Jasmone
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 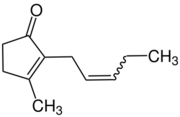
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
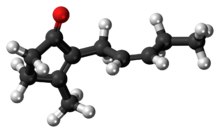
3-methyl-2-[(2Z)-pent-2-en-1-yl]cyclopent-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
cis-Jasmone
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C11H16O |
| Molar mass | 164.246 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless to pale yellow liquid |
| Density | 0.94 g/mL, liquid |
| Melting point | 203 to 205 °C (397 to 401 °F; 476 to 478 K) |
| Boiling point | 146 °C (295 °F; 419 K) at 27 mmHg |
Solubility in water
|
in water |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
- SizeSet
Jasmone is an organic compound, which is a volatile portion of the oil from jasmine flowers. It is a colorless to pale yellow liquid. Jasmone can exist in two isomeric forms with differing geometry around the pentenyl double bond, cis-jasmone and trans-jasmone. The natural extract contains only the cis form, while synthetic material is often a mixture of both, with the cis form predominating. Both forms have similar odors and chemical properties. Its structure was deduced by Lavoslav Ružička.[1]
Jasmone is produced by some plants by the metabolism of jasmonic acid, via a decarboxylation.[2] It can act as either an attractant or a repellent for various insects. Commercially, jasmone is used primarily in perfumes and cosmetics.
References
- ↑ Ruzicka, L.; Pfeiffer, M. (1933). "Über Jasminriechstoffe I. Die Konstitution des Jasmons". Helvetica Chimica Acta 16: 1208–1214. doi:10.1002/hlca.193301601153.
- ↑ Dąbrowska, P.; Boland, W. (2007). "iso-OPDA: An Early Precursor of cis-Jasmone in Plants?". ChemBioChem 8: 2281–2285. doi:10.1002/cbic.200700464.
 |
Categories: [Enones] [Cyclic ketones]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/01/2024 07:35:00 | 1 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Jasmone | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF