Indian Mars Exploration Missions
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki
 PSLV-XL C25 lifts off with Mars Orbiter Mission on 5 November 2013. | |
| Country | |
|---|---|
| Organization | ISRO |
| Purpose | Exploration of Mars |
| Status | Active |
| Programme history | |
| Cost | ₹454 crore (US$64 million)[1][2] |
| Duration | 2013–present |
| First flight | Mars Orbiter Mission, 5 November 2013 |
| Launch site(s) | Satish Dhawan Space Centre |
| Vehicle information | |
| Launch vehicle(s) | PSLV-XL |
The Indian Mars exploration missions are an ongoing series of outer space missions by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for the exploration of Mars. The exploration is currently in the primary phase with Orbiter missions.[3]
There has been a single mission so far that deployed an orbiter around the planet which later lost its contact with the earth in 2022.[4][5][6] A second mission planned for 2024 when the launch window opens.[7]
Programme structure
The early phase consists of Mars orbiter missions while the next phase could be aimed at soft landing on the Martian surface and deploying a rover for sample study.[8]
Phase I: Orbiters
Mars Orbiter Mission
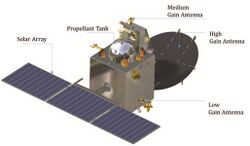
.png)
The first mission, which is also known as Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) was launched in 2013 which carried Mars Orbiter Mission orbiter. The original mission was expected to operate for 6 months, but it lived well past its expected lifetime and lost its contact with the earth in 2022, lasting for over seven years.
Mars Orbiter Mission 2
Mars Orbiter Mission-2 is a proposed second Indian orbiter mission to Mars. Unlike the previous orbiter, it will operate in a lower orbit with Periareon and Apoareon altitude closer to the Martian surface. It will also carry greater scientific payload that includes a hyperspectral camera, a very high resolution panchromatic camera and a radar to better understand the early stages of Mars, its early crust, recent basalts, and ongoing activities such as boulder falls.[9][10]
List of Missions
- Mission
Successful and inactive
Active
Unsuccessful
| Mission |
Launch Date |
Launch Vehicle |
Orbital Insertion Date | Landing Date | Return Date | Status | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Mission |
Extended Mission |
Expected Mission Duration |
Final Mission Duration |
Notes | |||||||
| Phase 1: Orbiters | |||||||||||
| Mars Orbiter Mission | 5 November 2013 | PSLV-XL | 24 September 2014 | – | – | Success | Success | 6 months | 7 years, 6 months, 8 days | First Indian interplanetary mission. | |
| Mars Orbiter Mission 2 | TBD | LVM3 | TBD | – | – | TBD | TBD | 1 year | TBD | Proposed second Indian Mars orbiter mission. | |
Gallery

One of the first images of the surface of Mars taken by the MOM-1 on 25 September 2014.
.png)
Dust storm on northern hemisphere of Mars as seen from MOM-1 on 28 September 2014.
.png)
Tharsis and Valles Marineris as captured by MOM-1.
.png)
Syrtis Major by MOM-1.
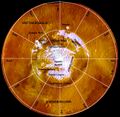
North pole of Mars by MOM-1.
See more on ISRO's website
See also
- Chandrayaan programme
- Indian Human Spaceflight Programme
- List of missions to Mars
References
- ↑ "'We are planning to send our first orbiter to Mars in 2013' | Deccan Chronicle". 2012-08-12. http://www.deccanchronicle.com/editorial/op-ed/‘we-are-planning-send-our-first-orbiter-mars-2013’-548.
- ↑ "Rocket science: how Isro flew to Mars cheap" (in en). 2013-11-06. https://www.hindustantimes.com/india/rocket-science-how-isro-flew-to-mars-cheap/story-WuxDKgSWXegskycsvxFtcO.html.
- ↑ "Mars Orbiter Mission Spacecraft". Indian Space Research Organisation. http://www.isro.gov.in/Spacecraft/mars-orbiter-mission-spacecraft.
- ↑ Kumar, Chethan (2 October 2022). "Designed to last six months, India's Mars Orbiter bids adieu after 8 long years". The Times of India. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/designed-to-last-six-months-indias-mars-orbiter-bids-adieu-after-8-long-years/articleshow/94599977.cms.
- ↑ "With drained battery & no fuel, India's Mars Orbiter craft quietly bids adieu". https://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2022/oct/02/with-drained-battery-no-fuel-indias-mars-orbiter-craft-quietly-bids-adieu-2504219.html.
- ↑ "SCIENCE PROGRAMME OFFICE (SPO), ISRO HEADQUARTERS". https://www.isro.gov.in/MOM_NationalMeet_2022SEP.html. "It was also discussed that despite being designed for a life-span of six months as a technology demonstrator, the Mars Orbiter Mission has lived for about eight years in the Martian orbit with a gamut of significant scientific results on Mars as well as on the Solar corona, before losing communication with the ground station as a result of a long eclipse in April 2022. During the national meet, ISRO deliberated that the propellant must have been exhausted, and therefore, the desired attitude pointing could not be achieved for sustained power generation. It was declared that the spacecraft is non-recoverable, and attended its end-of-life. The mission will be ever-regarded as a remarkable technological and scientific feat in the history of planetary exploration."
- ↑ MOM Orbiter enters 6th year, ISRO eyes Mangalyaan-2. Rasheed Kappan, The Deccan Herald. 25 September 2019.
- ↑ Megala, S (3 July 2023). 'Journey to the Unknown: Scientific Quest for Chandrayaan-3 at the Moon' by Smt. S. Megala. Event occurs at 1 hour 2 minutes 5 seconds.
- ↑ Neeraj Srivastava; S. Vijayan; Amit Basu Sarbadhikari (2022-09-27), "Future Exploration of the Inner Solar System: Scope and the Focus Areas", Planetary Sciences Division (PSDN), Physical Research Laboratory
- ↑ Bagla, Pallava (17 February 2017). "India eyes a return to Mars and a first run at Venus". Science. doi:10.1126/science.aal0781. https://www.science.org/content/article/india-eyes-return-mars-and-first-run-venus.
External links
- Mars Colour Camera images from ISRO
 |
Categories: [Missions to Mars] [Proposed space probes]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/12/2025 13:26:27 | 13 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Astronomy:Indian_Mars_exploration_missions | License: CC BY-SA 3.0


.jpg)
.jpg)

 KSF
KSF