Circle
 From Nwe
From Nwe - This article is about the shape and mathematical concept of circle. For other uses of the term, see Circle (disambiguation).
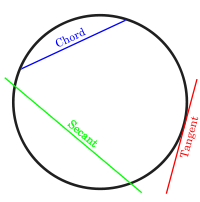
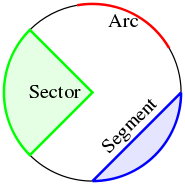
In Euclidean geometry, a circle is the set of all points in a plane at a fixed distance, called the radius, from a given point, the center. The length of the circle is called its circumference, and any continuous portion of the circle is called an arc.
A circle is a simple closed curve that divides the plane into an interior and exterior. The interior of the circle is called a disk.
Mathematically, a circle can be understood in several other ways as well. For instance, it is a special case of an ellipse in which the two foci coincide (that is, they are the same point). Alternatively, a circle can be thought of as the conic section attained when a right circular cone is intersected with a plane perpendicular to the axis of the cone.
Properties
All circles have similar properties. Some of these are noted below.
- For any circle, the area enclosed and the square of its radius are in a fixed proportion, equal to the mathematical constant π.
- For any circle, the circumference and radius are in a fixed proportion, equal to 2π.
- The circle is the shape with the highest area for a given length of perimeter.
- The circle is a highly symmetrical shape. Every line through the center forms a line of reflection symmetry. In addition, there is rotational symmetry around the center for every angle. The symmetry group is called the orthogonal group O(2,R), and the group of rotations alone is called the circle group T.
- The circle centered at the origin with radius 1 is called the unit circle.
Chord properties
A line segment that connects one point of a circle to another is called a chord. The diameter is a chord that runs through the center of the circle.
- The diameter is longest chord of the circle.
- Chords equidistant from the center of a circle are equal in length. Conversely, chords that are equal in length are equidistant from the center.
- A line drawn through the center of a circle perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord. Alternatively, one can state that a line drawn through the center of a circle bisecting a chord is perpendicular to the chord. This line is called the perpendicular bisector of the chord. Thus, one could also state that the perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the center of the circle.
- If a central angle and an inscribed angle of a circle are subtended by the same chord and on the same side of the chord, then the central angle is twice the inscribed angle.
- If two angles are inscribed on the same chord and on the same side of the chord, then they are equal.
- If two angles are inscribed on the same chord and on opposite sides of the chord, then they are supplemental.
- An inscribed angle subtended by a diameter is a right angle.
Sagitta properties
- The sagitta is a line segment drawn perpendicular to a chord, between the midpoint of that chord and the circumference of the circle.
- Given the length of a chord, y, and the length x of the sagitta, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to calculate the radius of the unique circle which will fit around the 2 lines :
Tangent properties
- The line drawn perpendicular to the end point of a radius is a tangent to the circle.
- A line drawn perpendicular to a tangent at the point of contact with a circle passes through the center of the circle.
- Tangents drawn from a point outside the circle are equal in length.
- Two tangents can always be drawn from a point outside of the circle.
Theorems
- The chord theorem states that if two chords, CD and EF, intersect at G, then . (Chord theorem)
- If a tangent from an external point D meets the circle at C and a secant from the external point D meets the circle at G and E respectively, then . (tangent-secant theorem)
- If two secants, DG and DE, also cut the circle at H and F respectively, then . (Corollary of the tangent-secant theorem)
- The angle between a tangent and chord is equal to the subtended angle on the opposite side of the chord. (Tangent chord property)
- If the angle subtended by the chord at the center is 90 degrees then l = √(2) × r, where l is the length of the chord and r is the radius of the circle.
- If two secants are inscribed in the circle as shown at right, then the measurement of angle A is equal to one half the difference of the measurements of the enclosed arcs (DE and BC). This is the secant-secant theorem.
Analytic results
Equation of a circle
In an x-y coordinate system, the circle with center (a, b) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) such that
If the circle is centered at the origin (0, 0), then this formula can be simplified to
and its tangent will be
where , are the coordinates of the common point.
When expressed in parametric equations, (x, y) can be written using the trigonometric functions sine and cosine as
where t is a parametric variable, understood as the angle the ray to (x, y) makes with the x-axis.
In homogeneous coordinates each conic section with equation of a circle is
It can be proven that a conic section is a circle if and only if the point I(1,i,0) and J(1,-i,0) lie on the conic section. These points are called the circular points at infinity.
In polar coordinates the equation of a circle is
In the complex plane, a circle with a center at c and radius r has the equation . Since , the slightly generalized equation for real p, q and complex g is sometimes called a generalized circle. It is important to note that not all generalized circles are actually circles.
Slope
The slope of a circle at a point (x, y) can be expressed with the following formula, assuming the center is at the origin and (x, y) is on the circle:
More generally, the slope at a point (x, y) on the circle , (i.e., the circle centered at [a, b] with radius r units), is given by
provided that , of course.
Area enclosed
- The area enclosed by a circle is
that is, approximately 79 percent of the circumscribed square.
Circumference
- Length of a circle's circumference is
- Alternate formula for circumference:
Given that the ratio circumference c to the Area A is
The r and the π can be canceled, leaving
Therefore solving for c:
So the circumference is equal to 2 times the area, divided by the radius. This can be used to calculate the circumference when a value for π cannot be computed.
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is
Inscribed angles
An inscribed angle is exactly half of the corresponding central angle (see Figure). Hence, all inscribed angles that subtend the same arc have the same value (cf. the blue and green angles in the Figure). Angles inscribed on the arc are supplementary. In particular, every inscribed angle that subtends a diameter is a right angle.
An alternative definition of a circle
Apollonius of Perga showed that a circle may also be defined as the set of points having a constant ratio of distances to two foci, A and B.
The proof is as follows. A line segment PC bisects the interior angle APB, since the segments are similar:
Analogously, a line segment PD bisects the corresponding exterior angle. Since the interior and exterior angles sum to , the angle CPD is exactly , i.e., a right angle. The set of points P that form a right angle with a given line segment CD form a circle, of which CD is the diameter.
As a point of clarification, note that C and D are determined by A, B, and the desired ratio (i.e. A and B are not arbitrary points lying on an extension of the diameter of an existing circle).
Calculating the parameters of a circle

Given three non-collinear points lying on the circle
Radius
The radius of the circle is given by
Center
The center of the circle is given by
where
Plane unit normal
A unit normal of the plane containing the circle is given by
Parametric Equation
Given the radius, , center, , a point on the circle, and a unit normal of the plane containing the circle, , the parametric equation of the circle starting from the point and proceeding counterclockwise is given by the following equation:
See also
- Area of a disk
- Ball (mathematics)
- Degree (angle)
- Ellipse
- Pi
- Sphere
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Altshiller-Court, Nathan. 2007. College Geometry: An Introduction to the Modern Geometry of the Triangle and the Circle. New York, NY: Dover Publications. ISBN 0486458059.
- Arnone, Wendy. 2001. Geometry for Dummies. Hoboken, NJ: For Dummies (Wiley). ISBN 0764553240.
- Pedoe, Dan. 1997. Circles: A Mathematical View. Washington, DC: The Mathematical Association of America. ISBN 0883855186.
External links
All links retrieved February 22, 2017.
- Interactive Java applets – for the properties of and elementary constructions involving circles.
- Interactive Standard Form Equation of Circle – Click and drag points to see standard form equation in action.
- What Is Circle? – at cut-the-knot.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/03/2023 21:41:34 | 70 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Circle | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:















































![{\displaystyle \mathrm {R} \left(s\right)=\mathrm {P_{c}} +\cos \left({\frac {\mathrm {s} }{\mathrm {r} }}\right)\left(P_{0}-P_{c}\right)+\sin \left({\frac {\mathrm {s} }{\mathrm {r} }}\right)\left[{\hat {n}}\times \left(P_{0}-P_{c}\right)\right]}](tmp/RL8aIKpMazia/data/media/images/aa1fbce82a74ad26f16104b42e88aebfdd104d10.jpg)
 KSF
KSF