Virtual Machine Manager
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki Short description: Software
 | |
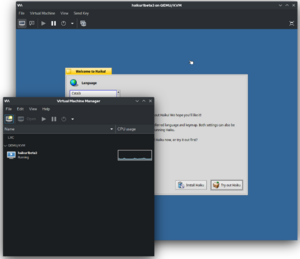 Virtual Machine Manager running Haiku (installation phase) | |
| Developer(s) | Red Hat |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 4.1.0
/ August 4, 2022[1] |
| Written in | Python[2] |
| Operating system | Linux |
| Type | Virtual machine |
| License | GPL v2+ |
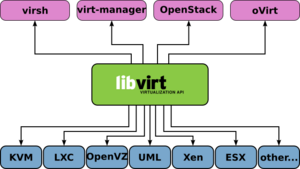
Virtual Machine Manager (virt-manager) is based on libvirt and supports several Hypervisors
In computing, the Red Hat Virtual Machine Manager, also known as virt-manager, is a desktop virtual machine monitor.[3]
Features
Virtual Machine Manager allows users to:
- create, edit, start and stop VMs
- view and control each VM's console
- see performance and utilization statistics for each VM
- view all running VMs and hosts, and their live performance or resource utilization statistics.
- use KVM, Xen or QEMU virtual machines, running either locally or remotely.
- use LXC containers
Support for FreeBSD's bhyve hypervisor has been included since 2014, though it remains disabled by default.[4]
Distributions including Virtual Machine Manager
Virtual Machine Manager comes as the virt-manager package in:
- Arch Linux[5]
- CentOS
- Debian (since lenny)
- Fedora (since version 6)
- FreeBSD (via Ports collection)[6]
- Frugalware
- Gentoo
- Mandriva Linux (since release 2007.1)
- MXLinux
- NetBSD (via pkgsrc)[7]
- NixOS
- OpenBSD (via Ports collection)[8]
- openSUSE (since release 10.3)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (versions 5 through 7 only)
- Scientific Linux
- Trisquel
- TrueOS
- Ubuntu (version 8.04 and above)
- Void Linux
See also
- libvirt, the API used by Virtual Machine Manager to create and manage virtual machines
References
- ↑ "Virtual Machine Manager Releases Page". https://github.com/virt-manager/virt-manager/releases.
- ↑ "virt-manager/virt-manager". https://github.com/virt-manager/virt-manager.
- ↑ Siever, Ellen; Figgins, Stephen; Love, Robert; Robbins, Arnold (2009-09-22). Linux in a Nutshell (6 ed.). O'Reilly. p. 850. ISBN 978-0-596-15448-6. "[...] the Red Hat Virtual Machine Manager application [...] is a collection of tools built using libvirt. This includes a few command-line tools as well as the GUI virt-manager application."
- ↑ "Add bhyve support". 11 April 2014. http://anzwix.com/a/virt-manager/AddBhyveSupport.
- ↑ "virt-manager 1.0.1-1 (any)". 25 March 2014. https://www.archlinux.org/packages/community/any/virt-manager/.
- ↑ "deskutils/virt-manager". Jan 2018. https://www.freshports.org/deskutils/virt-manager/.
- ↑ "sysutils/virt-manager". May 2014. http://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/pkgsrc/current/pkgsrc/sysutils/virt-manager/README.html.
- ↑ "sysutils/virt-manager". Nov 2015. http://cvsweb.openbsd.org/cgi-bin/cvsweb/ports/sysutils/virt-manager/.
External links
Documentation
While the Virtual Machine Manager project itself lacks documentation, there are third parties providing relevant information, e.g.:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux virtualization 7 documentation (VMM is not used in RHEL 8 and later):
- Getting Started with Virtual Machine Manager
- Fedora documentation:
- Getting started with virtualization
- Ubuntu official documentation:
- KVM/VirtManager
- Libvirt documentation:
- Documentation: index
- Documentation: Storage pools
- Documentation: Network management architecture
- Wiki: Virtual networking
Categories: [Free virtualization software] [Remote administration software]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/22/2024 11:18:52 | 11 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Software:Virtual_Machine_Manager | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF