Lithium Peroxide
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 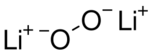
| |
 __ Li+ __ O−
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Dilithium peroxide, Lithium (I) peroxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
Li2O2 |
| Molar mass | 45.881 g/mol |
| Appearance | fine, white powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.31 g/cm3[1][2] |
| Melting point | Decomposes to Li2O at ~340°C [3] |
| Boiling point | NA |
Solubility in water
|
soluble |
| Structure | |
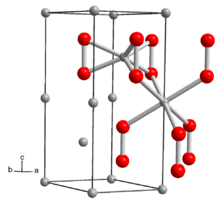
Crystal structure
|
hexagonal |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-13.82 kJ/g |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements
|
H271, H272, H314, H318 |
GHS precautionary statements
|
P210, P220, P221, P260, P264, P280, P283, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P306+360, P310, P321, P363, P370+378, P371+380+375, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
0
3
2 OX |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Sodium peroxide Potassium peroxide Rubidium peroxide Caesium peroxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
- SizeSet
Lithium peroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Li2O2. It is a white, nonhygroscopic solid. Because of its high oxygen:mass and oxygen:volume ratios, the solid has been used to remove CO2 from the atmosphere in spacecraft.[4]
Preparation
It is prepared by the reaction of hydrogen peroxide and lithium hydroxide. This reaction initially produces lithium hydroperoxide:[4][5]
- LiOH + H2O2 → LiOOH + H2O
This lithium hydroperoxide has also been described as lithium peroxide monoperoxohydrate trihydrate (Li2O2·H2O2·3H2O). Dehydration of this material gives the anhydrous peroxide salt:
- 2 LiOOH → Li2O2 + H2O2
Li2O2 decomposes at about 450 °C to give lithium oxide:
- 2 Li2O2 → 2 Li2O + O2
The structure of solid Li2O2 has been determined by X-ray crystallography and density functional theory. The solid features an eclipsed "ethane-like" Li6O2 subunits with an O-O distance of around 1.5 Å.[6]
Uses
It is used in air purifiers where weight is important, e.g., spacecraft to absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen in the reaction:[4]
- Li2O2 + CO2 → Li2CO3 + 1⁄2 O2
It absorbs more CO2 than does the same weight of lithium hydroxide and offers the bonus of releasing oxygen.[7] Furthermore, unlike most other alkali metal peroxides, it is not hygroscopic.
The reversible lithium peroxide reaction is the basis for a prototype lithium–air battery. Using oxygen from the atmosphere allows the battery to eliminate storage of oxygen for its reaction, saving battery weight and size.[8]
The successful combination of a lithium-air battery overlain with an air-permeable mesh solar cell was announced by The Ohio State University in 2014.[9] The combination of two functions in one device (a "solar battery") is expected to reduce costs significantly compared to separate devices and controllers as are currently employed.
See also
- Lithium oxide
References
- ↑ "Physical Constants of Inorganic Compounds," in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 91st Edition (Internet Version 2011), W. M. Haynes, ed., CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, Florida. (pp: 4-72).
- ↑ Speight, James G. (2005). Lange's Handbook of Chemistry (16th Edition). (pp: 1.40). McGraw-Hill. Online version available at: http://www.knovel.com/web/portal/browse/display?_EXT_KNOVEL_DISPLAY_bookid=1347&VerticalID=0
- ↑ Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.,2013,15, 11025. doi:10.1039/c3cp51056e
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon Press. p. 98. ISBN 978-0-08-022057-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=OezvAAAAMAAJ&q=0-08-022057-6&dq=0-08-022057-6&source=bl&ots=m4tIRxdwSk&sig=XQTTjw5EN9n5z62JB3d0vaUEn0Y&hl=en&sa=X&ei=UoAWUN7-EM6ziQfyxIDoCQ&ved=0CD8Q6AEwBA.
- ↑ E. Dönges "Lithium and Sodium Peroxides" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 979.
- ↑ L. G. Cota and P. de la Mora "On the structure of lithium peroxide, Li2O2" Acta Crystallogr. 2005, vol. B61, pages 133-136. doi:10.1107/S0108768105003629
- ↑ Ulrich Wietelmann, Richard J. Bauer "Lithium and Lithium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_393.pub2
- ↑ Girishkumar, G.; B. McCloskey; AC Luntz; S. Swanson; W. Wilcke (July 2, 2010). "Lithium- air battery: Promise and challenges". The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 1 (14): 2193–2203. doi:10.1021/jz1005384.
- ↑ [1] Patent-pending device invented at The Ohio State University: the world’s first solar battery.
External links
- WebElements entry
 |
Categories: [Peroxides] [Lithium compounds] [Oxidizing agents]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 04/14/2023 21:58:26 | 8 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Lithium_peroxide | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
 KSF
KSF