Benzofuran
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki Short description: Heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Benzofuran[1] | |||
| Other names
Benzofuran[1]
Coumarone Benzo[b]furan | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number
|
| ||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
Beilstein Reference
|
107704 | ||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| EC Number |
| ||
Gmelin Reference
|
260881 | ||
| KEGG |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
| ||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
| UN number | 1993 | ||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula
|
C8H6O | ||
| Molar mass | 118.135 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | −18 °C (0 °F; 255 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 173 °C (343 °F; 446 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
GHS hazard statements
|
H226, H351, H412 | ||
GHS precautionary statements
|
P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P273, P280, P281, P303+361+353, P308+313, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
500 mg/kg (mice).[2] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Benzothiophene, Indole, Indene, 2-Cumaranone | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
- SizeSet
- PairSizeSet
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the "parent" of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants.
Production
Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethylphenol.[2]
Laboratory methods
Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include:
- O-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation.[3]

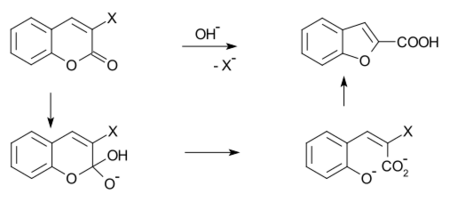
- Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide:[4][5][6]
- Diels–Alder reaction[clarification needed] of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles:[7]
- Diels–Alder reaction yielding a substituted benzofuran|450px
- Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols:[8]
- Benzofurans via Cycloisomerization|400px
Related compounds
- Substituted benzofurans
- Dibenzofuran, an analog with a second fused benzene ring.
- Furan, an analog without the fused benzene ring.
- Indole, an analog with a nitrogen instead of the oxygen atom.
- Benzothiophene, an analog with a sulfur instead of the oxygen atom.
- Isobenzofuran, the isomer with oxygen in the adjacent position.
- Aurone
- Thunberginol F
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 218. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Collin, G.; Höke, H. (2007). Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.l03_l01. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Burgstahler, A. W.; Worden, L. R. (1966). "Coumarone". Organic Syntheses 46: 28. http://www.orgsyn.org/Content/pdfs/procedures/cv5p0251.pdf.; Collective Volume, 5, pp. 251
- ↑ Perkin, W. H. (1870). "XXIX. On some New Bromine Derivatives of Coumarin". Journal of the Chemical Society 23: 368–371. doi:10.1039/JS8702300368. https://zenodo.org/record/2126035.
- ↑ Perkin, W. H. (1871). "IV. On some New Derivatives of Coumarin". Journal of the Chemical Society 24: 37–55. doi:10.1039/JS8712400037. https://zenodo.org/record/1848365.
- ↑ Bowden, K.; Battah, S. (1998). "Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds in Basic Solutions. Part 32. The Perkin Rearrangement". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 2 1998 (7): 1603–1606. doi:10.1039/a801538d.
- ↑ Kusurkar, R. S.; Bhosale, D. K. (1990). "Novel Synthesis of Benzosubstituted Benzofurans Via Diels-Alder Reaction". Synthetic Communications 20 (1): 101–109. doi:10.1080/00397919008054620.
- ↑ Fürstner, Alois; Davies, Paul (2005). "Heterocycles by PtCl2-Catalyzed Intramolecular Carboalkoxylation or Carboamination of Alkynes". Journal of the American Chemical Society 127 (43): 15024–15025. doi:10.1021/ja055659p. PMID 16248631.
 |
Categories: [Benzofurans] [IARC Group 2B carcinogens] [Simple aromatic rings]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 11/19/2024 17:06:54 | 18 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Benzofuran | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF