Tellurium Dichloride
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 
| |
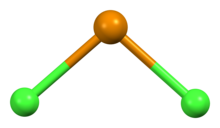
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
Cl2Te |
| Molar mass | 198.50 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | black solid[1] |
| Density | 6.9 g·cm−3[1] |
| Melting point | 208 °C[1] |
| Boiling point | 328 °C[1] |
Solubility in water
|
reacts[1] |
| Solubility | reacts with diethyl ether, insoluble in tetrachloromethane[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Ditellurium bromide, Te 2Br |
Other cations
|
Dichlorine monoxide, OCl 2 Sulfur dichloride, SCl 2 Selenium dichloride, SeCl 2 Polonium dichloride, PoCl 2 |
Related compounds
|
Tritellurium dichloride, Te 3Cl 2 Tellurium tetrachloride, TeCl 4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tellurium dichloride is a chloride of tellurium with the chemical formula TeCl2.
Preparation
Tellurium dichloride can be produced by reacting tellurium with difluorodichloromethane.[2][3]
It can also be produced by the comproportionation of tellurium and tellurium tetrachloride.[4]
Properties
Tellurium dichloride is a black solid that reacts with water. It will melt into a black liquid and vapourize into a purple gas.[1][5] The gas consists of monomeric TeCl2 molecules with Te–Cl bond lengths of 2.329 Å and a Cl–Te–Cl bond angle of 97.0°.[5]
Reactions
Tellurium dichloride reacts with barium chloride in water to form barium tellurite.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Perry, Dale (2011). Handbook of Inorganic Compounds. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8. OCLC 759865801.
- ↑ Gmelin, Leopold (1976) (in en, de). Tellurium. Springer-Verlag. OCLC 77834357.
- ↑ Aynsley, E. E. (1953). "598. The preparation and properties of tellurium dichloride". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed) (Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC)): 3016. doi:10.1039/jr9530003016. ISSN 0368-1769.
- ↑ Haaland, Arne (2008). Molecules and models : the molecular structures of main group element compounds. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-152860-6. OCLC 226969121.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Fernholt, Liv; Haaland, Arne; Volden, Hans V.; Kniep, Rüdiger (1985). "The molecular structure of tellurium dichloride, TeCl2, determined by gas electron diffraction". Journal of Molecular Structure (Elsevier BV) 128 (1-3): 29–31. doi:10.1016/0022-2860(85)85037-7. ISSN 0022-2860.
 |
Categories: [Chlorides] [Gases with color]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 05/09/2025 15:54:29 | 8 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Tellurium_dichloride | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF