Short description: Class of drugs
| Nonsteroidal estrogen |
|---|
| Drug class |
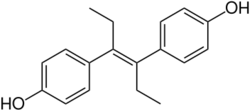 Diethylstilbestrol, one of the most well-known nonsteroidal estrogens. |
| Class identifiers |
|---|
| Synonyms | Nonsteroidal estrogen receptor agonists |
|---|
| ATC code | G03C |
|---|
| Biological target | Estrogen receptors (ERα, ERβ, mERs (e.g., GPER, others)) |
|---|
| Chemical class | Nonsteroidal |
|---|
A nonsteroidal estrogen is an estrogen with a nonsteroidal chemical structure.[1] The most well-known example is the stilbestrol estrogen diethylstilbestrol (DES).[1][2] Although nonsteroidal estrogens formerly had an important place in medicine, they have gradually fallen out of favor following the discovery of toxicities associated with high-dose DES starting in the early 1970s, and are now almost never used.[2][3][4] On the other hand, virtually all selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are nonsteroidal, with triphenylethylenes like tamoxifen and clomifene having been derived from DES,[5] and these drugs remain widely used in medicine for the treatment of breast cancer among other indications.[6] In addition to pharmaceutical drugs, many xenoestrogens, including phytoestrogens, mycoestrogens, and synthetic endocrine disruptors like bisphenol A, are nonsteroidal substances with estrogenic activity.[7]
Pharmacology
Nonsteroidal estrogens act as agonists of the estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ.
List of nonsteroidal estrogens
Synthetic
Pharmaceutical
- Stilbestrols: benzestrol, bifluranol, dienestrol, diethylstilbestrol, dimestrol, fosfestrol, furostilbestrol, hexestrol, mestilbol, methestrol, pentafluranol, phenestrol, terfluranol, stilbestrol esters
- Triphenylethylenes: chlorotrianisene, desmethylchlorotrianisene, estrobin (DBE), M2613, triphenylbromoethylene, triphenylchloroethylene, triphenyliodoethylene, triphenylmethylethylene
- Secosteroids (open-ring steroids): allenestrol, allenolic acid, bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, carbestrol, doisynoestrol, doisynolic acid, fenestrel, methallenestril
- Selective ERα or ERβ agonists: diarylpropionitrile, ERB-196, erteberel, FERb 033, GTx-758, prinaberel, propylpyrazoletriol, WAY-166818, WAY-214156
- Others: 2,8-dihydroxyhexahydrochrysene (2,8-DHHHC), paroxypropione, quadrosilan, tetrahydrochrysene
SERMs like tamoxifen and raloxifene can also be considered to be nonsteroidal estrogens in some tissues.[8]
Environmental
- Synthetic xenoestrogens: alkylphenols, bisphenols (e.g., bisphenol A), parabens, phthalates, polyhalogenated compounds
Natural
- Metalloestrogens: cadmium, others
- Mycoestrogens: taleranol (β-zearalanol), α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, zearalanone, zearalenone, zeranol (α-zearalanol)
- Phytoestrogens: coumestrol, daidzein, deoxymiroestrol, equol, genistein, miroestrol, many others
See also
- Selective estrogen receptor modulator
- Nonsteroidal antiandrogen
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Non-steroidal steroid receptor modulators". IDrugs 9 (7): 488–94. 2006. doi:10.2174/0929867053764671. PMID 16821162.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "The nonsteroidal effects of diethylstilbestrol: the rationale for androgen deprivation therapy without estrogen deprivation in the treatment of prostate cancer". J. Urol. 170 (5): 1703–8. 2003. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000077558.48257.3d. PMID 14532759.
- ↑ "Diethylstilbestrol (DES) update: recommendations for the identification and management of DES-exposed individuals". J Midwifery Womens Health 48 (1): 19–29. 2003. doi:10.1016/s1526-9523(02)00370-7. PMID 12589302.
- ↑ "Diethylstilbestrol exposure". Am Fam Physician 69 (10): 2395–400. 2004. PMID 15168959.
- ↑ Philipp Y. Maximov; Russell E. McDaniel; V. Craig Jordan (23 July 2013). Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 4–. ISBN 978-3-0348-0664-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=p-W5BAAAQBAJ&pg=PA4.
- ↑ Edward P. Gelmann; Charles L. Sawyers; Frank J. Rauscher, III (19 December 2013). Molecular Oncology. Cambridge University Press. pp. 885–. ISBN 978-0-521-87662-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=GrZEAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA885.
- ↑ "Endocrine disruptors: can biological effects and environmental risks be predicted?". Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 36 (1): 118–30. 2002. doi:10.1006/rtph.2002.1564. PMID 12383724.
- ↑ V. Craig Jordan (2013). Estrogen Action, Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators, and Women's Health: Progress and Promise. World Scientific. pp. 362–365. ISBN 978-1-84816-958-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=ejS6CgAAQBAJ&pg=PA362.
Further reading
- "Non-steroidal steroid receptor modulators". IDrugs 9 (7): 488–94. 2006. doi:10.2174/0929867053764671. PMID 16821162.
- "Estrogen receptor beta selective nonsteroidal estrogens: seeking clinical indications". Expert Opin Ther Pat 20 (4): 507–34. 2010. doi:10.1517/13543771003657164. PMID 20302450.
Estrogens and antiestrogens |
|---|
| Estrogens | | ER agonists |
- Steroidal: Alfatradiol
- Certain androgens/anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone, nandrolone esters) (via estrogenic metabolites)
- Certain progestins (e.g., norethisterone, noretynodrel, etynodiol diacetate]], tibolone)
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol acetate
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Epiestriol
- Epimestrol
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol†
- Estradiol
- Estradiol esters (e.g., estradiol acetate, estradiol benzoate, estradiol cypionate, estradiol enanthate, estradiol undecylate, [[Chemistry:Estradiol estradiol valerate, Polyestradiol phosphate|polyestradiol phosphate]], estradiol ester mixtures (Climacteron))
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estriol
- Estriol esters (e.g., estriol succinate, polyestriol phosphate)
- Estrone
- Estrone esters
- Estrone sulfate
- Estropipate (piperazine estrone sulfate)
- Ethinylestradiol#
- Ethinylestradiol sulfonate
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Nilestriol
- Prasterone (dehydroepiandrosterone; DHEA)
- Prasterone enanthate
- Prasterone sulfate
- Promestriene
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Nonsteroidal: Benzestrol
- Bifluranol
- Chlorotrianisene
- Dienestrol
- Diethylstilbestrol (stilbestrol)
- Diethylstilbestrol esters/ethers
- Dimestrol (diethylstilbestrol dimethyl ether)
- Fosfestrol (diethylstilbestrol diphosphate)
- Mestilbol (diethylstilbestrol monomethyl ether)
- Doisynoestrol (fenocycline)
- Hexestrol
- Methallenestril
- Methestrol dipropionate (promethestrol dipropionate)
- Paroxypropione
- Quadrosilan
- Triphenylbromoethylene
- Triphenylchloroethylene
- Zeranol
|
|---|
| Progonadotropins |
- Antiandrogens (e.g., bicalutamide)
- GnRH agonists (e.g., GnRH (gonadorelin), leuprorelin)
- Gonadotropins (e.g., FSH, LH)
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Antiestrogens | ER antagonists
(incl. SERMs/SERDs) |
- Acolbifene†
- Anordrin
- Bazedoxifene
- Broparestrol
- Clomifene#
- Cyclofenil
- Enclomifene†
- Epitiostanol
- Lasofoxifene
- Mepitiostane
- Ormeloxifene
- Ospemifene
- Raloxifene
- Tamoxifen#
- Toremifene
- Exclusively antagonistic: Fulvestrant
|
|---|
| Aromatase inhibitors |
- First-generation: Aminoglutethimide
- Testolactone
- Second-generation: Fadrozole
- Formestane
- Third-generation: Anastrozole
- Exemestane
- Letrozole
|
|---|
| Antigonadotropins |
- Androgens/Anabolic steroid|Anabolic steroid|Anabolic steroid]]]]s (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, nandrolone esters, oxandrolone, fluoxymesterone)
- D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
- GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin, goserelin)
- GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix, elagolix)
- Progestogens (e.g., chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, [[Chemistry:Medroxyprogesterone medroxyprogesterone acetate, Chemistry:Megestrol acetate|megestrol acetate]])
|
|---|
| Others |
- Mixed mechanism of action: Danazol
- Gestrinone
- Androstenedione immunogens: Androvax (androstenedione albumin)
- Ovandrotone albumin (Fecundin)
|
|---|
|
|---|
- #WHO-EM
- ‡Withdrawn from market
- Clinical trials:
- †Phase III
- §Never to phase III
- See also
- Estrogen receptor modulators
- Androgens and antiandrogens
- Progestogens and antiprogestogens
- List of estrogens
|
Estrogen receptor modulators |
|---|
| ER | | Agonists |
- Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
- 3α-Androstanediol
- 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3α-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Androstanediol
- 4-Androstenediol
- 4-Androstenedione
- 4-Hydroxyestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestrone
- 4-Methoxyestradiol
- 4-Methoxyestrone
- 5-Androstenediol
- 7-Oxo-DHEA
- 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 7α-Methylestradiol
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- 8,9-Dehydroestradiol
- 8,9-Dehydroestrone
- 8β-VE2
- 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED)
- 16α-Fluoroestradiol
- 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 16α-Iodoestradiol
- 16α-LE2
- 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol)
- 17α-Dihydroequilenin
- 17α-Dihydroequilin
- 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17β-Dihydroequilenin
- 17β-Dihydroequilin
- Abiraterone
- Abiraterone acetate
- Alestramustine
- Almestrone
- Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone (methandrostenolone), nandrolone and esters, many others; via estrogenic metabolites)
- Atrimustine
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Butolame
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Cyclodiol
- Cyclotriol
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol)
- Epimestrol
- Equilenin
- Equilin
- ERA-63 (ORG-37663)
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol
- Estradiol
- Estradiol esters
- Lipoidal estradiol
- Polyestradiol phosphate
- Estramustine
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estrapronicate
- Estrazinol
- Estriol
- Estriol esters
- Polyestriol phosphate
- Estrofurate
- Estromustine
- Estrone
- Estrone esters
- Estrone methyl ether
- Estropipate
- Etamestrol (eptamestrol)
- Ethinylestradiol
- Ethinylestradiol 3-benzoate
- Ethinylestradiol sulfonate
- Ethinylestriol
- Ethylestradiol
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Hexolame
- Hippulin
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Mytatrienediol
- Nilestriol
- Norethisterone
- Noretynodrel
- Orestrate
- Pentolame
- Prodiame
- Prolame
- Promestriene
- RU-16117
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Tibolone
- Nonsteroidal: (R,R)-THC
- (S,S)-THC
- 2,8-DHHHC
- β-LGND1
- β-LGND2 (GTx-878)
- AC-186
- Allenestrol
- Allenolic acid
- Benzestrol
- Bifluranol
- Bisdehydrodoisynolic acid
- Carbestrol
- D-15414
- DCW234
- Diarylpropionitrile
- Dienestrol
- Diethylstilbestrol
- Diethylstilbestrol esters
- Dimestrol (dianisylhexene)
- Doisynoestrol (fenocycline)
- Doisynolic acid
- Efavirenz
- ERB-196 (WAY-202196)
- Erteberel (SERBA-1, LY-500307)
- Estrobin (DBE)
- Fenestrel
- FERb 033
- Fosfestrol (diethylstilbestrol diphosphate)
- Furostilbestrol (diethylstilbestrol difuroate)
- GTx-758
- Hexestrol
- ICI-85966 (Stilbostat)
- Mestilbol
- Methallenestril
- Methestrol
- Methestrol dipropionate
- Paroxypropione
- Pentafluranol
- Phenestrol
- Prinaberel (ERB-041, WAY-202041)
- Propylpyrazoletriol
- Quadrosilan
- SC-4289
- SERBA-2
- SKF-82,958
- Terfluranol
- Triphenylbromoethylene
- Triphenylchloroethylene
- Triphenyliodoethylene
- Triphenylmethylethylene (triphenylpropene)
- WAY-166818
- WAY-169916
- WAY-200070
- WAY-204688 (SIM-688)
- WAY-214156
- Unknown/unsorted: ERB-26
- ERA-45
- ERB-79
- ZK-283197
- Xenoestrogens: Anise-related (e.g., anethole, anol, dianethole, dianol, photoanethole)
- Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin, phloretin, phlorizin (phloridzin), wedelolactone)
- Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol, psoralidin)
- Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF, 8-prenylnaringenin, apigenin, baicalein, baicalin, biochanin A, calycosin, catechin, daidzein, daidzin, ECG, EGCG, [[Chemistry:Epicateepicatechin, Chemistry:Equol|equol]], formononetin, glabrene, glabridin, Genistein|genistein]], genistin, glycitein, kaempferol, Chemistry:Liquiritigenin
|
|---|
Mixed
(SERMs) |
- 2-Phenylbenzofuran
- 2-Phenylbenzothiophene
- 4'-Hydroxynorendoxifen
- 27-Hydroxycholesterol
- Acefluranol
- Acolbifene
- Afimoxifene
- Anordiol
- Anordrin
- Arzoxifene
- Bazedoxifene
- Brilanestrant
- Broparestrol
- Chlorotrianisene
- Clomifene
- Clomifenoxide
- Cyclofenil
- D-15413
- Droloxifene
- Elacestrant
- Enclomifene
- Endoxifen
- Etacstil (GW-5638, DPC-974)
- Ethamoxytriphetol (MER-25)
- Femarelle
- Fispemifene
- GW-7604
- ICI-55548
- Idoxifene
- Lasofoxifene
- Levormeloxifene
- LN-1643
- LN-2299
- LY-117018
- Menerba
- Miproxifene
- Miproxifene phosphate
- Nafoxidine
- Nitromifene
- NNC 45-0095
- NNC 45-0320
- NNC 45-0781
- NNC 45-1506
- Ormeloxifene
- Ospemifene
- Panomifene
- Pipendoxifene
- Promensil
- Raloxifene
- Rimostil (P-081)
- Spironolactone
- SS1010
- Tamoxifen
- TAS-108 (SR-16234)
- Toremifene
- Trioxifene
- TZE-5323
- Y-134
- Zindoxifene
- Zuclomifene
|
|---|
| Antagonists |
- (R,R)-THC
- 7β-Hydroxy-DHEA
- Chloroindazole
- Cytestrol acetate
- EM-800
- Epitiostanol
- ERA-90
- ERB-88
- Fulvestrant (ICI-182780)
- Glyceollins (I, II, III, IV)
- ICI-164384
- Mepitiostane
- Methylepitiostanol
- Methylpiperidinopyrazole
- MIBE
- Oxabicycloheptene sulfonate
- Phenytoin
- PHTPP
- Prochloraz
- RU-58668
- SS1020
- TAS-108 (SR-16234)
- ZB716
- ZK-164015
- ZK-191703
- Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
|
|---|
|
|---|
| GPER | | Agonists |
- 2-Methoxyestradiol
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- Afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen)
- Atrazine
- Bisphenol A
- Daidzein
- DDT (p,p'-DDT, o',p'-DDE)
- Equol
- Estradiol
- Ethinylestradiol
- Fulvestrant (ICI-182780)
- G-1
- Genistein
- GPER-L1
- GPER-L2
- Hydroxytyrosol
- Kepone
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide
- Nonylphenol
- Oleuropein
- PCBs (2,2',5'-PCB-4-OH)
- Propylpyrazoletriol
- Quercetin
- Raloxifene
- Resveratrol
- Tamoxifen
- Tectoridin
- Zearalanone
- Zearalenol
- Zearalenone
- Zeranol (zearalanol))
|
|---|
| Antagonists |
- CCL18
- Estriol
- G-15
- G-36
- MIBE
|
|---|
|
|---|
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- Estrogens and antiestrogens
- Androgen receptor modulators
- Progesterone receptor modulators
- List of estrogens
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nonsteroidal estrogen. Read more |
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 


 KSF
KSF