Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus
 From Conservapedia
From Conservapedia 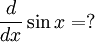
|
This article/section deals with mathematical concepts appropriate for late high school or early college. |
Contents
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus[edit]
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus is the remarkable result that the two fundamental operations of calculus are just inverses of each other. Those two operations are performed on functions from the real numbers to the real numbers, and are most easily visualized when the functions are expressed in terms of graphs. The operations are:
- Differentiation—find the slope of a function's graph at a given point.
- Integration—find the area under a graph between two given limits.
The Theorem[edit]
There are two parts to the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus[1]
Part 1[edit]
The first can be written as:
Let the function  be continuous function defined on a closed interval
be continuous function defined on a closed interval 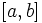 . Define
. Define 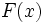 as:
as:
It follows that:
The first part states that if a function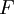 is the antiderivative of a function
is the antiderivative of a function 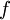 , then the derivative of
, then the derivative of 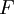 is
is 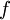 . In other words, antiderivative and derivative are opposite functions.
. In other words, antiderivative and derivative are opposite functions.
Part 2[edit]
If:
Then:
The second part begins with what we know from part 1.
It then states that the definite integral of the function 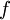 from
from 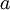 to
to 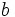 is equal to
is equal to 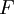 evaluated at
evaluated at 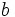 minus
minus 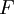 evaluated at
evaluated at 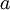 .
.
External links[edit]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Categories: [Calculus]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/16/2023 13:26:43 | 14 views
☰ Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Fundamental_theorem_of_calculus | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
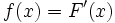

 KSF
KSF