Esp32
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 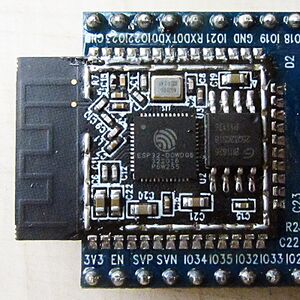 ESP-WROOM-32 module with ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip | |
| Manufacturer | Espressif Systems |
|---|---|
| Type | Microcontroller |
| Release date | September 6, 2016[1] |
| CPU | Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor @ 160 or 240 MHz |
| Memory | 320 KiB SRAM |
| Power | 3.3 V DC |
| Predecessor | ESP8266 |
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system on a chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs either a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations, Xtensa LX7 dual-core microprocessor or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor and includes built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power-management modules. ESP32 is created and developed by Espressif Systems, a Chinese company based in Shanghai, and is manufactured by TSMC using their 40 nm process.[2] It is a successor to the ESP8266 microcontroller.
Features

Features of the ESP32 include the following:[3]
- Processors:
- CPU: Xtensa dual-core (or single-core) 32-bit LX6 microprocessor, operating at 160 or 240 MHz and performing at up to 600 DMIPS
- Ultra low power (ULP) co-processor
- Memory: 520 KiB RAM, 448 KiB ROM
- Wireless connectivity:
- Wi-Fi: 802.11 b/g/n
- Bluetooth: v4.2 BR/EDR and BLE (shares the radio with Wi-Fi)
- Peripheral interfaces:
- 34 × programmable GPIOs
- 12-bit SAR ADC up to 18 channels
- 2 × 8-bit DACs
- 10 × touch sensors (capacitive sensing GPIOs)
- 4 × SPI
- 2 × I²S interfaces
- 2 × I²C interfaces
- 3 × UART
- SD/SDIO/CE-ATA/MMC/eMMC host controller
- SDIO/SPI slave controller
- Ethernet MAC interface with dedicated DMA and planned IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol support[4]
- CAN bus 2.0
- Infrared remote controller (TX/RX, up to 8 channels)
- Pulse counter (capable of full quadrature decoding)
- Motor PWM
- LED PWM (up to 16 channels)
- Ultra low power analog pre-amplifier
- Security:
- IEEE 802.11 standard security features all supported, including WPA, WPA2, WPA3 (depending on version)[5] and WLAN Authentication and Privacy Infrastructure (WAPI)
- Secure boot
- Flash encryption
- 1024-bit OTP, up to 768-bit for customers
- Cryptographic hardware acceleration: AES, SHA-2, RSA, elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), random number generator (RNG)
- Power management:
- Internal low-dropout regulator
- Individual power domain for RTC
- 5 μA deep sleep current
- Wake up from GPIO interrupt, timer, ADC measurements, capacitive touch sensor interrupt
ESP32-xx family
Since the release of the original ESP32, a number of variants have been introduced and announced. They form the ESP32 family of microcontrollers. These chips have different CPUs and capabilities, but all share the same SDK and are largely code-compatible. Additionally, the original ESP32 was revised (see ESP32 ECO V3, for example). See also https://gist.github.com/sekcompsci/2bf39e715d5fe47579fa184fa819f421
ESP32
- Xtensa single-/dual-core 32-bit LX6 microprocessor(s)
- Supports single-precision Floating Point Unit (FPU)
- Wi-Fi: 802.11 b/g/n
- Bluetooth: v4.2 BR/EDR and BLE (shares the radio with Wi-Fi)
- 34 × programmable GPIOs
- 12-bit SAR ADC up to 18 channels
- 2 x 8-bit DAC
ESP32-S2
- Single-core Xtensa LX7 CPU, up to 240 MHz
- NO Floating Point Unit (no FPU)[6]
- 320 KiB SRAM, 128 KiB ROM, and 16 KiB RTC SRAM
- Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz (IEEE 802.11b/g/n)[7]
- No Bluetooth
- 43 programmable GPIOs[7]
- 2 × 13-bit SAR ADCs, up to 20 channels
- USB OTG
ESP32-S3
- Dual-core Xtensa LX7 CPU, up to 240 MHz,[8] and supporting single-precision FPU
- Added instructions to accelerate machine learning applications
- 512 KiB SRAM, 384 KiB ROM, and 16 KiB RTC SRAM
- Capable of connecting to external PSRAM and Flash via Quad SPI or Octal SPI, and share the same 32 MiB address space
- Ultra-low power RISC-V (RV32IMC) coprocessor clocked at 17.5 MHz approximately
- Ultra-low power FSM coprocessor similar to previous ESP32 and ESP32-S2
- Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz (IEEE 802.11 b/g/n)[9]
- Bluetooth 5 (LE)
- 45 programmable GPIOs
- No integrated ethernet MAC
- 2 × 12-bit SAR ADCs, up to 20 channels
- USB OTG
ESP32-C2
- 32-bit RISC-V single-core processor that operates at up to 120 MHz, implementing RV32IMC ISA [10]
- State-of-the-art power and RF performance
- 576 KB ROM, 272 KB SRAM (16 KB for cache) on the chip
- 14 programmable GPIOs: SPI, UART, I2C, LED PWM controller, General DMA controller (GDMA), SAR ADC, Temperature sensor
ESP32-C3

- Single-core 32-bit RISC-V CPU, up to 160 MHz[11]
- 400 KiB SRAM, 384 KiB ROM, and 8 KiB RTC SRAM
- Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz (IEEE 802.11b/g/n)[12]
- Bluetooth 5 (LE)[12]
- 22 / 16 programmable GPIOs
- 2 ADC-12bit
- Pin compatible with ESP8266
ESP32-C6
- High performance 32-bit RISC-V CPU, up to 160 MHz,[13] implementing RV32IMAC
- Low power 32-bit RISC-V CPU, up to 20 MHz, implementing RV32IMAC
- 512 KiB SRAM and 320 KiB ROM
- IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) on 2.4 GHz, supporting 20 MHz bandwidth in 11ax mode, 20 or 40 MHz bandwidth in 11b/g/n mode
- IEEE 802.15.4 (Thread + Zigbee)
- Bluetooth 5.3 (LE)
- 30 (QFN40) / 22 (QFN32) programmable GPIOs
ESP32-H2
- Single-core 32-bit RISC-V CPU, up to 96 MHz
- 256 KB SRAM
- IEEE 802.15.4 (Thread + Zigbee)
- Bluetooth 5.3 (LE)
- 19 programmable GPIOs[14]
ESP32-P4
- High performance dual-core 32-bit RISC-V CPU, up to 400 MHz
- Supports single-precision Floating Point Unit (FPU)
- Low performance single-core 32-bit RISC-V CPU, up to 40 MHz
- 768 KB SRAM on high-performance core system.
- Integrated hardware accelerators for various media encoding protocols, including H.264.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are not implemented.
- If a wireless connection is required, it can be easily connected to the ESP32-C/S/H series.
- More than 50 programmable GPIOs[15]
Announced
ESP32-C5
- Single-core 32-bit RISC-V CPU, up to 240 MHz[16]
- 400 KiB SRAM and 384 KiB ROM
- IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) on 2.4 and 5 GHz, supporting 20 MHz bandwidth in 11ax mode, 20 or 40 MHz bandwidth in 11b/g/n mode
- Bluetooth 5 (LE)
- > 20 programmable GPIOs
QFN packaged chip and module
ESP32 is housed in quad-flat no-leads (QFN) packages of varying sizes with 49 pads. Specifically, 48 connection pads along the sides and one large thermal pad (connected to ground) on the bottom.
Chips
The ESP32 system on a chip integrated circuit is packaged in both 6 mm × 6 mm and 5 mm × 5 mm sized QFN packages.
| Series | Identifier | Processor cores |
Processor speed (MHz) |
Embedded flash memory (MiB) |
Embedded PSRAM memory (MiB) |
GPIOs | Package size |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESP32 | ||||||||
| ESP31B | 2 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 6 mm×6 mm | Pre-release SoC used for beta testing; no longer available. | |
| ESP32-D0WDQ6 | 2 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 6 mm×6 mm | Initial production release chip of the ESP32 series. Not Recommended for New Designs (NRND). | |
| ESP32-D0WD | 2 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 5 mm×5 mm | Smaller physical package variation similar to ESP32-D0WDQ6. Not Recommended for New Designs (NRND). | |
| ESP32-D0WDQ6-V3 | 2 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 6 mm×6 mm | Introduces some fixes to ESP32-D0WDQ6. Not Recommended for New Designs (NRND). | |
| ESP32-D2WD | 2 | 160 | 2 | 0 | 34 | 5 mm×5 mm | 2 MiB (16 Mibit) embedded flash memory variation. Removed. Not Recommended for New Designs (NRND). | |
| ESP32-S0WD | 1 | 160 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 5 mm×5 mm | Single-core processor variation. Not Recommended for New Designs (NRND). | |
| ESP32-D0WD-V3 | 2 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 5 mm×5 mm | Introduces some fixes to ESP32-D0WD. | |
| ESP32-D0WDR2-V3 | 2 | 240 | 0 | 2 | 34 | 5 mm×5 mm | ||
| ESP32-U4WDH | 2 | 240 | 4 | 0 | 34 | 5 mm×5 mm | Single-core processor and 4 MiB (32 Mibit) embedded flash memory variation. Also 1 CPU 160MHz variant existed. | |
| ESP32-S2 | ||||||||
| ESP32-S2 | 1 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 43 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S2R2 | 1 | 240 | 0 | 2 | 43 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S2FH2 | 1 | 240 | 2 | 0 | 43 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S2FH4 | 1 | 240 | 4 | 0 | 43 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S2FN4R2 | 1 | 240 | 4 | 2 | 43 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S3 | ||||||||
| ESP32-S3 | 2 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. With 3.3V and 1.8V VDD_SPI voltage. | |
| ESP32-S3R2 | 2 | 240 | 0 | 2 | 45 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S3R8 | 2 | 240 | 0 | 8 | 45 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S3R8V | 2 | 240 | 0 | 8 | 45 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. With 1.8V VDD_SPI voltage. | |
| ESP32-S3FN8 | 2 | 240 | 8 | 0 | 45 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-S3FH4R2 | 2 | 240 | 4 | 2 | 45 | 7 mm×7 mm | With USB OTG. | |
| ESP32-C2 | ||||||||
| ESP8684H1 | 1 | 120 | 1 | 0 | 14 | 4 mm×4 mm | With Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP8684H2 | 1 | 120 | 2 | 0 | 14 | 4 mm×4 mm | With Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP8684H4 | 1 | 120 | 4 | 0 | 14 | 4 mm×4 mm | With Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP32-C3 | ||||||||
| ESP32-C3 | 1 | 160 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 5 mm×5 mm | With Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP32-C3FN4 | 1 | 160 | 4 | 0 | 22 | 5 mm×5 mm | Not Recommended for New Designs (NRND). | |
| ESP32-C3FH4 | 1 | 160 | 4 | 0 | 22 | 5 mm×5 mm | With Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP32-C3FH4AZ | 1 | 160 | 4 | 0 | 16 | 5 mm×5 mm | With Bluetooth 5. SPI0/SPI1 pins for flash connection are not bonded. | |
| ESP8686H4 | 1 | - | 4 | 0 | - | 4 mm×4 mm | Not released. | |
| ESP8685H2 | 1 | 160 | 2 | 0 | 15 | 4 mm×4 mm | With Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP8685H4 | 1 | 160 | 4 | 0 | 15 | 4 mm×4 mm | With Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP32-C6 | ||||||||
| ESP32-C6 | 1 | 160 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 5 mm×5 mm | With Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP32-C6FH4 | 1 | 160 | 4 | 0 | 22 | 5 mm×5 mm | With Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5. | |
| ESP32-H2 | ||||||||
| ESP32-H2FH2 | 1 | 96 | 2 | 0 | 19 | 4 mm×4 mm | With Bluetooth 5 and Bluetooth Mesh. | |
| ESP32-H2FH4 | 1 | 96 | 4 | 0 | 19 | 4 mm×4 mm | With Bluetooth 5 and Bluetooth Mesh. |
In 2020, chips ESP32-D0WDQ6 and ESP32-D0WD also got a V3 version (ESP32 ECO V3), which fixes some of the bugs[17] and introduces improvements over the previous versions.
Modules
The ESP32 PICO system in package modules combine an ESP32 silicon chip, crystal oscillator, flash memory chip, filter capacitors, and RF matching links into a single 7 mm × 7 mm sized QFN package.
The first released PICO was the ESP32-PICO-D4 with 2 CPUs at 240MHz, 4MiB internal flash, a 40MHz oscillator and 34 GPIOs.[18]
Later, in 2020, the ESP32-PICO-V3 and ESP32-PICO-V3-02 modules were introduced both based on the ESP32 ECO V3 wafer.[19] [20]
In 2022 the ESP32-S3-PICO-1 module was introduced with USB OTG and internal PSRAM.[21]
| Identifier | Processor cores |
Processor speed (MHz) |
Embedded flash memory (MiB) |
Embedded PSRAM memory (MiB) |
GPIOs | Package size |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESP32-PICO-D4 | 2 | 240 | 4 | 0 | 34 | 7 mm×7 mm | |
| ESP32-PICO-V3 | 2 | 240 | 4 | 0 | 31 | 7 mm×7 mm | Based on ESP32 with ECO V3 wafer. |
| ESP32-PICO-V3-02 | 2 | 240 | 8 | 2 | 29 | 7 mm×7 mm | Based on ESP32 with ECO V3 wafer. |
| ESP32-S3-PICO-1-N8R2 | 2 | 240 | 8 | 2 | 39 | 7 mm×7 mm | Includes USB OTG. |
| ESP32-S3-PICO-1-N8R8 | 2 | 240 | 8 | 8 | 39 | 7 mm×7 mm | Includes USB OTG. |
Printed circuit boards
Surface-mount module boards
ESP32 based surface-mount printed circuit board modules directly contain the ESP32 SoC and are designed to be easily integrated onto other circuit boards. Meandered inverted-F antenna designs are used for the PCB trace antennas on the modules listed below. In addition to flash memory, some modules include pseudostatic RAM (pSRAM).
| Vendor | Name | Antenna | Flash memory (MiB) | PSRAM (MiB) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Espressif | ESP-WROOM-03 | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | |
| ESP32-WROOM-32 | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | First publicly available ESP32 module board created by Espressif.[22] FCC Part 15.247 tested (FCC ID: 2AC7Z-ESPWROOM32).[23] Based on ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip. Originally named "ESP-WROOM-32". | |
| ESP32-WROOM-32E | PCB trace | 4,8,16 | 0 | Same as ESP32-WROOM-32 but with the Eco V3 processor revisions[24] | |
| ESP32-WROOM-32D | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Revision of the ESP-WROOM-32 module which uses an ESP32-D0WD chip instead of an ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip.[25] Originally named "ESP-WROOM-32D". | |
| ESP32-SOLO-1 | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Similar to the ESP32-WROOM-32D module, but uses the single-core ESP32-S0WD chip instead of the dual-core ESP32-D0WD. | |
| ESP32-WROOM-32U | U.FL socket | 4 | 0 | Alternative to the ESP-WROOM-32D module which has a U.FL connector for external antenna in lieu of a PCB trace antenna.[25] | |
| ESP32-WROVER | PCB trace | 4 | 4 | ESP32 module board with 4 MiB pSRAM created by Espressif. FCC part 15.247 tested (FCC ID 2AC7Z-ESP32WROVER). Uses 40 MHz crystal oscillator. Does not include U.FL connector. Based on ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip. Since June 2018, new modules have been upgraded to 8 MiB pSRAM. | |
| ESP32-WROVER-I | U.FL socket, PCB trace | 4 | 4 | Variation of ESP32-WROVER module configured to use an on-board U.FL compatible connector. PCB trace antenna not connected by default. | |
| ESP32-WROVER-B | PCB trace | 4 | 8 | Revision of ESP32-WROVER module with 8 MiB pSRAM (instead of 4 MiB pSRAM) operating at 3.3V (instead of 1.8V in previous versions) and ESP32-D0WD (instead of ESP32-D0WDQ6). FCC part 15.247 tested (FCC ID 2AC7Z-ESP32WROVERB). Does not include U.FL connector. (Custom order option for flash capacity of 8 MiB or 16 MiB also available.) | |
| ESP32-WROVER-IB | U.FL socket, PCB trace | 4 | 8 | Variation of ESP32-WROVER-B module configured to use an on-board U.FL compatible connector. PCB trace antenna not connected by default. | |
| ESP32-WROVER-E | PCB trace | 4,8,16 | 2,8 | Revision of ESP32-WROVER module with 2 or 8 MiB pSRAM (instead of 4 MiB pSRAM) operating at 3.3V (instead of 1.8V in previous versions) and ESP32-D0WD-V3, or in 2MB pSRAM models, ESP32-D0WDR2-V3. FCC part 15.247 tested (FCC ID 2AC7Z-ESP32WROVERE). Does not include U.FL connector. (Custom order option for flash capacity of 2 MiB, 8 MiB, or 16 MiB also available.)[26] | |
| ESP32-WROVER-IE | U.FL socket, PCB trace | 4,8,16 | 2,8 | Variation of ESP32-WROVER-E module configured to use an on-board U.FL compatible connector. PCB trace antenna not connected by default. | |
| ESP32-PICO-V3-ZERO | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Based on ESP32-PICO-V3 SiP. It is designed as a module for Alexa Connect Kit (ACK) and connecting with Amazon Alexa. | |
| Ai-Thinker | ESP32-S | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Ai-Thinker's equivalent to Espressif's ESP-WROOM-32 module. (Same form factor and general specifications.)[27] Previously branded as "ESP-32S" with the hyphen before "32S", the initial release of the ESP-32S module replaced the previously announced, but never released, ESP3212 module. |
| ESP32-A1S | U.FL socket, PCB trace | 8 | 4 | Contains an extra AC101 audio codec IC whose IO-pins (line, mic, etc.) are led to the board pins. Comes separately or soldered onto a corresponding audio development board ("ESP32-Audio-Kit").[28][29][30] | |
| AnalogLamb | ESP-32S-ALB | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Clone of the ESP-32S module (ESP-WROOM-32 compatible footprint). Seen with a green solder mask coating.[31] |
| ALB-WROOM | PCB trace | 16 | 0 | Variation of ESP-32S-ALB with 16 MiB of flash memory.[31] | |
| ALB32-WROVER | PCB trace | 4 | 4 | ESP32 module board with 4 MiB pSRAM with the same footprint as the ESP-WROOM-32 module.[32] | |
| DFRobot | ESP-WROOM-32 | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Module board similar to Espressif Systems's ESP-WROOM-32, but is not FCC certified, and uses 26 MHz or 32 kHz crystal oscillator.[33] |
| eBox & Widora | ESP32-Bit | Ceramic, U.FL socket | 4 | 0 | Module has a ceramic antenna and an U.FL antenna connector. This module has a different footprint than the ESP-WROOM-32/ESP-32S modules. |
| Goouuu Tech | ESP-32F | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Module board similar to Espressif Systems's ESP-WROOM-32. FCC certified (ID 2AM77-ESP-32F). |
| IntoRobot | W32 | PCB trace | 4 | 0 | Module similar in appearance to Espressif's ESP-WROOM-32, but footprint pinout differs.[34] |
| W33 | Ceramic, U.FL socket | 4 | 0 | Differs from IntoRobot W32 module in its antenna configuration. | |
| ITEAD | PSH-C32 | PCB trace | 1[35] | 0 | Module has unusually small flash memory on board. Also, footprint is unique and differs from all other ESP32 modules.[36] |
| Pycom[37] | W01 | (Not included.) | 8 | 4 | OEM module version of the WiPy 2.0. Supports Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. FCC ID 2AJMTWIPY01R. |
| L01 | (Not included.) | 8 | 4 | OEM module version of the LoPy. Supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LoRa. FCC ID 2AJMTLOPY01R. | |
| L04 | (Not included.) | 8 | 4 | OEM module version of the LoPy4. Supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRa, and Sigfox. | |
| S01 | (Not included.) | 8 | 4 | Discontinued. OEM module version of the SiPy. Supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Sigfox (14 dBm and 22 dBm). | |
| G01 | (Not included.) | 8 | 4 | OEM module version of the GPy. Supports Cellular LTE-CAT M1/NB1, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. | |
| u-blox | NINA-W131 | (Not included.) | 2 | 0 | Belongs to the u-blox NINA-W13 series of Wi-Fi modules.[38] |
| NINA-W132 | PIFA | 2 | 0 | Belongs to the u-blox NINA-W13 series of Wi-Fi modules.[38] On board planar inverted-F antenna (PIFA) is shaped (cut & bent) metal, not a PCB trace. |
Development and other boards

Development & break-out boards extend wiring and may add functionality, often building upon ESP32 module boards and making them easier to use for development purposes (especially with breadboards).
| Vendor | Name | Surface-mount module used | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Espressif | ESP_Module_Testboard | ESP-WROOM-03 | Break-out board included with ESP-WROOM-03 beta modules.[39][40] |
| ESP32_Demo Board_V2 | ESP-WROOM-32 | Development & demonstration board created by Espressif.[41][42] | |
| ESP32-DevKitC | ESP32-WROOM-32, v4 comes with ESP32-WROOM-DA(Dual Antenna), ESP32-WROVER or ESP32-Solo (Single core variant) | Compact development board created by Espressif.[43] Silkscreen labeling on PCB reads "Core Board". | |
| ESP-WROVER-KIT | ESP-WROOM-32 or ESP32-WROVER | Large development board created by Espressif.[44] Previously named ESP32-DevKitJ.[45] | |
| ESP32-PICO-KIT | ESP32-PICO-D4 | Small development board with micro usb and two header rows of 17 pins. FCC ID 2AC7Z-ESP32PICOKIT. | |
| Adafruit | HUZZAH32 | ESP-WROOM-32 | Also referred to as the "ESP32 Feather Board", the HUZZAH32 is a compact development board/module that is compatible with the Adafruit Feather family of products. |
| Ai-Thinker | NodeMCU-32S | ESP-32S | NodeMCU-like development board.[46] |
| ESP32-CAM | ESP32-S | Compact (27 mm x 40.5 mm) board with ribbon cable Camera Serial Interface with support for 1600 x 1200 pixel OV2640 or 640 x 480 OV7670 camera. Has 9 usable IO pins and microSD card slot.[47] | |
| AnalogLamb | ESP32 Development Board | ESP-32S-ALB or ALB-WROOM | Development board similar to Espressif's ESP32-DevKitC with on board a CP2102 USB/serial bridge. 4 MiB variation uses ESP-32S-ALB; 16 MiB variation uses ALB-WROOM module.[48] |
| Maple ESP32 | ESP-32S-ALB | Development board with Arduino-style connections and CP2104 USB/serial interface.[49] | |
| April Brother | ESPea32 | † | Development board with perfboard area that may be optionally cut-off. |
| ArduCAM | ESP32 UNO | ESP-32S | Arduino Uno-like development board based on ESP32 IoT UNO framework with support for SPI ArduCAM, battery pins and uSD card slot.[50] |
| Arduino | Aruino Nano ESP32 | U-Blox NORA-W106-10B (based on ESP32-S3 IC) | Arduino Nano footprint |
| Banana pi | BPI:bit | ESP-32S | a development for Webduino and Arduino |
| BPI-UNO32 | ESP32-S | a development board for Arduino | |
| DoIT | ESPduino32 | ESP-WROOM-32 | Full-featured Arduino Uno-like development board compatible with Arduino Shields. It also adds additional SPI & IO pins. The board is a clone of WeMos D1 R32 with a USB Type B socket. |
| ESP32 DEVKIT V1 | ESP-WROOM-32 | The ESP32 DevKit V1 is probably the most popular among hobbyists and educators for its ease of use and versatility in various electronic projects. The pinout[51] It's one of the most copied. | |
| EzSBC | ESP32-01 Breakout and Development Board | ESP-WROOM-32 | Full-featured development board with two tri-color LEDs and fits on a breadboard. |
| Gravitech & MakerAsia | Nano32 | † | Development board that directly incorporates the ESP32 chip. |
| HydraBus | HydraESP32 | ESP-WROOM-32 or ESP-32S | HydraESP32 HydraBus v1.1 Rev1 shield/breakout board for ESP-WROOM-32 or ESP-32S. This shield can be used with or without a HydraBus board. |
| Noduino | Quantum | † | Arduino-style development board that directly incorporates the ESP32 chip. |
| Olimex | ESP32-Gateway | ESP32-WROOM32 | Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/Ethernet |
| ESP32-DevKit-LiPo | ESP32-WROOM-32 | pin compatible with ESP32-CoreBoard, but adds Lipo charger and ability to work on LiPo. | |
| ESP32-POE-ISO | ESP32-WROOM-32/UE | Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/Ethernet development board with Power over Ethernet and 2W of isolated DC power | |
| ESP32-POE | ESP32-WROOM-32 | Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/Ethernet development board with Power over Ethernet | |
| ESP32-PRO | † | Wi-Fi/Bluetooth and PIC32MX270F256DT microcontroller and 32 Mb SPI flash and 32 Mb PSRAM. ESP32-PRO-C includes external crypto engine with ATECC508A | |
| ESP32-EVB | ESP32-WROOM32 | Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/Ethernet development board with MicroSD, CAN, IR, LiPo, and two relays. | |
| ESP32-ADF | ESP32-WROVER-B | audio development framework board with stereo microphones, speakers, audio output jack. | |
| Pycom | WiPy | † | MicroPython programmable Wi-Fi & Bluetooth IoT development platform with a 1 km Wi-Fi range. WiPy versions 2.0 and 3.0 use ESP32. |
| LoPy | † | Triple network Pycom board featuring LoRa, Wi-Fi (1 km range), and BLE. | |
| LoPy4 | ? | Quadruple network Pycom board featuring LoRa, Sigfox, Wi-Fi (1 km range), and BLE. | |
| SiPy | † | Triple network Pycom board featuring Sigfox, Wi-Fi (1 km range), and BLE. | |
| GPy | † | Triple network Pycom board featuring LTE-M, Wi-Fi (1 km range), and BLE. | |
| FiPy | † | Quintuple network Pycom board featuring LTE-M, LoRa, Sigfox, Wi-Fi (1 km range), and BLE. | |
| SparkFun | ESP32 Thing | † | Compact development board with FTDI FT231x USB/serial interface and LiPo charger built-in. |
| SunDUINO | ESP32 MiniBoard | ESP-WROOM-32 | Breakout compatible with the Espressif ESP32-DevKitC. Lacks on-board USB-UART. |
| ESP32 MiniBoard v2 | ESP32-Wrover-B/IB | Breakout board with Silabs CP2102, battery charger. Compatible with Espressif DEVkit. | |
| ESP32 SunDUINO | ESP-WROOM-32 or ESP-32S | Arduino-style development board. Lacks on-board USB-UART. | |
| SwitchDoc Labs | BC24 | ESP-WROOM-32 | ESP32 Breakout with 24 SK6812RGBW LEDs with Grove Connectors for easy prototyping. Comes with USB-UART and Feather compatible pinout.[52] |
| Watterott | ESP-WROOM32-Breakout | ESP-WROOM-32 | Breakout which is compatible with the Espressif ESP32-DevKitC. |
| WEMOS[53] | LOLIN32 [Retired][54] | ESP-WROOM-32 | |
| LOLIN32 Lite [Retired][55] | † | ESP32-D0WDQ6 | |
| LOLIN32 Pro [Retired][56] | ESP32-WROVER | MicroSD card slot (supports SD and SPI mode) | |
| LOLIN D32[57] | ESP-WROOM-32 | ||
| LOLIN D32 Pro[58] | ESP32-WROVER | I2C port, TFT port and Micro SD Card slot (support SPI mode) | |
| Widora | Air | † | Compact ESP32 development board. |
| MagicBit | Magic Bit Core | ESP-WROOM-32 | Compact ESP32 development board with displays and several sensors onboard to make learning embedded development convenient. |
† ESP32 SoC incorporated directly onto development board; no module board used.
Programming
Programming languages, frameworks, platforms, and environments used for ESP32 programming:
- ESP-IDF[59][60] – Espressif’s official IoT Development Framework for the ESP32, ESP32-S, ESP32-C and ESP32-H series of SoCs.
- Arduino-ESP32[61] – Arduino core for the ESP32, ESP32-S2, ESP32-S3 and ESP32-C3.
- Espruino – JavaScript SDK and firmware closely emulating Node.js
- MicroPython (and CircuitPython) – lean implementation of Python 3 for microcontrollers
- Lua Network/IoT toolkit for ESP32-Wrover[62]
- Moddable SDK[63] - modern JavaScript and TypeScript with networking, graphics, and ECMA-419 [64] APIs
- Mongoose OS – an operating system for connected products on microcontrollers; programmable with JavaScript or C. A recommended platform by Espressif Systems,[65] AWS IoT,[66] and Google Cloud IoT.[67]
- mruby for the ESP32
- NodeMCU – Lua-based firmware
- PlatformIO[68]
- Rust[69][70]
- Visual Studio Code with the officially supported Espressif Integrated Development Framework (ESP-IDF) Extension[71]
- Zerynth – Python for IoT and microcontrollers, including the ESP32
- Matlab
- Matlab Simulink
- ESPHome — ESPHome is a system to control your ESP8266/ESP32 by simple yet powerful configuration files and control them remotely through home automation systems.
Reception and use
Commercial and industrial use of ESP32:
Use in commercial devices
- Alibaba Group's IoT LED wristband, used by participants at the group's 2017 annual gathering. Each wristband operated as a "pixel", receiving commands for coordinated LED light control, allowing formation of a "live and wireless" screen.[72]
- DingTalk's M1, a biometric attendance-tracking system.[73]
- LIFX Mini, a series of remotely controllable, LED based light bulbs.[74]
- Pium, a home fragrance and aromatherapy device.[75]
- HardKernel's Odroid Go, an ESP32 based handheld gaming device kit made to commemorate Odroid's 10th anniversary.[76]
- Playdate, a handheld video game console jointly developed by Panic Inc. and Teenage Engineering.
- Octopus Energy Mini, an ESP32-C6 based real-time energy monitor.[77]
Use in industrial devices
- TECHBASE's Moduino X series X1 and X2 modules are ESP32-WROVER / ESP32-WROVER-B based computers for industrial automation and monitoring, supporting digital inputs/outputs, analog inputs, and various computer networking interfaces.[78]
- NORVI IIOT Industrial Devices with ESP32-WROVER / ESP32-WROVER-B SOC for industrial automation and monitoring with digital inputs, analog inputs, relay outputs and multiple communications interfaces. Supports LoRa and Nb-IoT as expansion modules.[79]
See also
- Internet of things
References
- ↑ "Espressif Announces the Launch of ESP32 Cloud on Chip and Funding by Fosun Group". Espressif Systems. 2016-09-07. https://www.espressif.com/en/media_overview/news/20160907-esp32briefing#:~:text=Sep 7, 2016-,Espressif announces the launch of ESP32 Cloud on Chip and,MCU at Shanghai Parkyard Hotel.. Retrieved 2021-03-29.
- ↑ "ESP32 Overview". Espressif Systems. https://espressif.com/en/products/hardware/esp32/overview. Retrieved 2016-09-01.
- ↑ "ESP32 Datasheet". Espressif Systems. 2017-03-06. https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32_datasheet_en.pdf. Retrieved 2017-03-14.
- ↑ "IEEE 1588 (PTP) Support (IDFGH-110) #1223". Espressif. 7 November 2021. https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf/issues/1223#ref-issue-482153951.
- ↑ "Certificates | Espressif Systems". https://www.espressif.com/en/support/documents/certificates.
- ↑ Landsmeer, Lennart (2021-04-08). "No, the ESP32-S2 is not faster at floating point operations (and how do you actually speed up division on the ESP32?)". The Weekend Writeup. https://blog.llandsmeer.com/tech/2021/04/08/esp32-s2-fpu.html.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "ESP32-S2_datasheet". Espressif. 2021-06-02. https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-s2_datasheet_en.pdf.
- ↑ Lewis, James (2021-01-01). "Espressif's New ESP32-S3 Adds AI Features for IoT Devices". https://www.hackster.io/news/espressif-s-new-esp32-s3-adds-ai-features-for-iot-devices-b42b902abdf5/.
- ↑ "ESP32-S3". https://www.espressif.com/en/products/socs/esp32-s3.
- ↑ https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-c3_datasheet_en.pdf
- ↑ List, Jenny (2020-11-22). "Espressif Leaks ESP32-C3: A WiFi SOC That's RISC-V and is ESP8266 Pin-Compatible". Hackaday. https://hackaday.com/2020/11/22/espressif-leaks-esp32-c3-a-wifi-soc-thats-risc-v-and-is-esp8266-pin-compatible/.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "ESP32-C3 Datasheet". https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-c3_datasheet_en.pdf.
- ↑ "Announcing ESP32-C6, a Wi-Fi 6 + Bluetooth 5 (LE) SoC" (Press release). Espressif. 2021-04-09. Retrieved 2021-04-22.
- ↑ "Announcing ESP32-H2, an IEEE 802.15.4 + Bluetooth 5 (LE) RISC-V SoC | Espressif Systems" (in en). https://www.espressif.com/en/news/ESP32_H2.
- ↑ "Espressif Reveals ESP32-P4: A High-Performance MCU with Numerous IO-Connectivity and Security Features | Espressif Systems" (in en). https://www.espressif.com.cn/en/news/ESP32-P4.
- ↑ "Announcing ESP32-C5: Espressif's first Dual-Band Wi-Fi 6 MCU" (Press release). Espressif. 2022-06-20.
- ↑ Espressif (2020-09-25). "Eco workarounds and bugs in ESP32". https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/eco_and_workarounds_for_bugs_in_esp32_en.pdf. Retrieved 2022-04-06.
- ↑ "ESP32-PICO-D4 Datasheet (v.2.0)". Espressif. April 2022. https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-pico-d4_datasheet_en.pdf.
- ↑ "ESP32-PICO-V3 Datasheet (v.1.3)". Espressif. 29 March 2022. https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-pico-v3_datasheet_en.pdf.
- ↑ "ESP32-PICO-V3-02 Datasheet (v.1.0)". Espressif. 1 September 2021. https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-pico-v3-02_datasheet_en.pdf.
- ↑ "ESP32-S3-PICO-1 (v.1.0)". Espressif. 21 August 2023. https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-s3-pico-1_datasheet_en.pdf.
- ↑ "ESP-WROOM-32 Datasheet". Espressif Systems. 2016-08-22. https://espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp_wroom_32_datasheet_en.pdf. Retrieved 2016-09-02.
- ↑ "FCC Part 15.247 Test Report for Espressif Systems (Shanghai) Pte. Ltd.". Bay Area Compliance Laboratories Corp.. 2016-11-10. https://fccid.io/document.php?id=3212932. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
- ↑ "ESP32 modules". Espressif Systems. https://espressif.com/en/products/modules. Retrieved 2022-04-06.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 "ESP-WROOM-32D/ESP32-WROOM-32U Datasheet". Espressif Systems. http://espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp-wroom-32d_esp32-wroom-32u_datasheet_en.pdf. Retrieved 2017-11-28.
- ↑ "ESP32-WROVER-E & ESP32-WORVER-IE Datasheet". Espressif Systems. 2023-02-19. https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-wrover-e_esp32-wrover-ie_datasheet_en.pdf. Retrieved 2023-03-18.
- ↑ Baoshi (2016-10-11). "Ai-Thinker ESP-32S Decap Photos". https://twitter.com/ba0sh1/status/785980988077723648. Retrieved 2016-10-22.
- ↑ "ESP32-A1S Product Specification". https://www.makerfabs.com/desfile/files/ESP32-A1S Product Specification.pdf. Retrieved 2021-03-24.
- ↑ "ESP32 series module topic". https://docs.ai-thinker.com/esp32. Retrieved 2021-03-24.
- ↑ "Seeed Drops New ESP32-Audio Development Kit for Audio-Related IoT Projects". https://www.hackster.io/news/seeed-drops-new-esp32-audio-development-kit-for-audio-related-iot-projects-ad38d1f02637. Retrieved 2021-03-24.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "ESP-32S-ALB/ALB-WROOM". AnalogLamb. https://www.analoglamb.com/product/esp-32s-alb/.
- ↑ "ALB32-WROVER is an ESP-WROOM-32 Compatible Module with 32 Mbit PSRAM, up to 128 Mbit Flash". CNXSoft. https://www.cnx-software.com/2018/03/09/alb32-wrover-is-an-esp-wroom-32-compatible-module-with-32-mbit-psram-up-to-128-mbit-flash/.
- ↑ "(SKU:TEL0111)ESP32 WiFi&Bluetooth Module/ESP-WROOM-32". DFRobot. http://wiki.dfrobot.com.cn/index.php?title=(SKU:TEL0111)ESP32_WiFi&Bluetooth_Module/ESP-WROOM-32.
- ↑ "硬件功能 (Hardware Function)". IntoRobot. http://docs.intorobot.com/hardware/w323-datasheet/#--3.
- ↑ ITEAD (2017-02-15). "PSH-C32 Schematic". https://www.itead.cc/wiki/File:PSH_C32.SCHMATIC.pdf. Retrieved 2017-02-23.
- ↑ ITEAD. "PSH-C32". https://www.itead.cc/wiki/PSH-C32. Retrieved 2017-02-23.
- ↑ Pycom. "Pycom OEM Products". https://www.pycom.io/product-category/oem-products/. Retrieved 2017-03-14.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "NINA-W13 series". u-blox. https://www.u-blox.com/en/product/nina-w13-series.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedSparkfunFristImpressions - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedAdafruitVideoESP32BetaModule - ↑ William Hooi (2016-09-01). "So looking forward…". https://twitter.com/willhooi/status/771519098731630592. Retrieved 2016-09-02.
- ↑ Aditya Tannu (2016-09-02). "Look what I just got!". https://twitter.com/Ady/status/771791275313934336. Retrieved 2016-09-02.
- ↑ "ESP32-DevKitC Getting Started Guide". Espressif Systems. 2016-09-21. https://espressif.com/en/content/esp32-devkitc-getting-started-guide. Retrieved 2016-09-21.
- ↑ "ESP-WROVER-KIT". Espressif Systems. https://espressif.com/en/products/hardware/esp-wrover-kit/overview. Retrieved 2017-02-19.
- ↑ "ESP32 Camera Demo". Ivan Grokhotkov. 2016-11-28. https://github.com/igrr/esp32-cam-demo/blob/master/README.md#esp32. Retrieved 2016-12-02.
- ↑ ESP32.net (2016-10-28). "Ai-Thinker NodeMCU-32S Development Board Appears on AliExpress". https://twitter.com/ESP32net/status/792085121394364418. Retrieved 2016-10-28.
- ↑ "ESP32-CAM camera development board | 安信可科技". https://docs.ai-thinker.com/en/esp32-cam.
- ↑ "ESP32 Development Board – Developer Edition". AnalogLamb. https://www.analoglamb.com/product/esp32-development-board/.
- ↑ "Maple ESP32 – ESP32 Board with Micro SD Interface, USB to USART & Compatible with Arduino Interface". AnalogLamb. https://www.analoglamb.com/product/maple-esp32/.
- ↑ ESP32 UNO by ArduCam. "Arduino Uno-like development board". https://www.arducam.com/arducam-iotai-esp32-camera-module-arduino-uno-r3-board/.
- ↑ "DOIT ESP32 DEV KIT v1 high-resolution pinout and specs". Mischianti. https://mischianti.org/doit-esp32-dev-kit-v1-high-resolution-pinout-and-specs/.
- ↑ "BC24 / ESP32 Development Board – Big Circle 24". SwitchDoc Labs. https://shop.switchdoc.com/products/the-bc24-esp32-based-24-rgbw-pixels-with-grove-connectors.
- ↑ "Products [WEMOS Electronics"]. https://wiki.wemos.cc/start. Retrieved 2018-01-25.
- ↑ "LOLIN32 (Retired) [WEMOS Electronics"] (in en). https://wiki.wemos.cc/products:lolin32:lolin32.
- ↑ "LOLIN32 Lite (Retired) [WEMOS Electronics"] (in en). https://wiki.wemos.cc/products:lolin32:lolin32_lite.
- ↑ "LOLIN32 Pro (Retired) [WEMOS Electronics"] (in en). https://wiki.wemos.cc/products:lolin32:lolin32_pro.
- ↑ "D32 [WEMOS Electronics"] (in en). https://wiki.wemos.cc/products:d32:d32.
- ↑ "D32 Pro [WEMOS Electronics"] (in en). https://wiki.wemos.cc/products:d32:d32_pro.
- ↑ "IoT Development Framework I Espressif Systems". https://www.espressif.com/en/products/sdks/esp-idf.
- ↑ Espressif IoT Development Framework, Espressif Systems, 2023-08-29, https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf, retrieved 2023-08-29
- ↑ Arduino core for the ESP32, ESP32-S2, ESP32-S3 and ESP32-C3, Espressif Systems, 2023-08-28, https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32, retrieved 2023-08-29
- ↑ "Lua Network/IoT toolkit for ESP32-Wrover". Real Time Logic. https://github.com/RealTimeLogic/LspAppMgr-ESP32. Retrieved 2021-04-12.
- ↑ "Moddable SDK". https://github.com/Moddable-OpenSource/moddable.
- ↑ [XXXX "ECMA-419 - ECMAScript® embedded systems API specification"]. XXXX.
- ↑ "Third-Party Platforms That Support Espressif Hardware". Espressif Systems. http://espressif.com/en/support/download/sdk. Retrieved 2017-10-20.
- ↑ Tim Mattison (2017-04-13). "AWS IoT on Mongoose OS, Part 1". https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/apn/aws-iot-on-mongoose-os-part-1/.
- ↑ "Google Cloud IoT Partners". https://cloud.google.com/iot/partners/. Retrieved 2017-10-20.
- ↑ "Espressif 32 — PlatformIO". https://docs.platformio.org/en/latest/platforms/espressif32.html.
- ↑ Hiari, Omar. "ESP32 and Rust Make a Winning Combination". Apollo Labs. https://apollolabsblog.hashnode.dev/unlocking-possibilities-4-reasons-why-esp32-and-rust-make-a-winning-combination.
- ↑ "The Rust on ESP Book". https://esp-rs.github.io/book/.
- ↑ "Getting Started with VS Code IDE - ESP32 - — ESP-IDF Programming Guide latest documentation". https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/get-started/vscode-setup.html?highlight=vscode.
- ↑ "Alibaba's IoT Wrist Bands Based on ESP32". 2017-09-30. http://espressif.com/en/media_overview/news/alibaba’s-iot-wrist-bands-based-esp32.
- ↑ "DingTalk's New Biometric Attendance Monitor Based on ESP32". Espressif Systems. 2017-06-02. http://espressif.com/en/media_overview/news/dingtalk’s-new-biometric-attendance-monitor-based-esp32.
- ↑ @ESP32net (2017-11-07). "FCC internal photos exhibit for the LIFX Mini Wi-Fi LED light (FCC ID 2AA53-MINI) show inclusion of ESP32…". https://twitter.com/ESP32net/status/928100660285005827.
- ↑ "New ESP32-based Aromatherapy Device". Espressif Systems. 2017-07-31. http://espressif.com/en/media_overview/news/new-esp32-based-aromatherapy-device.
- ↑ "ODROID | Hardkernel". 2018-07-06. https://www.hardkernel.com/main/products/prdt_info.php?g_code=G152875062626.
- ↑ "Octopus Home Mini FAQ" (in en-gb). https://octopus.energy/octopus-home-mini-faq/.
- ↑ "Moduino X Series - Industrial IoT module based on ESP32". TECHBASE Group. http://moduino.techbase.eu/.
- ↑ "NORVI IIoT - Industrial Controllers based on ESP32". ICONIC DEVICES Ltd.. https://norvi.lk/.
External links
- Espressif ESP32 Overview
- Espressif ESP32 Resources
- Espressif ESP-IDF Programming Guide
- Espressif ESP32 Forums
 |
Categories: [Microcontrollers]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/23/2024 06:45:45 | 4 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Engineering:ESP32 | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF