
Categories: [Syndromes affecting the heart]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/01/2025 01:40:14 | 16 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Medicine:Syndromes_affecting_the_heart | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF