Azirine
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2H-Azirine
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
Beilstein Reference
|
1633516 |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C2H3N |
| Molar mass | 41.053 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
- SizeSet
Azirines are three-membered heterocyclic unsaturated (i.e. they contain a double bond) compounds containing a nitrogen atom and related to the saturated analogue aziridine.[1] They are highly reactive yet have been reported in a few natural products such as Dysidazirine. There are two isomers of azirine: 1H-Azirines with a carbon-carbon double bond are not stable and rearrange to the tautomeric 2H-azirine, a compound with a carbon-nitrogen double bond. 2H-Azirines can be considered strained imines and are isolable.
Preparation
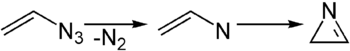
2H-Azirine is most often obtained by the thermolysis of vinyl azides.[2] During this reaction, a nitrene is formed as an intermediate. Alternatively, they can be obtained by oxidation of the corresponding aziridine. Azirine can be generated during photolysis of isoxazole.[3] Due to the weak N-O bond, the isoxazole ring tends to collapse under UV irradiation, rearranging to azirine. [4]
Substituted azirines can be produced via the Neber rearrangement.
Reactions
Photolysis of azirines (under 300 nm) is a very efficient way to generate nitrile ylides. These nitrile ylides are dipolar compounds and can be trapped by a variety of dipolarophiles to yield heterocyclic compounds, e.g. pyrrolines.
The strained ring system also undergoes reactions that favor ring opening and can act as a nucleophile or an electrophile.
Azirines readily hydrolyse to give aminoketones which are themselves susceptible to self-condensation.
See also
- Dysidazirine, one of only a few naturally-occurring azirines
References
- ↑ Teresa M. V. D. Pinho e Melo and Antonio M. d’A. Rocha Gonsalves (2004). "Exploiting 2-Halo-2H-Azirine Chemistry". Current Organic Synthesis 1 (3): 275–292. doi:10.2174/1570179043366729. http://www.bentham.org/cos/contabs/cos1-3.htm#5.
- ↑ "2H-Azirines as synthetic tools in organic chemistry". Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001 (13): 2401–2414. 2001. doi:3.0.CO;2-U">10.1002/1099-0690(200107)2001:13<2401::AID-EJOC2401>3.0.CO;2-U.
- ↑ Edwin F. Ullman (1966). "Photochemical Transposition of Ring Atoms in Five-Membered Heterocycles. The Photorearrangement of 3,5-Diphenylisoxazole". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 88 (8): 1844–1845. doi:10.1021/ja00960a066.
- ↑ Cheng, K.; Qi, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Xiao, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z. et al. (2022). "Developing Isoxazole as a Native Photo-Cross-Linker for Photoaffinity Labeling and Chemoproteomics.". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61 (47): e202209947. doi:10.1002/anie.202209947.
 |
Categories: [Nitrogen heterocycles] [Imines]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/13/2024 10:58:33 | 5 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Azirine | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF