Propyl Benzoate
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 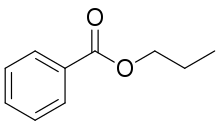
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propyl benzoate | |
| Other names
n-propyl benzoate, benzoic acid propyl ester
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C10H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 164.201 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless oily liquid, nutty odor |
| Density | 1.0230 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −51.6 °C (−60.9 °F; 221.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K)[2] |
Solubility in water
|
insoluble |
| Solubility | miscible with ethanol, diethyl ether[1] |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
|
-105.00·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Flash point | 98 °C (208 °F; 371 K)[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Methyl benzoate Ethyl benzoate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Propyl benzoate is an organic chemical compound used as a food additive. It is an ester.
Uses
Propyl benzoate has a nutty odor and sweet fruity or nut-like taste, and as such, it is used as a synthetic flavoring agent in foods. It also has antimicrobial properties and is used as a preservative in cosmetics. It occurs naturally in the sweet cherry and in clove stems, as well as in butter.[2][3]
Reactions
Propyl benzoate can be synthesized by the transesterification of methyl benzoate with propanol.[3] Propyl benzoate can also be synthesized by means of Fischer esterification of benzoic acid with propanol.
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 3–484. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Ash, Michael; Ash, Irene (2004). Handbook of Preservatives. Synapse Information Resources. p. 508. ISBN 1-890595-66-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=XZ2QB7bu5LwC&pg=PA404. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Burdock, George A. (1997). Encyclopedia of Food and Color Additives. CRC Press. pp. 2340. ISBN 978-0-8493-9416-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=JAVvqWBsBK0C&q="Propyl+benzoate"&pg=PA2340.
Categories: [Food additives] [Preservatives] [Benzoate esters]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/23/2022 13:36:39 | 10 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Propyl_benzoate | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
 KSF
KSF