California Elections, 2012
 From Ballotpedia
From Ballotpedia | California's 2012 elections U.S. Senate • U.S. House • State Senate • State Assembly • State ballot measures • Candidate ballot access |
| Other elections | |
|---|---|
| View elections by state and year: | |
| Contents |
|---|
| 1 2012 Elections |
| 2 Eligibility to Vote |
| 2.1 Primary election |
| 2.2 General election |
| 3 Voting absentee |
| 3.1 Eligibility |
| 3.2 Deadlines |
| 3.3 Military and overseas voting |
| 4 Voting early |
| 5 See also |
| 6 References |
The state of California held elections in 2012. Below are the dates of note:
- Signature filing deadline: March 9, 2012 & dates vary for state ballot measures
- Primary date: June 5, 2012
- General election date: November 6, 2012
| On the 2012 ballot | Click here for all November 6, 2012 Election Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Senate (1 seat) | Preview Article | ||
| U.S. House (53 seats) | |||
| State Executives | N/A | ||
| State Senate (20 seats) | Preview Article | ||
| State Assembly (80 seats) | |||
| Ballot measures (13 measures) | Preview Article | ||
2012 Elections[edit]
For election results in the 50 states, see our November 6, 2012 election results page
Elections by type[edit]
U.S. Senate[edit]
U.S. House[edit]
| Members of the U.S. House from California -- Partisan Breakdown | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | As of November 2012 | After the 2012 Election | |
| Democratic Party | 34 | 38 | |
| Republican Party | 19 | 15 | |
| Total | 53 | 53 | |
State Senate[edit]
- See also: California State Senate elections, 2012
Heading into the election, Democrats maintained partisan control in the state senate.
| California State Senate | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | As of November 5, 2012 | After the 2012 Election | |
| Democratic Party | 25 | 26 | |
| Republican Party | 15 | 12 | |
| Vacancy | 0 | 2 | |
| Total | 40 | 40 | |
State House[edit]
Heading into the election, Democrats maintained partisan control in the state assembly.
| California State Assembly | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | As of November 5, 2012 | After the 2012 Election | |
| Democratic Party | 52 | 56 | |
| Republican Party | 28 | 24 | |
| Total | 80 | 80 | |
Ballot measures[edit]
- See also: California 2012 ballot measures
June 5:
| Type | Title | Subject | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CICA | Proposition 28 | Term limits | Removes the limit of two 4-year terms for state senators; removes the limit of three 2-year terms for state representatives; creates a lifetime term limit of twelve years in the state legislature | |
| CISS | Proposition 29 | Taxes | Increases the tax on cigarettes to fund cancer research |
November 6:
| Type | Title | Subject | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CICA | Proposition 30 | Taxes | Increases the state sales and income taxes for seven years | |
| CICA/SS | Proposition 31 | State budget | Establishes a two-year budget cycle; prohibits the state legislature from expending more than $25 million without creating budgetary offsets or other spending cuts; permits the governor to enact budget cuts during declared fiscal emergencies; requires performance reviews of state programs; and allows local governments to change procedures for locally administered programs that are state-funded | |
| CISS | Proposition 32 | Labor | Bans unions and corporations from contributing payroll-deducted funds to state and local candidates; bans government contractors from contributing to candidates that may award government contracts | |
| CISS | Proposition 33 | Insurance | Allows insurers to set prices based on whether the driver previously carried insurance coverage with any insurance company over the last five years | |
| CISS | Proposition 34 | Death penalty | Abolishes the death penalty and replaces it with a maximum life sentence without the opportunity for parole; applies the abolition and new sentencing retroactively; allocates $100 million to law enforcement for rape and homicide investigations | |
| CISS | Proposition 35 | Law enforcement | Increases maximum sentencing for human trafficking to 15 years to life and $1.5 million in fines; allocates collected fines to victims of human trafficking and law enforcement; requires persons convicted to be registered as a sex offender; requires human trafficking training for law enforcement | |
| CISS | Proposition 36 | Law enforcement | Changes the three-strikes sentencing system established by a 1994 ballot initiative, Proposition 184, to impose life sentences when new felony convictions are serious or violent; allows resentencing for convicts serving life sentences for felonies that were not serious or violent, except in the case of rape, murder, or child molestation | |
| CISS | Proposition 37 | Regulations | Requires labeling for foods that are genetically modified and prohibits labeling such foods as "natural" | |
| CISS | Proposition 38 | Taxes | Increases state income taxes (using a sliding scale) by .4% for lowest individual earners to 2.2% for individuals earning over $2.5 million to fund education and early childhood programs | |
| CISS | Proposition 39 | Taxes | Requires out-of-state businesses to calculate income taxes based on percentage of sales in California; repeals current law that allowed out-of-state businesses to choose tax liability formulas; dedicates half of the revenue ($500-$550 million) annually for five years from the expected increase in revenue under the initiative to fund fhe Clean Energy Job Creation Fund, which was designed under the initiative to "support projects intended to improve energy efficiency and expand the use of alternative energy" | |
| VR | Proposition 40 | Redistricting | Upholds or rejects the State Senate districts drawn by the Citizens Redistricting Commission, which were certified by the commission on August 15, 2011, and that took effect on June 5, 2012 |
Local measures[edit]
Ballotpedia tracked local ballot elections in 11 states. Those states included: Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Illinois, Michigan, Missouri, Ohio, Oregon, Washington and Wisconsin.
For the state of California, below is a glimpse of some of the local measures that appeared or were scheduled to appear on ballots in 2012.
- City of Piedmont Parcel Tax, Measure D (March 2008)
- City of Calexico Appointed City Clerk and City Treasurer, Measures P and Q (June 2012)
- City of Fresno Financial Practices Charter Amendment, Measure F (November 2012)
- Blanchard/Santa Paula Public Library Increase in Appropriations Limit, Measure U (November 2012)
- City of Cotati Prohibition on Roundabout Construction, Measure U (November 2012)
- Santa Rosa Design-Build Procurement, Measure S (November 2012)
- Method of Election to the Santa Rosa City Council, Measure Q (November 2012)
- City of Hughson Length of Mayoral Term, Measure U (November 2012)
- Indian Wells Rotation in the Office of Mayor, Measure Q (November 2012)
- City of Eastvale Appropriations Limit, Measure BB (November 2012)
...click here for all 2012 California local measures.
Recalls[edit]
- See also: Political recall efforts and Recall campaigns in California
San Fernando[edit]
San Fernando, California city councilors Mario Hernandez, Maribel De La Torre, and Brenda Esqueda all faced recall elections.[1] While Hernandez resigned from his post in July 2012, his name still appeared on the recall ballot in accordance with the laws governing recall in California. Activity on the city council was more reminiscent of a soap opera than of a local government. At a November 2011 city council meeting, Hernandez, who was married at the time, announced that he was having an affair with De La Torre.[2] In June 2012, Hernandez and De La Torre had a violent altercation that resulted in De La Torre being charged with vandalism and battery.[3] Meanwhile, Esqueda was openly having an extra-marital affair with police sergeant Alvaro Castellon. All three city councilors were accused of interfering with a police investigation that involved Castellon allegedly making criminal threats against a police cadet who was having an affair with Chief of Police Anthony Ruelas.[4] The police cadet, Maria Barajas, sued the city, claiming that Castellon told her she "could disappear."
The three recall targets were accused of retaliating against recall supporters by selectively enforcing obscure city codes, and voting for a controversial "decorum ordinance" that would physically remove and impose fines on those who are considered "out of order" at city council meetings.[5][6]
Orange Cove[edit]
Frank Martinez and Glenda Hill, members of the Orange Cove City Council, were also up for recall on November 6. Former Orange Cove Mayor Victor Lopez organized the recall effort. He said Martinez and Hill were "running the city into a bankruptcy." Lopez was running as a replacement candidate in the election, meaning that if either Martinez or Hill were recalled, he could take one of their seats on the council.[7]
Eligibility to Vote[edit]
Primary election[edit]
- See also: Voting in the 2012 primary elections
California was one of 16 states to use an open primary system. California's system was an open Top 2 Primary Election, in which the top two candidates move to the general election. The deadline to register to vote was 15 days prior to each local and statewide Election Day.[8] (Information about registering to vote)
General election[edit]
- See also: Voting in the 2012 general elections
The deadline to register to vote was 15 days prior to the election day, which in 2012 was October 22.[9]
- Voter ID info
- Same-day registration: None
Voting absentee[edit]
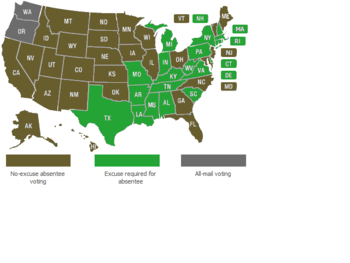
- See also: Absentee Voting
California provides for universal, automatic mail-in voting in all elections. Local election officials automatically deliver mail-in ballots to all registered voters. Voters may also choose to cast their ballots in person.[10][11]
Voting early[edit]
- See also: Early voting
California is one of 34 states that permits early voting with no specific restrictions as to who can vote early. Early voting dates in California are determined by individual counties. County information can be accessed here.
See also[edit]
Footnotes[edit]
- ↑ CBS Los Angeles, "San Fernando City Council Schedules Recall Election," July 17, 2012
- ↑ CBS Los Angeles, "San Fernando Mayor Announces Affair With City Councilwoman In Front Of Wife, Residents," November 28, 2011
- ↑ Los Angeles Times, "San Fernando councilwoman charged with attack on ex-lover," July 13, 2012
- ↑ San Fernando Valley Sun, "Council Meeting Brings More Innuendo, Accusations and Public In-Fighting," accessed February 23, 2012 (dead link)
- ↑ San Fernando Valley Sun, "San Fernando Residents Allege Reprisals for Support of Recall ," May 17, 2012 (dead link)
- ↑ San Fernando Valley Sun, "San Fernando City Council Passes Controversial Decorum Ordinance Despite Public Protest," June 7, 2012 (dead link)
- ↑ Fresno Bee, "Ex-Orange Cove mayor Victor Lopez leads recall," August 16, 2012
- ↑ California Secretary of State, "Election FAQS" accessed April 17, 2012
- ↑ California Secretary of State, "Election Voter Registration," accessed May 15, 2012
- ↑ California Legislative Information, "Cal. Election Code § 3000.5," accessed October 29, 2025
- ↑ California Legislative Information, "AB-37 Elections: vote by mail ballots," accessed October 29, 2025
Categories: [California elections, 2012] [2012 election state pages]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/08/2026 00:01:35 | 25 views
☰ Source: https://ballotpedia.org/California_elections,_2012 | License: CC BY-SA 3.0




 KSF
KSF