Scopolin
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 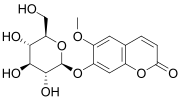
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
7-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-6-methoxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
6-Methoxy-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C16H18O9 |
| Molar mass | 354.311 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
- SizeSet
Scopolin is a glucoside of scopoletin formed by the action of the enzyme scopoletin glucosyltransferase.[1] It occurs in Chamaemelum nobile.[2]
References
- ↑ Hino F, Okazaki M and Miura Y (1982). "Effect of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on glucosylation of scopoletin to scopolin in tobacco tissue-culture". Plant Physiol. 69 (4): 810–813. doi:10.1104/pp.69.4.810. PMID 16662301.
- ↑ Hänsel, Rudolf; Sticher, Otto (2010) (in de). Pharmakognosie – Phytopharmazie (9th ed.). Springer Medizin Verlag. pp. 1076. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-00963-1. ISBN 978-3-642-00962-4. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-642-00963-1.
Bibliography
- Steck, Warren (1967). "Biosynthesis of Scopolin in Tobacco". Canadian Journal of Biochemistry 45 (6): 889–896. doi:10.1139/o67-099. ISSN 1208-6002. PMID 6034703.
- Steck, Warren (1967). "The Biosynthetic Pathway from Caffeic Acid to Scopolin in Tobacco Leaves". Canadian Journal of Biochemistry 45 (12): 1995–2003. doi:10.1139/o67-233. ISSN 1208-6002. PMID 6082583.
 |
Categories: [O-methylated coumarins] [Phenol glucosides]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/21/2024 14:56:47 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Scopolin | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF