Reduction (Orthopedic Surgery)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Reduction (orthopedic surgery) | |
|---|---|
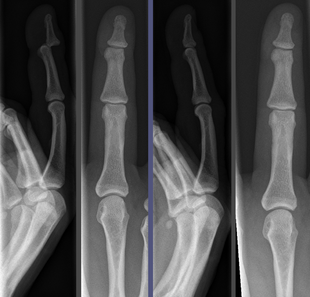 Joint dislocation in the DIP of the third finger before (left images) and after (right images) reduction. | |
| ICD-9-CM | 79 |
Reduction is a surgical procedure to repair a fracture or dislocation to the correct alignment.
Description
When a bone fractures, the fragments lose their alignment in the form of displacement or angulation. For the fractured bone to heal without any deformity the bony fragments must be re-aligned to their normal anatomical position. Orthopedic surgery attempts to recreate the normal anatomy of the fractured bone by reduction of the displacement.[citation needed] This sense of the term "reduction" does not imply any sort of removal or quantitative decrease but rather implies a restoration: re ("back [to initial position]") + ducere ("lead"/"bring"), i.e., "bringing back to normal".
Because the process of reduction can briefly be intensely painful, it is commonly done under a short-acting anesthetic, sedative, or nerve block.
Once the fragments are reduced, the reduction is maintained by application of casts, traction, or held by plates, screws, or other implants, which may in turn be external or internal. It is very important to verify the accuracy of reduction by clinical tests and X-ray, especially in the case of joint dislocations.
Types
Reduction can be by "closed" or "open" methods:
- Closed reduction is the manipulation of the bone fragments without surgical exposure of the fragments.
- Open reduction is where the fracture fragments are exposed through surgical dissection of tissues.
References
- "Closed reduction of a fractured bone". Medline Plus. 11 June 2008. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/patientinstructions/000521.htm.
- "Sedation-assisted Orthopedic Reduction in Emergency Medicine". Western J Emerg Med. 14 (1): 47–54. 2013. doi:10.5811/westjem.2012.4.12455. PMID 23447756. PMC 3582522. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/780004_3. (primary source)
- Mercier LR (2008). "2". Practical Orthopedics (6th ed.). ISBN 978-0-323-03618-4.
 |
Categories: [Orthopedic surgical procedures]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/16/2024 19:00:49 | 39 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Medicine:Reduction_(orthopedic_surgery) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF