Laplace Transform
 From Conservapedia
From Conservapedia Laplace transforms are one of the ways of solving linear ordinary differential equations (Linear ODEs) with constant coefficients. This technique allows us to transform a Linear ODE into a linear algebraic equation.
Definition[edit]
The unilateral Laplace transform is defined by
Given the integral converges. A necessary condition for this integral to converge is
Examples[edit]
Consider the following initial value problem
where 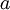 is constant, subject to
is constant, subject to
To solve this problem using laplace transform, first apply laplace transform to both sides of the equation, obtaining:
Or
The integral on the right hand side is
If 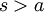 ,
,
For the left side, if we apply integration by parts,
Substitution into the left side will get
For the transformation to converge,
Therefore, substituting the initial condition y(0)=0 the left side becomes
Equating the two sides of the equation:
If 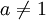 , we can use partial fractions to changet the right side into
, we can use partial fractions to changet the right side into
and the solution is obtained by noticing:
Substituting the inverse transform we have
Which leads to the answer
References[edit]
- D. Lomen and D. Lovelock, Differential Equations Graphics. Model. Data., John Wiley and Sons, Toronto, 1999.
- Laplace transform on Wolfram Mathworld
Categories: [Mathematics]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/09/2023 05:58:51 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Laplace_transform | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: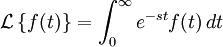
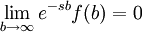
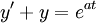
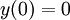
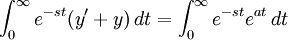
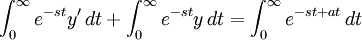
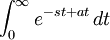
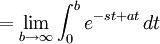
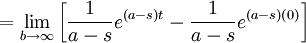
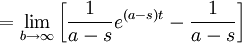
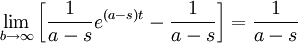
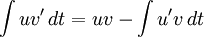
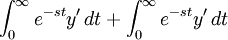
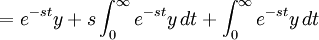
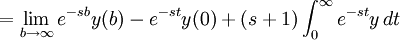
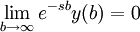
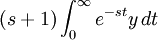
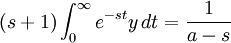
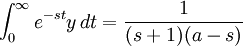
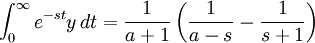
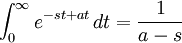
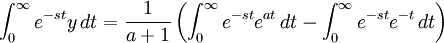
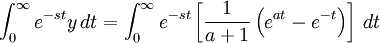
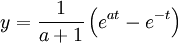
 KSF
KSF