Communication Physics
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 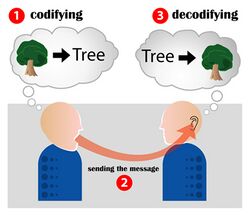
Communication physics is one of the applied branches of physics. It deals with various kinds of communication systems.[1] These can range from basic ideas such as mobile phone communication to quantum communication via quantum entanglement.[2] Communication physics is also a journal edition created in 2018 published by Nature Research that aims to publish research that involves a different way of thinking in the research field.[3]
Applications
Communication physics aims to study and explain how a communication system works. This can be applied in a hard science way via Computer Communication or in the way of how people communicate.[1]
An example of communication physics is how computers can transmit and receive data through networks. This would also deal with explaining how these devices encode and decode messages.
See also
- Electronic communication
- Optical communication
- Computer communication
- Telephone
- Telegraph
- Radio
- Television
- Mobile phone communication
- Nanoscale network
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sostrin, Jesse (2013), Sostrin, Jesse, ed., "Communication Physics: What Holds Patterns Together" (in en), Re-Making Communication at Work (New York: Palgrave Macmillan US): pp. 81–87, doi:10.1057/9781137332769_8, ISBN 978-1-137-33276-9, https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137332769_8, retrieved 2023-03-26
- ↑ Smart, Scott E.; Hu, Zixuan; Kais, Sabre; Mazziotti, David A. (2022-01-25). "Relaxation of stationary states on a quantum computer yields a unique spectroscopic fingerprint of the computer’s noise" (in en). Communications Physics 5 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1038/s42005-022-00803-8. ISSN 2399-3650. https://www.nature.com/articles/s42005-022-00803-8.
- ↑ "Introducing Communications Physics" (in en). Communications Physics 1 (1): 1–2. 2018-02-22. doi:10.1038/s42005-018-0008-5. ISSN 2399-3650. https://www.nature.com/articles/s42005-018-0008-5.
 |
Categories: [Applied and interdisciplinary physics] [Telecommunication theory]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 05/31/2024 02:33:18 | 25 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Communication_physics | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF