Lasri Condensation
 From Handwiki
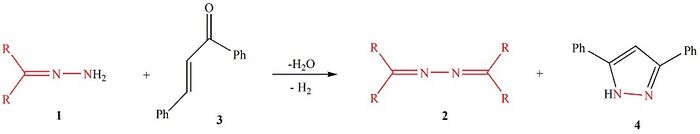
From Handwiki The Lasri condensation[non-primary source needed] is an organic chemistry reaction where chalcone reacts with a hydrazone to furnish an azine and 3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole.[1] It is named after the Portuguese-Moroccan chemist Jamal Lasri.[2][non-primary source needed]
Mechanism
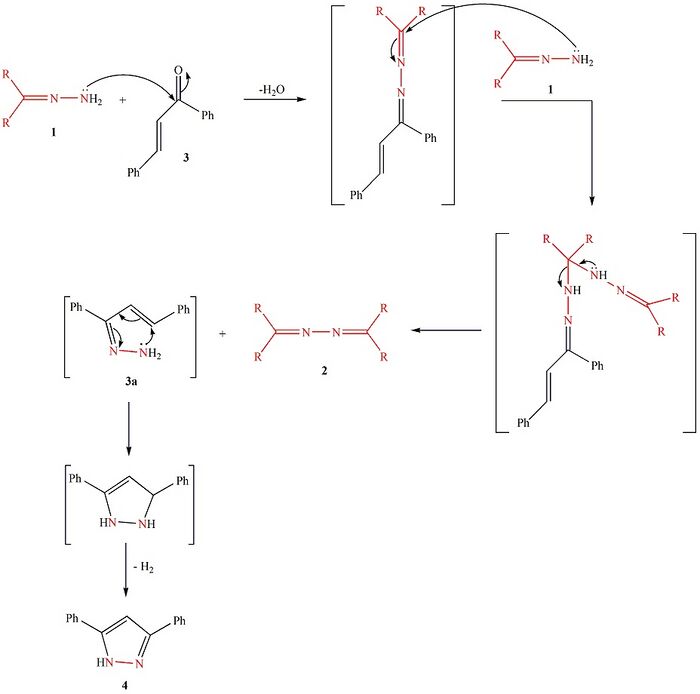
The reaction is started with nucleophilic attack of the amino moiety of hydrazone 1 on the carbonyl group of (E)-1,3-diphenyl-2-propenone 3 to produce the azine intermediate 1-((E)-1,3-diphenylallylidene)-2-(diarylmethylene)hydrazine. This asymmetrical azine then undergoes nucleophilic attack from its diaryl imino sp2-carbon atom by the amino NH2 moiety of hydrazone 1 to afford a second intermediate where the C(sp3)—N bond is cleaved to furnish the symmetrical azine 2. The other product, 1,3-diphenyl-2-propenone hydrazone 3a, cyclizes to afford 2,3-dihydro-3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole[3] which is then rapidly dehydrogenated to yield 3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole 4.[4] In this reaction hydrazone 1 is a source of nitrogen for 3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole 4. Additionally, the reaction does not require the use of any catalyst or promoter.
References
- ↑ Lasri, Jamal; Ismail, Ali I. (2018). "Metal-free and FeCl3-catalyzed synthesis of azines and 3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole from hydrazones and/or ketones monitored by high resolution ESI+-MS". Indian Journal of Chemistry, Section B 57 (3): 362–373. http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/43824.
- ↑ "جمال العسري - CV". http://www.kau.edu.sa/CVEn.aspx?Site_ID=0061741&Lng=EN. Retrieved 28 May 2017.
- ↑ Zhang, Ze; Tan, Ya-Jun; Wang, Chun-Shan; Wu, Hao-Hao (2014). "One-pot synthesis of 3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazoles from chalcones and hydrazine under mechanochemical ball milling". Heterocycles 89 (1): 103–112. doi:10.3987/COM-13-12867.
- ↑ Outirite, Moha; Lebrini, Mounim; Lagrenée, Michel; Bentiss, Fouad (2008). "New one step synthesis of 3,5-disubstituted pyrazoles under microwave irradiation and classical heating". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 45 (2): 503–505. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570450231.
Categories: [Name reactions] [Condensation reactions] [Pyrazoles] [Hydrazines]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 12/07/2024 10:01:36 | 6 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Lasri_condensation | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF