Bilateria
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki
| Bilaterians Temporal range: Ediacaran–Present, 560–0 Ma[1]
PreЄ
Є
O
S
D
C
P
T
J
K
Pg
N
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Diversity of bilaterians | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Subkingdom: | Eumetazoa |
| Clade: | ParaHoxozoa |
| Clade: | Bilateria Hatschek, 1888 |
| Phyla | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Triploblasts Lankester, 1873 | |
Bilateria (/ˌbaɪləˈtɪəriə/) is a large clade/infrakingdom of animals called bilaterians, characterized by bilateral symmetry (i.e. having a left and a right side that are mirror images of each other) during embryonic development. This means their body plans are laid around a longitudinal axis (rostral–caudal axis) with a front (or "head") and a rear (or "tail") end, as well as a left–right–symmetrical belly (ventral) and back (dorsal) surface.[2] Nearly all bilaterians maintain a bilaterally symmetrical body as adults; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which achieve secondary pentaradial symmetry as adults, but are bilaterally symmetrical as an embryo. Cephalization is also a characteristic feature among most bilaterians, where the special sense organs and central nerve ganglia become concentrated at the front/rostral end.
Bilaterians constitute one of the five main metazoan lineages, the other four being Porifera (sponges), Cnidaria (jellyfish, hydrae, sea anemones and corals), Ctenophora (comb jellies) and Placozoa (tiny "flat animals"). Most so-called "higher-order" animals are bilaterians. For the most part, bilateral embryos are triploblastic, having three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. Except for a few phyla (i.e. flatworms and gnathostomulids), bilaterians have complete digestive tracts with a separate mouth and anus. Some bilaterians lack body cavities (acoelomates, i.e. Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha and Gnathostomulida), while others display primary body cavities (deriving from the blastocoel, as pseudocoeloms) or secondary cavities (that appear de novo, for example the coelom).
Body plan
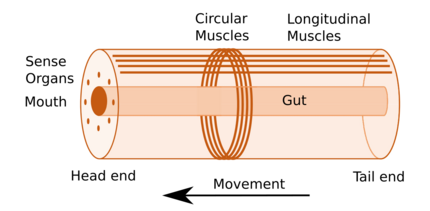
Some of the earliest bilaterians were wormlike, and a bilaterian body can be conceptualized as a cylinder with a gut running between two openings, the mouth and the anus. Around the gut it has an internal body cavity, a coelom or pseudocoelom.[lower-alpha 1] Animals with this bilaterally symmetric body plan have a head (anterior) end and a tail (posterior) end as well as a back (dorsal) and a belly (ventral); therefore they also have a left side and a right side.[4][2]
Having a front end means that this part of the body encounters stimuli, such as food, favouring cephalisation, the development of a head with sense organs and a mouth.[5] The body stretches back from the head, and many bilaterians have a combination of circular muscles that constrict the body, making it longer, and an opposing set of longitudinal muscles, that shorten the body;[2] these enable soft-bodied animals with a hydrostatic skeleton to move by peristalsis.[6] Most bilaterians (Nephrozoans) have a gut that extends through the body from mouth to anus, while Xenacoelomorphs have a bag gut with one opening. Many bilaterian phyla have primary larvae which swim with cilia and have an apical organ containing sensory cells. However, there are exceptions to each of these characteristics; for example, adult echinoderms are radially symmetric (unlike their larvae), and certain parasitic worms have extremely plesiomorphic body structures.[4][2]
Evolution

The hypothetical most recent common ancestor of all bilateria is termed the "Urbilaterian".[8][9] The nature of the first bilaterian is a matter of debate. One side suggests that acoelomates gave rise to the other groups (planuloid–aceloid hypothesis by Ludwig von Graff, Elie Metchnikoff, Libbie Hyman, or Luitfried von Salvini-Plawen (nl)), while the other poses that the first bilaterian was a coelomate organism and the main acoelomate phyla (flatworms and gastrotrichs) have lost body cavities secondarily (the Archicoelomata hypothesis and its variations such as the Gastrea by Haeckel or Sedgwick, the Bilaterosgastrea by Gösta Jägersten, or the Trochaea by Nielsen).
One hypothesis is that the original bilaterian was a bottom dwelling worm with a single body opening, similar to Xenoturbella.[3] Alternatively, it may have resembled the planula larvae of some cnidaria, which have some bilateral symmetry.[10] However, there is evidence that it was segmented, as the mechanism for creating segments is shared between vertebrates (deuterostomes) and arthropods (protostomes).[11]
Fossil record
The first evidence of bilateria in the fossil record comes from trace fossils in Ediacaran sediments, and the first bona fide bilaterian fossil is Kimberella, dating to 555 million years ago.[12] Earlier fossils are controversial; the fossil Vernanimalcula may be the earliest known bilaterian, but may also represent an infilled bubble.[13][14] Fossil embryos are known from around the time of Vernanimalcula (580 million years ago), but none of these have bilaterian affinities.[15] Burrows believed to have been created by bilaterian life forms have been found in the Tacuarí Formation of Uruguay, and were believed to be at least 585 million years old.[16] However, more recent evidence shows these fossils are actually late Paleozoic instead of Ediacaran.[17]
Phylogeny
The Bilateria has traditionally been divided into two main lineages or superphyla.[18] The deuterostomes include the echinoderms, hemichordates, chordates, and a few smaller phyla. The protostomes include most of the rest, such as arthropods, annelids, mollusks, flatworms, and so forth. There are a number of differences, most notably in how the embryo develops. In particular, the first opening of the embryo becomes the mouth in protostomes, and the anus in deuterostomes. Many taxonomists now recognize at least two more superphyla among the protostomes, Ecdysozoa[19] (molting animals) and Spiralia.[19][20][21][22] The arrow worms (Chaetognatha) have proven difficult to classify; recent studies place them in the gnathifera.[23][24][25]
The traditional division of Bilateria into Deuterostomia and Protostomia was challenged when new morphological and molecular evidence found support for a sister relationship between the acoelomate taxa, Acoela and Nemertodermatida (together called Acoelomorpha), and the remaining bilaterians.[18] The latter clade was called Nephrozoa by Jondelius et al. (2002) and Eubilateria by Baguña and Riutort (2004).[18] The acoelomorph taxa had previously been considered flatworms with secondarily lost characteristics, but the new relationship suggested that the simple acoelomate worm form was the original bilaterian bodyplan and that the coelom, the digestive tract, excretory organs, and nerve cords developed in the Nephrozoa.[18][26] Subsequently the acoelomorphs were placed in phylum Xenacoelomorpha, together with the xenoturbellids, and the sister relationship between Xenacoelomorpha and Nephrozoa confirmed in phylogenomic analyses.[26]
A modern consensus phylogenetic tree for Bilateria is shown below, although the positions of certain clades are still controversial (dashed lines) and the tree has changed considerably since 2000.[27][25][28][29][30]
| Planulozoa |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 680 Mya |
A different hypothesis is that the Ambulacraria are sister to Xenacoelomorpha together forming the Xenambulacraria. The Xenambulacraria may be sister to the Chordata or to the Centroneuralia (corresponding to Nephrozoa without Ambulacraria, or to Chordata + Protostomia). The phylogenetic tree shown below depicts the latter proposal. Also, the validity of Deuterostomia (without Protostomia emerging from it) is under discussion.[31] The cladogram indicates approximately when some clades radiated into newer clades, in millions of years ago (Mya).[32] While the below tree depicts Chordata as a sister group to Protostomia according to analyses by Philippe et al., the authors nonetheless caution that "the support values are very low, meaning there is no solid evidence to refute the traditional protostome and deuterostome dichotomy".[33]
| ParaHoxozoa |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 680 Mya |
See also
- Embryological origins of the mouth and anus
Notes
- ↑ The earliest Bilateria may have had only a single opening, and no coelom.[3]
References
- ↑ Martin, M. W.; Grazhdankin, D. V.; Bowring, S. A.; Evans, D. A.; Fedonkin, M. A.; Kirschvink, J. L. (5 May 2000). "Age of Neoproterozoic bilatarian [sic] body and trace fossils, White Sea, Russia: implications for metazoan evolution". Science 288 (5467): 841–45. doi:10.1126/science.288.5467.841. PMID 10797002. Bibcode: 2000Sci...288..841M.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Brusca, Richard C. (2016). "Introduction to the Bilateria and the Phylum Xenacoelomorpha: Triploblasty and Bilateral Symmetry Provide New Avenues for Animal Radiation". Invertebrates. Sinauer Associates. pp. 345–372. ISBN 978-1-60535-375-3. http://www.sinauer.com/media/wysiwyg/samples/Brusca3e_Chapter_9.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Cannon, Johanna Taylor; Vellutini, Bruno Cossermelli; Smith, Julian; Ronquist, Fredrik; Jondelius, Ulf; Hejnol, Andreas (2016). "Xenacoelomorpha is the sister group to Nephrozoa". Nature 530 (7588): 89–93. doi:10.1038/nature16520. PMID 26842059. Bibcode: 2016Natur.530...89C. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:nrm:diva-1844.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Minelli, Alessandro (2009). Perspectives in Animal Phylogeny and Evolution. Oxford University Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-19-856620-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=jIASDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA53.
- ↑ Finnerty, John R. (November 2005). "Did internal transport, rather than directed locomotion, favor the evolution of bilateral symmetry in animals?". BioEssays 27 (11): 1174–1180. doi:10.1002/bies.20299. PMID 16237677. http://faculty.weber.edu/rmeyers/PDFs/Finnerty - symmetry evol.pdf. Retrieved 2018-03-07.
- ↑ Quillin, K. J. (May 1998). "Ontogenetic scaling of hydrostatic skeletons: geometric, static stress and dynamic stress scaling of the earthworm lumbricus terrestris". The Journal of Experimental Biology 201 (12): 1871–83. doi:10.1242/jeb.201.12.1871. PMID 9600869. http://jeb.biologists.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9600869.
- ↑ Evans, Scott D.; Hughes, Ian V.; Gehling, James G.; Droser, Mary L. (7 April 2020). "Discovery of the oldest bilaterian from the Ediacaran of South Australia". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117 (14): 7845–7850. doi:10.1073/pnas.2001045117. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 32205432. Bibcode: 2020PNAS..117.7845E.
- ↑ Knoll, Andrew H.; Carroll, Sean B. (25 June 1999). "Early Animal Evolution: Emerging Views from Comparative Biology and Geology". Science 284 (5423): 2129–2137. doi:10.1126/science.284.5423.2129. PMID 10381872.
- ↑ Balavoine, G.; Adoutte, Andre (2003). "The segmented Urbilateria: A testable scenario". Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 (1): 137–147. doi:10.1093/icb/43.1.137. PMID 21680418.
- ↑ Baguñà, Jaume; Martinez, Pere; Paps, Jordi; Riutort, Marta (April 2008). "Back in time: a new systematic proposal for the Bilateria". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 363 (1496): 1481–1491. doi:10.1098/rstb.2007.2238. PMID 18192186.
- ↑ Held, Lewis I. (2014). How the Snake Lost its Legs. Curious Tales from the Frontier of Evo-Devo. Cambridge University Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-107-62139-8.
- ↑ Fedonkin, M. A.; Waggoner, B. M. (November 1997). "The Late Precambrian fossil Kimberella is a mollusc-like bilaterian organism". Nature 388 (6645): 868–871. doi:10.1038/42242. Bibcode: 1997Natur.388..868F.
- ↑ Bengtson, S.; Budd, G. (19 November 2004). "Comment on 'small bilaterian fossils from 40 to 55 million years before the Cambrian'.". Science 306 (5700): 1291a. doi:10.1126/science.1101338. PMID 15550644.
- ↑ Bengtson, S.; Donoghue, P. C. J.; Cunningham, J. A.; Yin, C. (2012). "A merciful death for the 'earliest bilaterian,' Vernanimalcula". Evolution & Development 14 (5): 421–427. doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2012.00562.x. PMID 22947315. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:nrm:diva-597.
- ↑ Hagadorn, J. W.; Xiao, S.; Donoghue, P. C. J.; Bengtson, S.; Gostling, N. J.; Pawlowska, M.; Raff, E. C.; Raff, R. A. et al. (13 October 2006). "Cellular and Subcellular Structure of Neoproterozoic Animal Embryos". Science 314 (5797): 291–294. doi:10.1126/science.1133129. PMID 17038620. Bibcode: 2006Sci...314..291H.
- ↑ Pecoits, E.; Konhauser, K. O.; Aubet, N. R.; Heaman, L. M.; Veroslavsky, G.; Stern, R. A.; Gingras, M. K. (June 29, 2012). "Bilaterian burrows and grazing behavior at >585 million years ago". Science 336 (6089): 1693–1696. doi:10.1126/science.1216295. PMID 22745427. Bibcode: 2012Sci...336.1693P.
- ↑ Verde, Mariano (15 September 2022). "Revisiting the supposed oldest bilaterian trace fossils from Uruguay: Late Paleozoic, not Ediacaran". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 602. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111158. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031018222003285.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 Nielsen, Claus (2008). "Six major steps in animal evolution: are we derived sponge larvae?". Evol. Dev. 10 (2): 241–257. doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00231.x. PMID 18315817.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Halanych, K.; Bacheller, J.; Aguinaldo, A.; Liva, S.; Hillis, D.; Lake, J. (17 March 1995). "Evidence from 18S ribosomal DNA that the lophophorates are protostome animals". Science 267 (5204): 1641–1643. doi:10.1126/science.7886451. PMID 7886451. Bibcode: 1995Sci...267.1641H.
- ↑ Paps, J.; Baguna, J.; Riutort, M. (14 July 2009). "Bilaterian phylogeny: a broad sampling of 13 nuclear genes provides a new Lophotrochozoa phylogeny and supports a paraphyletic basal Acoelomorpha". Molecular Biology and Evolution 26 (10): 2397–2406. doi:10.1093/molbev/msp150. PMID 19602542.
- ↑ Telford, Maximilian J. (15 April 2008). "Resolving animal phylogeny: A sledgehammer for a tough nut?". Developmental Cell 14 (4): 457–459. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.03.016. PMID 18410719.
- ↑ Kimball, John W. (3 March 2010). "The Invertebrate Animals". http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/I/Invertebrates.html.
- abbridged by author from
- ↑ Helfenbein, Kevin G.; Fourcade, H. Matthew; Vanjani, Rohit G.; Boore, Jeffrey L. (20 July 2004). "The mitochondrial genome of Paraspadella gotoi is highly reduced and reveals that chaetognaths are a sister group to protostomes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101 (29): 10639–10643. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400941101. PMID 15249679. Bibcode: 2004PNAS..10110639H.
- ↑ Papillon, Daniel; Perez, Yvan; Caubit, Xavier; Yannick Le, Parco (November 2004). "Identification of chaetognaths as protostomes is supported by the analysis of their mitochondrial genome". Molecular Biology and Evolution 21 (11): 2122–2129. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh229. PMID 15306659.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Fröbius, Andreas C.; Funch, Peter (2017-04-04). "Rotiferan Hox genes give new insights into the evolution of metazoan bodyplans". Nature Communications 8 (1): 9. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00020-w. PMID 28377584. Bibcode: 2017NatCo...8....9F.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Cannon, Johanna Taylor; Vellutini, Bruno Cossermelli; Smith, Julian; Ronquist, Fredrik; Jondelius, Ulf; Hejnol, Andreas (2016). "Xenacoelomorpha is the sister group to Nephrozoa". Nature 530 (7588): 89–93. doi:10.1038/nature16520. PMID 26842059. Bibcode: 2016Natur.530...89C. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:nrm:diva-1844.
- ↑ Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Giribet, Gonzalo; Dunn, Casey W.; Hejnol, Andreas; Kristensen, Reinhardt M.; Neves, Ricardo C. et al. (June 2011). "Higher-level metazoan relationships: recent progress and remaining questions". Organisms, Diversity & Evolution 11 (2): 151–172. doi:10.1007/s13127-011-0044-4. http://nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:HUL.InstRepos:27755241.
- ↑ Smith, Martin R.; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2014). "Hallucigenia's onychophoran-like claws and the case for Tactopoda". Nature 514 (7522): 363–366. doi:10.1038/nature13576. PMID 25132546. Bibcode: 2014Natur.514..363S. http://dro.dur.ac.uk/19108/1/19108.pdf.
- ↑ "Ecdysozoa". http://palaeos.com/metazoa/ecdysozoa/ecdysozoa.html.
- ↑ Yamasaki, Hiroshi; Fujimoto, Shinta; Miyazaki, Katsumi (June 2015). "Phylogenetic position of Loricifera inferred from nearly complete 18S and 28S rRNA gene sequences". Zoological Letters 1: 18. doi:10.1186/s40851-015-0017-0. PMID 26605063.
- ↑ Kapli, Paschalia; Natsidis, Paschalis; Leite, Daniel J.; Fursman, Maximilian; Jeffrie, Nadia; Rahman, Imran A. et al. (2021-03-19). "Lack of support for Deuterostomia prompts reinterpretation of the first Bilateria" (in en). Science Advances 7 (12): eabe2741. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abe2741. ISSN 2375-2548. PMID 33741592. Bibcode: 2021SciA....7.2741K.
- ↑ Peterson, Kevin J.; Cotton, James A.; Gehling, James G.; Pisani, Davide (2008-04-27). "The Ediacaran emergence of bilaterians: congruence between the genetic and the geological fossil records". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences 363 (1496): 1435–1443. doi:10.1098/rstb.2007.2233. PMID 18192191.
- ↑ Philippe, Hervé; Poustka, Albert J.; Chiodin, Marta; Hoff, Katharina J.; Dessimoz, Christophe; Tomiczek, Bartlomiej et al. (2019). "Mitigating anticipated effects of systematic errors supports sister-group relationship between Xenacoelomorpha and Ambulacraria". Current Biology 29 (11): 1818–1826.e6. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.04.009. ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 31104936.
External links
- Tree of Life web project — Bilateria
- University of California Museum of Paleontology — Systematics of the Metazoa
Wikidata ☰ Q5173 entry
 |
Categories: [Ediacaran first appearances]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 12/29/2024 17:25:15 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Biology:Bilateria | License: CC BY-SA 3.0



.jpg)


 KSF
KSF