Natural Element Method
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 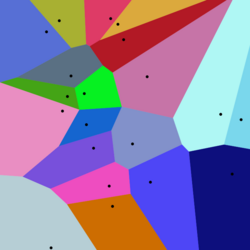
20 points and their Voronoi cells
The natural element method (NEM)[1][2][3] is a meshless method to solve partial differential equation, where the elements do not have a predefined shape as in the finite element method, but depend on the geometry.[4][5][6]
A Voronoi diagram partitioning the space is used to create each of these elements.
Natural neighbor interpolation functions are then used to model the unknown function within each element.
Applications
When the simulation is dynamic, this method prevents the elements to be ill-formed, having the possibility to easily redefine them at each time step depending on the geometry.
References
- ↑ Sukumar, N.; Moran, B.; Belytschko, T. (21 June 1998). "The natural element method in solid mechanics". International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 43 (5): 839–887. doi:3.0.CO;2-R">10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19981115)43:5<839::AID-NME423>3.0.CO;2-R. Bibcode: 1998IJNME..43..839S.
- ↑ J. Yvonnet; D. Ryckelynck; P. Lorong; F. Chinesta (2004). "A new extension of the natural element method for non‐convex and discontinuous problems: the constrained natural element method (C‐NEM)". International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 60 (8): 1451–1474. doi:10.1002/nme.1016. Bibcode: 2004IJNME..60.1451Y. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01508695/file/YRLC.pdf.
- ↑ "Large deformation analysis of elastic bodies by nonlinear Petrov–Galerkin natural element method". Advances in Mechanical Engineering. April 2019. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332678382.
- ↑ Lu, Ping; Shu, Yang; Lu, Dahai; Jiang, Kaiyong; Liu, Bin; Huang, Changbiao (2017-01-01). "Research on Natural Element Method and the application to simulate metal forming processes". Procedia Engineering. International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity, ICTP 2017, 17-22 September 2017, Cambridge, United Kingdom (ScienceDirect) 207: 1087–1092. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.1135.
- ↑ "What is the difference between nem (natural element method) and cnem (constrained natural element method)?" (in en). https://www.researchgate.net/post/What_is_the_difference_between_nem_natural_element_method_and_cnem_constrained_natural_element_method.
- ↑ Botelho, D. P.; Marechal, Y.; Ramdane, B. (November 2016). "Vector interpolation on natural element method: Mesh sensitivity analysis". 2016 IEEE Conference on Electromagnetic Field Computation (CEFC). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. p. 1. doi:10.1109/CEFC.2016.7816353. ISBN 978-1-5090-1032-5.
 |
Categories: [Numerical differential equations] [Numerical analysis] [Computational fluid dynamics] [Computational mathematics] [Simulation]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/06/2024 11:45:59 | 5 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Natural_element_method | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF