Viral Disease
 From Mdwiki
From Mdwiki | Viral disease | |
|---|---|
| Other names: viral infection | |
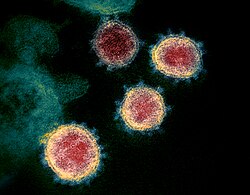 | |
| Transmission electron micrograph of Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virions | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.[1]
Structure[edit | edit source]
Basic structural characteristics, such as genome type, virion shape and replication site, generally share the same features among virus species within the same family.[citation needed]
- Double-stranded DNA families: three are non-enveloped (Adenoviridae, Papillomaviridae and Polyomaviridae) and two are enveloped (Herpesviridae and Poxviridae). All of the non-enveloped families have icosahedral capsids.
- Partly double-stranded DNA viruses: Hepadnaviridae. These viruses are enveloped.
- One family of single-stranded DNA viruses infects humans: Parvoviridae. These viruses are non-enveloped.
- Positive single-stranded RNA families: three non-enveloped (Astroviridae, Caliciviridae and Picornaviridae) and four enveloped (Coronaviridae, Flaviviridae, Retroviridae and Togaviridae). All the non-enveloped families have icosahedral nucleocapsids.
- Negative single-stranded RNA families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, Orthomyxoviridae, ParamyxoviridaeParamyxoviridae and Rhabdoviridae. All are enveloped with helical nucleocapsids.
- Double-stranded RNA genome: Reoviridae.
- The Hepatitis D virus has not yet been assigned to a family, but is clearly distinct from the other families infecting humans.
- Viruses known to infect humans that have not been associated with disease: the family Anelloviridae and the genus Dependovirus. Both of these taxa are non-enveloped single-stranded DNA viruses.
-
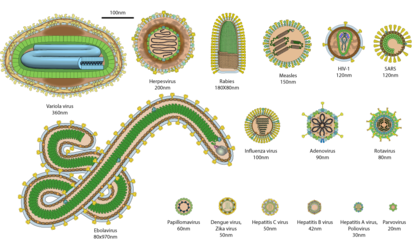
Virions of some of the most common human viruses with their relative size. Nucleic acids are not to scale. SARS stands as for SARS as for COVID-19, variola viruses for smallpox.
-
Immunohistochemical staining of liver biopsy specimen, strong cytoplasmic staining for hepatitis A virus antigen was noted
Viral families[edit | edit source]
Human-infecting virus families offer rules that may assist physicians and medical microbiologists/virologists.[citation needed]
As a general rule, DNA viruses replicate within the cell nucleus while RNA viruses replicate within the cytoplasm. Exceptions are known to this rule: poxviruses replicate within the cytoplasm and orthomyxoviruses and hepatitis D virus (RNA viruses) replicate within the nucleus.[citation needed]
- Segmented genomes: Bunyaviridae, Orthomyxoviridae, Arenaviridae, and Reoviridae (acronym BOAR). All are RNA viruses.
- Viruses transmitted almost exclusively by arthropods: Bunyavirus, Flavivirus, and Togavirus. Some Reoviruses are transmitted from arthropod vectors. All are RNA viruses.[2]
- One family of enveloped viruses causes gastroenteritis (Coronaviridae). All other viruses associated with gastroenteritis are non-enveloped.
Baltimore Group[edit | edit source]
This group of analysts defined multiple categories of virus. Groups:[citation needed]
- I - dsDNA
- II - ssDNA
- III - dsRNA
- IV - positive-sense ssRNA
- V - negative-sense ssRNA
- VI - ssRNA-RT
- VII - dsDNA-RT
Clinically important virus families[edit | edit source]
Clinical characteristics[edit | edit source]
The clinical characteristics of viruses may differ substantially among species within the same family:
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Taylor, M.P.; Kobiler, O.; Enquist, L. W. (2012). "Alphaherpesvirus axon-to-cell spread involves limited virion transmission". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. PNAS. 106 (42): 17046–17051. Bibcode:2012PNAS..10917046T. doi:10.1073/pnas.1212926109. PMC 3479527. PMID 23027939.
- ↑ Hunt, M. "Arboviruses". University of South Carolina School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2013-01-28. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ↑ 3.000 3.001 3.002 3.003 3.004 3.005 3.006 3.007 3.008 3.009 3.010 3.011 3.012 3.013 3.014 3.015 3.016 3.017 3.018 3.019 3.020 3.021 3.022 3.023 3.024 3.025 3.026 3.027 3.028 3.029 3.030 3.031 3.032 3.033 3.034 3.035 3.036 3.037 3.038 3.039 3.040 3.041 3.042 3.043 3.044 3.045 3.046 3.047 3.048 3.049 3.050 3.051 3.052 3.053 3.054 3.055 3.056 3.057 3.058 3.059 3.060 3.061 3.062 3.063 3.064 3.065 3.066 3.067 3.068 3.069 3.070 3.071 3.072 3.073 3.074 3.075 3.076 3.077 3.078 3.079 3.080 3.081 3.082 3.083 3.084 3.085 3.086 3.087 3.088 3.089 3.090 3.091 3.092 3.093 3.094 3.095 3.096 3.097 3.098 3.099 3.100 3.101 3.102 3.103 3.104 3.105 3.106 3.107 3.108 3.109 3.110 3.111 3.112 3.113 3.114 3.115 3.116 3.117 3.118 3.119 3.120 3.121 3.122 3.123 3.124 3.125 3.126 3.127 3.128 3.129 3.130 3.131 3.132 3.133 3.134 3.135 3.136 3.137 3.138 3.139 3.140 3.141 3.142 3.143 3.144 3.145 3.146 3.147 3.148 3.149 3.150 3.151 3.152 3.153 3.154 3.155 3.156 3.157 3.158 3.159 3.160 3.161 3.162 3.163 3.164 3.165 3.166 3.167 3.168 3.169 3.170 3.171 3.172 3.173 3.174 3.175 3.176 3.177 3.178 3.179 3.180 3.181 3.182 3.183 3.184 3.185 3.186 3.187 3.188 3.189 3.190 Fisher, Bruce; Harvey, Richard P.; Champe, Pamela C. (2007). Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews: Microbiology (PDF). Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews Series. Hagerstown MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 354–366. ISBN 978-0-7817-8215-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 October 2020. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17 4.18 4.19 4.20 4.21 4.22 4.23 4.24 4.25 4.26 4.27 4.28 4.29 4.30 4.31 4.32 4.33 4.34 4.35 4.36 4.37 4.38 Table 1 in: Dimitrov, Dimiter S. (2004). "Virus entry: molecular mechanisms and biomedical applications". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2 (2): 109–22. doi:10.1038/nrmicro817. ISSN 1740-1526. PMC 7097642. PMID 15043007. Archived from the original on 2022-12-21. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ↑ Adams, MJ; Carstens EB (Jul 2012). "Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2012)" (PDF). Arch. Virol. 157 (7): 1411–22. doi:10.1007/s00705-012-1299-6. PMC 7086667. PMID 22481600. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-08-11. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ↑ Whitley RJ (1996). Baron S; et al. (eds.). Herpesviruses. in: Baron's Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). Univ of Texas Medical Branch. ISBN 0-9631172-1-1. Archived from the original on 2007-10-29. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ↑ Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Pfaller MA (2005). Medical Microbiology (5th ed.). Elsevier Mosby. ISBN 978-0-323-03303-9.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 de Villiers EM, Fauquet C, Broker TR, Bernard HU, zur Hausen H (2004). "Classification of papillomaviruses". Virology. 324 (1): 17–27. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2004.03.033. PMID 15183049.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Page 273 Archived 2023-02-05 at the Wayback Machine in: Lennette's Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral Infections (Fourth ed.). CRC Press. 2010. ISBN 978-1420084962.
- ↑ Murillo A, Vera-Estrella R, Barkla BJ, Méndez E, Arias CF (2015). "Identification of Host Cell Factors Associated with Astrovirus Replication in Caco-2 Cells". J. Virol. 89 (20): 10359–70. doi:10.1128/JVI.01225-15. PMC 4580174. PMID 26246569.
- ↑ Stapleford, Kenneth A.; Miller, David J. (2010). "Role of Cellular Lipids in Positive-Sense RNA Virus Replication Complex Assembly and Function". Viruses. 2 (5): 1055–68. doi:10.3390/v2051055. ISSN 1999-4915. PMC 3187604. PMID 21994671.
- ↑ Cook, S.; Moureau, G.; Harbach, R. E.; Mukwaya, L.; Goodger, K.; Ssenfuka, F.; Gould, E.; Holmes, E. C.; de Lamballerie, X. (2009). "Isolation of a novel species of flavivirus and a new strain of Culex flavivirus (Flaviviridae) from a natural mosquito population in Uganda". Journal of General Virology. 90 (11): 2669–78. doi:10.1099/vir.0.014183-0. ISSN 0022-1317. PMC 2885038. PMID 19656970.
- ↑ Simon-Loriere, Etienne; Holmes, Edward C. (2011). "Why do RNA viruses recombine?". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 9 (8): 617–26. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2614. ISSN 1740-1526. PMC 3324781. PMID 21725337.
- ↑ "2018.013S.R.Matonaviridae". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Retrieved 2020-05-28.[dead link]
- ↑ Tuthill, Tobias J.; Groppelli, Elisabetta; Hogle, James M.; Rowlands, David J. (2010). "Picornaviruses". Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. 343: 43–89. doi:10.1007/82_2010_37. ISBN 978-3-642-13331-2. ISSN 0070-217X. PMC 3018333. PMID 20397067.
- ↑ "Pneumoviridae ~ ViralZone page". viralzone.expasy.org. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2020-08-17.
- ↑ Repass GL, Palmer WC, Stancampiano FF (September 2014). "Hand, foot, and mouth disease: Identifying and managing an acute viral syndrome". Cleve Clin J Med. 81 (9): 537–43. doi:10.3949/ccjm.81a.13132. PMID 25183845. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 30.4 30.5 "Babies Born with CMV (Congenital CMV Infection)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. April 13, 2017. Archived from the original on August 7, 2010. Retrieved June 17, 2017.
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
External links[edit | edit source]
| Classification |
|---|
Categories: [Pathogenic microbes] [Viral diseases]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/25/2024 00:43:55 | 12 views
☰ Source: https://mdwiki.org/wiki/Viral_disease | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
.png)
 KSF
KSF