N-(N-Butyl)Thiophosphoric Triamide
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 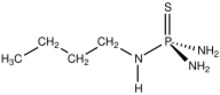
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Agrotain
N-butylphosphorothioic triamide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C4H14N3PS |
| Molar mass | 167.21 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements
|
H318, H361 |
GHS precautionary statements
|
P201, P202, P280, P281, P305+351+338, P308+313, P310, P405, P501 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
N-(n-butyl)thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT) is the organophosphorus compound with the formula SP(NH2)2(NHC4H9). A white solid, NBPT is an "enhanced efficiency fertilizer", intended to limit the release of nitrogen-containing gases following fertilization.[1] Regarding its chemical structure, the molecule features tetrahedral phosphorus bonded to sulfur and three amido groups.
Use
NBPT functions as an inhibitor of the enzyme urease.[2] Urease, pervasive in soil microorganisms, converts urea into ammonia, which is susceptible to volatilization if produced faster than it can utilized by plants. Approximately 0.5% by weight NBPT is mixed with the urea.[3]
See also
- Phenyl phosphorodiamidate, another urease inhibitor
References
- ↑ Rose, Terry J.; Wood, Rachel H.; Rose, Michael T.; Van Zwieten, Lukas (2018). "A re-evaluation of the agronomic effectiveness of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP and the Urease Inhibitor NBPT". Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 252: 69–73. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2017.10.008.
- ↑ Pan, Baobao; Lam, Shu Kee; Mosier, Arvin; Luo, Yiqi; Chen, Deli (2016). "Ammonia Volatilization from Synthetic Fertilizers and its Mitigation Strategies: A Global Synthesis". Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 232: 283–289. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2016.08.019.
- ↑ Zaman, M.; Zaman, S.; Quin, B.F; Kurepin, L.V; Shaheen, S.; Nawaz, S.; Dawar, K.M (2014). "Improving Pasture Growth and Urea Efficiency Using N inhibitor, Molybdenum and Elemental Sulphur". Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition. doi:10.4067/S0718-95162014005000020.
Categories: [Thiophosphoryl compounds] [Fertilizers]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 05/17/2024 21:30:55 | 14 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:N-(n-butyl)thiophosphoric_triamide | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF