Geos (8-Bit Operating System)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki  | |
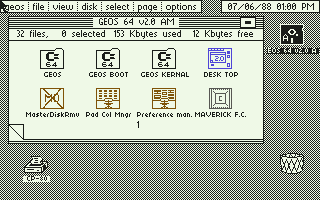 GEOS for the Commodore 64. Mimicking Commodore's own OS core naming, Berkeley called GEOS' core a "kernal" (cf. kernel). | |
| Developer | Berkeley Softworks (later GeoWorks) |
|---|---|
| Written in | Assembly language |
| Working state | Discontinued, historic |
| Initial release | 1986 |
| |Final release|Latest release}} | GEOS 2.0 |
| Available in | English, German and Spanish[1][2] |
| Platforms | Commodore 64, Commodore 128, Commodore Plus/4, Apple II, MEGA65 |
| Default user interface | Graphical user interface |
| License | Proprietary software |
GEOS (Graphic Environment Operating System) is a discontinued operating system from Berkeley Softworks (later GeoWorks). Originally designed for the Commodore 64 with its version being released in 1986, enhanced versions of GEOS later became available in 1987 for the Commodore 128 and in 1988 for the Apple II series of computers. A lesser-known version was also released for the Commodore Plus/4.
GEOS closely resembles early versions of the classic Mac OS and includes a graphical word processor (geoWrite) and paint program (geoPaint).
A December 1987 survey by the Commodore-dedicated magazine Compute!'s Gazette found that nearly half of respondents used GEOS.[3](p4) For many years, Commodore bundled GEOS with its redesigned and cost-reduced C64, the C64C. At its peak, GEOS was the third-most-popular microcomputer operating system in the world in terms of units shipped, trailing only MS-DOS and Mac OS (besides the original Commodore 64's KERNAL).[citation needed]
Other GEOS-compatible software packages were available from Berkeley Softworks or from third parties, including a reasonably sophisticated desktop publishing application called geoPublish and a spreadsheet called geoCalc. While geoPublish is not as sophisticated as Aldus Pagemaker and geoCalc not as sophisticated as Microsoft Excel, the packages provide reasonable functionality, and Berkeley Softworks founder Brian Dougherty claimed the company ran its business using its own software on Commodore 8-bit computers for several years.
Development
_-_restored.jpg)
Written by a group of programmers at Berkeley Softworks, the GEOS Design Team:[4] Jim DeFrisco, Dave Durran, Michael Farr, Doug Fults, Chris Hawley, Clayton Jung, and Tony Requist, led by Dougherty, who cut their teeth on limited-resource video game machines such as the Atari 2600, GEOS was revered[citation needed] for what it could accomplish on machines with 64–128 kB of RAM memory and 1–2 MHz of 8-bit processing power.
Unlike many pieces of proprietary software for the C64 and C128, GEOS takes full advantage of many of the add-ons and improvements available for these systems. Commodore's 1351 mouse is supported by GEOS, as are its various RAM expansion units. GEOS 128 also fully supports the C128's 640×200 high-resolution VDC display mode through a compatible RGB monitor.
The C64 version of GEOS incorporates a built-in fast loader, called diskTurbo, that significantly increases the speed of drive access on the slow 1541. GEOS is the first Commodore software that could use a floppy disk as swap space or virtual memory.[5] GEOS 128 can take advantage of the C128's enhanced "burst mode" in conjunction with the 1571 and 1581 drives. The Commodore version of GEOS uses a copy protection scheme that renders users' disks unbootable if it detects that the disk has been illegally duplicated.[6]
Via Berkeley's special geoCable interface converter or other third-party interfaces to connect standard RS-232 or Centronics printers to the Commodore serial bus, GEOS supports a wide variety of printers, including HP PCL printers and the Apple LaserWriter. This ability to print to high-end printers was a major factor in making GEOS a desktop publishing platform.
The Apple II version of GEOS was released as freeware in August 2003. The Commodore 64/128 versions followed in February 2004.
The latest GEOS desktop suite for IBM PC compatibles is Breadbox Ensemble. Revivals were seen in the OmniGo handhelds, Brother GeoBook line of laptop-appliances, and the NewDeal Office package for PCs. Related code found its way to earlier "Zoomer" PDAs, creating an unclear lineage to Palm, Inc.'s later work. Nokia used GEOS as a base operating system for their Nokia Communicator series, before switching to EPOC (Symbian).
GEOS versions

- 1986: GEOS for Commodore 64
- 1987: GEOS for Commodore C128, Commodore Plus/4 (unofficial)
- 1988: GEOS for Apple II, GEOS V2.0 for Commodore C64, GEOS V2.1 for Apple II
- 1989: GEOS V2.0 for Commodore C128[7]
- 2022: GEOS for Atari (unofficial)
Reverse engineering efforts
On August 19, 2016, Michael Steil posted in his blog[8] that the source code for GEOS 2.0 for Commodore C64 had been fully reverse-engineered and suitable for the cc65 compiler suite. The reverse-engineered source code has been made available at GitHub.[9]
GEOS products and applications
Dozens of official and third-party applications and other products were produced for GEOS. Among the most important and popular were the following:
- geoBASIC
- geoCable
- geoCalc
- geoChart
- geoDex
- geoDraw
- geoFAX
- geoFile
- geoFont
- geoLabel
- geoPaint
- geoPrint
- geoProgrammer
- geoPublish
- geoSpell
- geoWrite
- geoWrite Workshop
- geoRAM
- Writer 64 (Timeworks)[10]
See also
- Contiki
- GEOS (16-bit operating system)
- List of computer system emulators
- List of operating systems
References
- ↑ "GEOS en castellano". https://commodoremania.com/foro/index.php?topic=229.0.
- ↑ "GEOS Drean Commodore version 1.2". https://www.retrocomputacion.com/forum/software_com/106008/geos-drean-commodore-version-1-2-manual-escaneado-ripeado-100/.
- ↑ Elko, Lance (1988-05-01). "Editor's Notes" (in en-us). Compute!'s Gazette 6 (59). ISSN 0737-3716. https://archive.org/stream/1988-05-computegazette/Compute_Gazette_Issue_59_1988_May#page/n4/mode/1up. Retrieved 2021-02-11.
- ↑ GEOS User's Manual, Version 1.2 , Printed: October 1986, Berkeley Softworks, 2150 Shattuck Avenue, Berkeley, California 94704
- ↑ "GEOS: A Whole New World for your Commodore". https://www.scribd.com/doc/54813745/Run-Issue-30-1986-Jun.
- ↑ "Info magazine Issue 14". 1987. https://archive.org/stream/info-magazine-14/Info_Issue_14_1987_Spring_Summer#page/n9/mode/1up.
- ↑ "GUIdebook > Timelines > GEOS/GeoWorks". http://www.guidebookgallery.org/timelines/geos.
- ↑ "Reverse-Engineered GEOS 2.0 for C64 Source Code – pagetable.com". http://www.pagetable.com/?p=869.
- ↑ GitHub - mist64/geos: Source code of GEOS 2.0 for the Commodore 64 and 128
- ↑ Guerra, Bob (May 1989). "Writer 64". Compute!: pp. 78. https://archive.org/stream/1989-05-compute-magazine/Compute_Issue_108_1989_May#page/n79/mode/2up.
Further reading
- Farr, Michael (1987-02-15). The Official GEOS Programmer's Reference Guide. For Commodore 64/64C/128. Includes versions 1.0, 1.1, and 1.2. Berkeley Softworks. Bantam Books. ISBN 978-0553344042. OCLC 16684486. https://archive.org/details/officialgeosprog00farr.
- Tornsdorf, Manfred; Kerkoh, Rüdiger (1988-05-01). GEOS Inside and Out: An introduction to GEOS, its applications and internals (2nd ed.). Abacus Software Inc. ISBN 978-0916439811. OCLC 18446175.
External links
- Breadbox Home of the GEOS operating system (down, archived here at the Internet Archive)
- The Commodore GEOS FAQ v1.5.0 – By Bo Zimmermann
- GEOS: The Graphical Operating System A lengthy review of GEOS and its history
 |
Categories: [Operating system families] [Graphical user interfaces] [Proprietary operating systems]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/09/2024 20:22:16 | 9 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Software:GEOS_(8-bit_operating_system) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF