Short description: Chemical compound
Salicin[1]

|
|
| Names
|
| IUPAC name
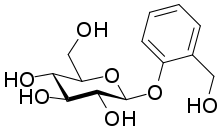
2-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl β-D-glucopyranoside
|
Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-[2-(hydroxymethyl)phenoxy]oxane-3,4,5-triol |
| Other names
Salicin; D-(−)-Salicin; Salicoside
|
| Identifiers
|
CAS Number
|
- 138-52-3
 Y Y
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations
|
Glc(b)-O-Ph(2-CH2OH)
|
| ChemSpider
|
- 388601
 N N
|
| KEGG
|
- C01451
 N N
|
|
|
|
| RTECS number
|
|
| UNII
|
- 4649620TBZ
 Y Y
|
InChI
InChI=1/C13H18O7/c14/h1-4,9-18H,5-6H2
|
SMILES
OCc1ccccc1O[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O
|
| Properties
|
Chemical formula
|
C13H18O7
|
| Molar mass
|
286.280 g·mol−1
|
| Appearance
|
White crystals
|
| Density
|
1.434 g/cm3[2]
|
| Melting point
|
207 °C (405 °F; 480 K)[2]
|
| Boiling point
|
240 decomp.[2]
|
Solubility in water
|
43 g/L
|
| Solubility in Ethanol
|
3 g/L
|
| Solubility in DMSO
|
20 g/L
|
| Solubility in dimethyl formamide
|
30 g/L
|
| Hazards
|
| Main hazards
|
Skin sensitizer / Contact dermatitis[3]
|
| GHS pictograms
|

|
| GHS Signal word
|
Warning
|
GHS hazard statements
|
H317
|
GHS precautionary statements
|
P261, P272, P280, P302+352, P333+313, P362, P363, P501
|
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond)
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
 N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?)
|
| Infobox references
|
|
|
|
Salicin is an alcoholic β-glucoside. Salicin is produced in (and named after) willow (Salix) bark. It is a biosynthetic precursor to salicylaldehyde.[4]
Medicinal aspects
Salicin is found in the bark of and leaves of willows, poplars and various other plants. Derivates are found in castoreum. Salicin from meadowsweet was used in the synthesis of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid),[5] in 1899 by scientists at Bayer. Salicin tastes bitter like quinine.[6]
Salicin may cause an allergic skin reaction (skin sensitization; category 1).[3]
Mild side effects are standard, with rare occurrences of nausea, vomiting, rash, dizziness and breathing problems. Overdose from high quantities of salicin can be toxic, damaging kidneys, causing stomach ulcers, diarrhea, bleeding or digestive discomfort. Some people may be allergic or sensitive to salicylates and suffer reactions similar to those produced by aspirin. People should not take salicin if they have asthma, diabetes, gout, gastritis, hemophilia, stomach ulcers; also contraindicated are children under 16, and pregnant and breastfeeding women.[7]
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 8293
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Haynes, William M., ed (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 3.312. ISBN 9781498754293.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 PubChem
- ↑ Pasteels, J. M.; Rowell-Rahier, M.; Braekman, J. C.; Dupont, A. (1983). "Salicin from host plant as precursor of salicylaldehyde in defensive secretion of Chrysomeline larvae". Physiological Entomology 8 (3): 307–314. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3032.1983.tb00362.x. https://dipot.ulb.ac.be/dspace/bitstream/2013/95098/4/ac2db4af-9a60-4c77-bdb4-6fa9e75d3003.txt.
- ↑ "History of Aspirin". http://inventors.about.com/library/inventors/blaspirin.htm.
- ↑ Daniells, S (2006-10-09). "Symrise explores cheaper alternatives in bitter-maskers". www.foodnavigator.com. http://www.foodnavigator.com/Science-Nutrition/Symrise-explores-cheaper-alternatives-in-bitter-maskers.
- ↑ "Willow bark | University of Maryland Medical Center". http://umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/herb/willow-bark.
Analgesics (N02A, N02B) |
|---|
| Opioids | | Opiates/opium |
- Codeine# (+paracetamol, +aspirin)
- Morphine# (+naltrexone)
- Opium
- Laudanum
- Paregoric
|
|---|
| Semisynthetic |
- Acetyldihydrocodeine
- Benzylmorphine
- Buprenorphine (+naloxone)
- Desomorphine
- Diamorphine (heroin)
- Dihydrocodeine (+paracetamol)
- Dihydromorphine
- Ethylmorphine
- Hydrocodone (+paracetamol, +ibuprofen, +aspirin)
- Hydromorphinol
- Hydromorphone
- Nicocodeine
- Nicodicodine
- Nicomorphine
- Oxycodone (+paracetamol, +aspirin, oxycodone/ibuprofen
|
|---|
| Synthetic |
- Alfentanil
- Alphaprodine
- Anileridine
- Butorphanol
- Carfentanil
- Dextromoramide
- Dextropropoxyphene
- Dezocine
- Fentanyl# (+fluanisone)
- Ketobemidone
- Levorphanol
- Lofentanil
- Meptazinol
- Methadone#
- Nalbuphine
- NFEPP
- Pentazocine
- Pethidine (meperidine)
- Phenadoxone
- Phenazocine
- Piminodine
- Piritramide
- Propiram
- Remifentanil
- Sufentanil
- Tapentadol
- Tilidine
- Tramadol
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Paracetamol-type |
- Acetanilide‡
- Bucetin‡
- Butacetin‡
- Paracetamol (acetaminophen)#
- Parapropamol‡
- Phenacetin‡
- Propacetamol‡
|
|---|
| NSAIDs | | Propionates |
- Fenoprofen
- Flurbiprofen
- Ibuprofen#
- Ketoprofen
- Naproxen
- Oxaprozin
|
|---|
| Oxicams | |
|---|
| Acetates |
- Diclofenac
- Indometacin
- Ketorolac
- Nabumetone
- Sulindac
- Tolmetin
|
|---|
| COX-2 inhibitors |
- Celecoxib
- Etoricoxib
- Lumiracoxib
- Parecoxib
- Rofecoxib ‡
- Valdecoxib ‡
|
|---|
| Fenamates |
- Meclofenamic acid
- Mefenamic acid
|
|---|
| Salicylates |
- Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid)# (+paracetamol/caffeine)
- Benorylate
- Diflunisal
- Ethenzamide
- Magnesium salicylate
- Salicin
- Salicylamide
- Salsalate
- Wintergreen (methyl salicylate)
|
|---|
| Pyrazolones |
- Aminophenazone‡
- Ampyrone
- Metamizole (dipyrone)
- Nifenazone
- Phenazone
- Propyphenazone (+paracetamol/caffeine)
|
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Cannabinoids |
- Cannabidiol
- Cannabis
- Nabilone
- Nabiximols
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (dronabinol)
|
|---|
Ion channel
modulators | | Calcium blockers |
- Gabapentin
- Gabapentin enacarbil
- Mirogabalin
- Pregabalin
- Ziconotide
|
|---|
| Sodium blockers |
- Carbamazepine
- Lacosamide
- Local anesthetics (e.g., cocaine, lidocaine)
- Mexiletine
- Nefopam
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline#)
- Nav1.7/1.8-selective: DSP-2230§
- Funapide§
- PF-05089771§
|
|---|
| Potassium openers | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Myorelaxants |
- Carisoprodol
- Chlorzoxazone
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Mephenoxalone
- Methocarbamol
- Orphenadrine
|
|---|
| Others |
- Analgesic adjuvant
- Analgecine
- Camphor
- Capsaicin
- Clonidine
- Ketamine
- Menthol
- Methoxyflurane
- Nefopam
- Proglumide
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline#)
|
|---|
- #WHO-EM
- ‡Withdrawn from market
- Clinical trials:
- †Phase III
- §Never to phase III
|
Glycosides |
|---|
| Bond |
- O-glycosidic bond
- N-glycosidic bond
- S-glycosidic bond
- C-glycosidic bond
|
|---|
| Geometry |
- α-Glycoside
- β-Glycoside
- 1,4-Glycoside
- 1,6-Glycoside
|
|---|
| Glycone |
- Fructoside
- Galactoside
- Glucoside
- Glucuronide
- Rhamnoside
- Riboside
|
|---|
| Aglycone |
- Alcoholic glycoside
- Cardiac glycoside
- Bufadienolide
- Cardenolide
- Cyanogenic glycoside
- Glycosylamine
- Phenolic glycoside
- Anthraquinone glycoside
- Coumarin glycoside
- Flavonoid glycoside
- Saponin
- Steviol glycoside
- Thioglycoside
|
|---|
Salicylates |
|---|
- Salicylic acid
- Aspirin
- Aloxiprin
- Methyl salicylate
- Magnesium salicylate
- Ethyl salicylate
- Bismuth subsalicylate
- Sodium salicylate
- Salicylamide
- Salicin
- Benorilate
- Salsalate
- Ethenzamide
- Diflunisal
- Trolamine salicylate
- Homosalate
- Salicylmethylecgonine
- Octyl salicylate
- Aluminon
- Benzyl salicylate
- Copper aspirinate
- Potassium salicylate
|
Prostanoid signaling modulators |
|---|
Receptor
(ligands) | |
|---|
Enzyme
(inhibitors) | COX
(PTGS) | |
|---|
| PGD2S |
- Retinoids
- Selenium (selenium tetrachloride, sodium selenite, selenium disulfide)
|
|---|
| PGES | HQL-79 |
|---|
| PGFS | Bimatoprost |
|---|
| PGI2S | Tranylcypromine |
|---|
| TXAS |
- Camonagrel
- Dazmegrel
- Dazoxiben
- Furegrelate
- Isbogrel
- Midazogrel
- Nafagrel
- Nicogrelate
- Ozagrel
- Picotamide
- Pirmagrel
- Ridogrel
- Rolafagrel
- Samixogrel
- Terbogrel
- U63557A
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Others |
- Precursors: Linoleic acid
- γ-Linolenic acid (gamolenic acid)
- Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid
- Diacylglycerol
- Arachidonic acid
- Prostaglandin G2
- Prostaglandin H2
|
|---|
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- Leukotriene signaling modulators
- Nuclear receptor modulators
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salicin. Read more |
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 





 KSF
KSF