Nitrogen Oxide
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
- Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO
2), nitrogen(IV) oxide - Nitrogen trioxide (NO
3), or nitrate radical - Nitrous oxide (N
2O), nitrogen(0,II) oxide - Dinitrogen dioxide (N
2O
2), nitrogen(II) oxide dimer - Dinitrogen trioxide (N
2O
3), nitrogen(II,IV) oxide - Dinitrogen tetroxide (N
2O
4), nitrogen(IV) oxide dimer - Dinitrogen pentoxide (N
2O
5), nitrogen(V) oxide, or nitronium nitrate [NO
2]+
[NO
3]− - Nitrosylazide (N
4O), nitrogen(−I,0,I,II) oxide - Oxatetrazole (N
4O) - Trinitramide (N(NO
2)
3 or N
4O
6), nitrogen(0,IV) oxide
Anions
- Nitroxide (O=N−
) - Nitrite (O=N–O−
or NO−
2) - Nitrate (NO−
3) - Peroxynitrite (O=N–O–O−
or NO−
3) - Peroxynitrate (O
2N–O–O−
or NO−
4) - Orthonitrate (NO3−
4, analogous to phosphate PO3−
4) - Hyponitrite (−
O–N=N–O−
or N
2O2−
2) - Trioxodinitrate or hyponitrate ([O
2NNO]2− or [N
2O
3]2−) - Nitroxylate ((−
O–)
2N–N(–O−
)
2 or N
2O4−
4) - Dinitramide (O
2N–N−
–NO
2 or N
3O−
4)
Cations
- Nitrosonium (N≡O+
or [NO]+
) - Nitronium (O=N+
=O or [NO
2]+
)
Atmospheric sciences
In atmospheric chemistry:
- NO {x} (or NOx) refers to the sum of NO and NO
2.[1][2] - NO {y} (or NOy) refers to the sum of NO
x and all oxidized atmospheric odd-nitrogen species (e.g. the sum of NO
x, HNO
3, HNO
2, etc.) - NO
z (or NOz) = NO
y − NO
x
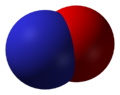 Nitric oxide, NO
Nitric oxide, NO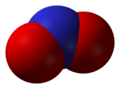 Nitrogen dioxide, NO
Nitrogen dioxide, NO
2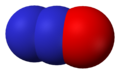 Nitrous oxide, N
Nitrous oxide, N
2O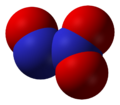 Dinitrogen trioxide, N
Dinitrogen trioxide, N
2O
3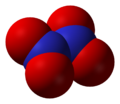 Dinitrogen tetroxide, N
Dinitrogen tetroxide, N
2O
4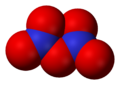 Dinitrogen pentoxide, N
Dinitrogen pentoxide, N
2O
5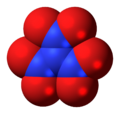 Trinitramide, N
Trinitramide, N
4O
6
Stability
Due to relatively weak N–O bonding, all nitrogen oxides are unstable with respect to N
2 and O
2, which is the principle behind the catalytic converter and prevents the combustion of the atmosphere.
See also
- Nitrate
- Nitrogen oxide sensor
- Sulfur nitrides, which are valence isoelectronic with nitrogen oxides
References
- ↑ United States Clean Air Act, 42 U.S.C. § 7602
- ↑ Seinfeld, John H.; Pandis, Spyros N. (1997), Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 0-471-17816-0, https://archive.org/details/atmosphericchemi0000sein
 |
Categories: [Industrial gases]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 01/21/2023 17:35:47 | 6 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Nitrogen_oxide | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
 KSF
KSF