Hafnium Trifluoromethanesulfonate
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 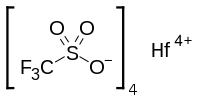
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Hafnium(IV) trifluoromethanesulfonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
Hf(OTf)4 |
| Molar mass | 774.8 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless solid |
| Melting point | 350 °C (662 °F; 623 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | irritantant |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements
|
H314, H315, H318, H319, H335 |
GHS precautionary statements
|
P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Hafnium tetrachloride Hafnium tetrafluoride Hafnium(IV) bromide Hafnium(IV) iodide |
Other cations
|
Titanium(IV) triflate Zirconium(IV) triflate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
- SizeSet
Hafnium(IV) triflate or hafnium trifluoromethansulfonate is an inorganic substance with the idealized formula Hf(OSO2CF3)4, also written as Hf(OTf)4. Hafnium triflate is used as an impure mixture as a catalyst. Hafnium (IV) has an ionic radius of intermediate range (Al < Ti < Hf < Zr < Sc < Ln) and has an oxophilic hard character typical of group IV metals. This solid is a stronger Lewis acid than its typical precursor hafnium tetrachloride, HfCl4, because of the strong electron-withdrawing nature of the four triflate groups, which makes it a great Lewis acid and has many uses including as a great catalyst at low Lewis acid loadings for electrophilic aromatic substitution and nucleophilic substitution reactions.[1]
Preparation
The compound was first synthesized by the Kobayashi group in 1995 via the reaction of HfCl4 and triflic acid.[2] This solid is air stable, easy to handle, and commercially available.[3]
Uses
Electrophilic Substitutions
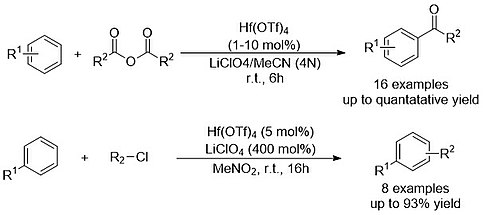
Friedel-Craft acylation or alkylation reactions are some of the most important synthetic methodologies to introduce carbonyl or alkyl groups onto aromatic compounds.[4] The first Hf(OTf)4 catalyzed Friedel-Crafts acylation was developed by Kobayashi et al. in 1995.[2][5] The authors demonstrated that Friedel-Crafts acylation could be achieved in excellent yield between arenes and acid anhydrides when utilizing Hf(OTf)4 as a catalyst. Hf(OTf)4, was the most effective in comparison to other Lewis acids including BF3 • OEt2, Sc(OTf)3, and Zr(OTf)4. Similalrly, Hf(OTf)4 shows excellent activity in Friedel-Crafts alkylation’s, and enabled the alkylation of benzene with benzylic and tertiary alkyl chlorides.
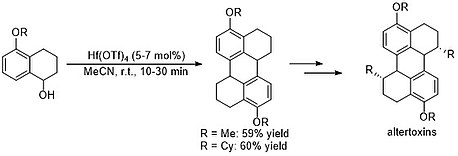
Hf(OTf)4-catalyzed Friedel-Crafts alkylation has been utilized in the total synthesis of the altertoxin III framework. This approach provided a more efficient synthesis of the fused-ring structure compared to previous methods.[6]
Hf(OTf)4, alongside Sc(OTf)3 and In(OTf)3, has been shown to activate alkynes and enable electrophilic substitution. In 2004 Song and Lee et al. reported Hf(OTf)4-catalyzed Friedel-Crafts alkenylation of benzene with alkenyl derivatives.[7]
4_alkynes.jpg)
Nucleophilic Substitutions
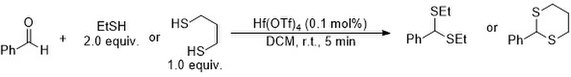
In 2008, Zhu et al. demonstrated that Hf(OTf)4 was an effective catalyst for the thioacetalization of aldehydes and ketones.[8] In the absence of Lewis acid this reaction can occur in glycerol at 90 °C. Hf(OTf)4 accelerated the reaction rate under milder conditions with only 0.1 mol% catalyst loading. For example, Hf(OTf)4 catalyzes the reaction between benzaldehyde and 2.0 equiv. of either ethanethiol or 1.0 equiv. of propane-1,3,-dithiol readily in quantitative yield.
This methodology was utilized in the total synthesis of (-)-leucomidine B from an enantioenriched monoacid synthesized via a Hf(OTf)4 catalyzed thioacetalization.[9]
-leucomidine_B.jpg)
In 2009, Nakamura et al. demonstrated that Hf(OTf)4 was uniquely able to catalyzed a Prins reaction between an aryl aldehyde and an O-protected/unprotected cyclohex-3-ene-1,2-dimethanol.[10]
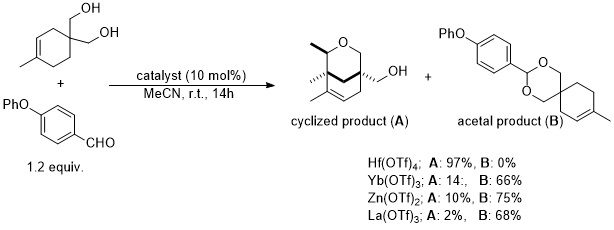
References
- ↑ Ishitani, Haruro; Suzuki, Hirotsugu; Saito, Yuki; Yamashita, Yasuhiro; Kobayashi, Shū (2015). "Hafnium Trifluoromethanesulfonate [Hf(OTf)4 as a Unique Lewis Acid in Organic Synthesis"] (in en). European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2015 (25): 5485–5499. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201500423. ISSN 1099-0690. https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejoc.201500423.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hachiya, Iwao; Moriwaki, Mitsuhiro; Kobayashi, Shu (1995-07-01). "Hafnium(IV) Trifluoromethanesulfonate, An Efficient Catalyst for the Friedel–Crafts Acylation and Alkylation Reactions". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 68 (7): 2053–2060. doi:10.1246/bcsj.68.2053. ISSN 0009-2673. https://www.journal.csj.jp/doi/10.1246/bcsj.68.2053.
- ↑ Li, Zhiya; Plancq, Baptiste; Ollevier, Thierry (2011) (in en), Hafnium(IV) Trifluoromethanesulfonate, American Cancer Society, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn01315, ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/047084289X.rn01315, retrieved 2021-06-12
- ↑ Calloway, N. O. (1935-12-01). "The Friedel-Crafts Syntheses.". Chemical Reviews 17 (3): 327–392. doi:10.1021/cr60058a002. ISSN 0009-2665. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr60058a002.
- ↑ Hachiya, Iwao; Moriwaki, Mitsuhiro; Kobayashi, Shu (1995-01-16). "Catalytic Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions using hafnium triflate as a catalyst in lithium perchlorate-nitromethane" (in en). Tetrahedron Letters 36 (3): 409–412. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(94)02221-V. ISSN 0040-4039. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/004040399402221V.
- ↑ Geiseler, Oliver; Müller, Monika; Podlech, Joachim (2013-05-06). "Synthesis of the altertoxin III framework" (in en). Tetrahedron 69 (18): 3683–3689. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2013.03.013. ISSN 0040-4020. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0040402013003633.
- ↑ Song, Choong Eui; Jung, Da-un; Choung, Su Yhen; Roh, Eun Joo; Lee, Sang-gi (2004). "Dramatic Enhancement of Catalytic Activity in an Ionic Liquid: Highly Practical Friedel–Crafts Alkenylation of Arenes with Alkynes Catalyzed by Metal Triflates". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 43 (45): 6183–6185. doi:10.1002/anie.200460292. ISSN 1521-3773. PMID 15549737. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.200460292.
- ↑ Wu, Yan-Chao; Zhu, Jieping (2008-12-05). "Hafnium Trifluoromethanesulfonate (Hafnium Triflate) as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Chemoselective Thioacetalization and Transthioacetalization of Carbonyl Compounds". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 73 (23): 9522–9524. doi:10.1021/jo8021988. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 18991383. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo8021988.
- ↑ Gualtierotti, Jean-Baptiste; Pasche, Delphine; Wang, Qian; Zhu, Jieping (2014). "Phosphoric Acid Catalyzed Desymmetrization of Bicyclic Bislactones Bearing an All-Carbon Stereogenic Center: Total Syntheses of (−)-Rhazinilam and (−)-Leucomidine B" (in en). Angewandte Chemie International Edition 53 (37): 9926–9930. doi:10.1002/anie.201405842. ISSN 1521-3773. PMID 25048385. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.201405842.
- ↑ Nakamura, Masayuki; Niiyama, Kenji; Yamakawa, Takeru (2009-11-25). "Versatile method for the synthesis of 4-substituted 6-methyl-3-oxabicyclo[3.3.1non-6-ene-1-methanol derivatives: Prins-type cyclization reaction catalyzed by hafnium triflate"] (in en). Tetrahedron Letters 50 (47): 6462–6465. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.08.120. ISSN 0040-4039. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0040403909016943.
Categories: [Hafnium compounds]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/02/2022 11:29:52 | 3 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Hafnium_trifluoromethanesulfonate | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
 KSF
KSF