Lucifer Yellow
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 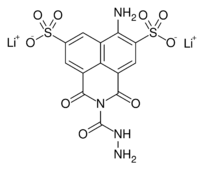
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dilithium 6-amino-2-(hydrazinecarbonyl)-1,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-5,8-disulfonate | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C13H10Li2N4O9S2 |
| Molar mass | 444.24 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
- SizeSet
Lucifer yellow is a fluorescent dye used in cell biology.[1] The key property of Lucifer yellow is that it can be readily visualized in both living and fixed cells using a fluorescence microscope. Lucifer yellow was invented by Walter W. Stewart at the National Institutes of Health and patented in 1978.[2]
Preparations
For common usage it is compounded with carbohydrazide (CH) and prepared as a lithium salt. The CH group allows it to be covalently linked to surrounding biomolecules during aldehyde fixation.[3]
Other cations such as ammonium or potassium can be used when lithium is undesirable, but the resulting salts are less soluble in water.
Lucifer yellow can also be compounded as a vinyl sulfone, with ethylenediamine, or with cadaverine. [clarification needed]
References
- ↑ Hanani, Menachem (January 2012). "Lucifer yellow – an angel rather than the devil". Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 16 (2): 22–31. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01378.x. PMID 21740513.
- ↑ Patent description
- ↑ "Lucifer Yellow CH, Lithium Salt". Molecular Probes. http://www.lifetechnologies.com/order/catalog/product/L453. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
External links
- Invitrogen's manual for Lucifer yellow
- Molecular structure and spectra of Lucifer yellow CH (lithium salt)
 |
Categories: [Fluorescent dyes] [Hydrazides] [Sulfonates] [Heterocyclic compounds with 3 rings] [Nitrogen heterocycles] [Lithium compounds]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/29/2024 12:51:12 | 3 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Lucifer_yellow | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF