Nebula
 From Nwe
From Nwe A nebula (pl. nebulae, nebulæ, or nebulas; derived from the Latin word for "mist" or "cloud"[1]) is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, and plasma. Originally, the term nebula was a general name for any extended astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way. For example, the Andromeda Galaxy was once referred to as the Andromeda Nebula before galaxies were discovered by Edwin Hubble. Many nebulae (known as diffuse nebulae) have poorly defined boundaries; others (such as planetary nebulae) may be described as discrete objects with identifiable boundaries.
Nebulae often contain star-forming regions, as observed in the Eagle Nebula, depicted in NASA's famous image known as the Pillars of Creation. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form larger masses, which attract further matter and eventually become large enough to form stars. The remaining materials are then believed to form planets and other objects similar to those in the Solar System.
Formation
Many nebulae are formed during the gravitational collapse of diffuse gases in the interstellar medium (ISM). As the material collapses under its own weight, massive stars may form in the center, and their ultraviolet radiation ionizes the surrounding gas, making it visible at optical wavelengths. Examples of this type of nebula are the Rosette Nebula and the Pelican Nebula. These nebulae vary in size, depending on the size of the original cloud of gas. The number of stars formed can vary as well. At the sites of star formation, the newly formed stars are sometimes known as young, loose clusters.
Some nebulae are formed as a consequence of supernova explosions, which are the death throes of massive, short-lived stars. The material thrown off from the supernova explosion is ionized by the supernova remnant. One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus. It is the result of a supernova recorded in the year 1054, and the center of the nebula contains a neutron star, created during the explosion.
Other nebulae may form as planetary nebulae (discussed below). This is the final stage of the life of a low-mass star, such as our Sun. Stars that have a mass of up to 8-10 solar masses evolve into red giants and slowly lose their outer layers during pulsations in their atmosphere. When a star has lost a sufficient amount of material, its temperature increases and the ultraviolet radiation it emits is capable of ionizing the surrounding nebula.[2]
Diffuse nebulae
Most nebulae can be described as diffuse nebulae, which means that they are extended and have no well-defined boundaries.[3] In visible light, these nebulae may be divided into emission nebulae and reflection nebulae, a categorization that is based on how the light we detect was created.
- Emission nebulae: They consist of a plasma of ionized gas, mostly ionized hydrogen and electrons.[4] When the ions recombine with the electrons, they emit spectral lines, particularly the red line of hydrogen.[5] Thus, emission nebulae have a reddish glow. These nebulae are often called HII regions, which refers to the presence of ionized hydrogen.
- Reflection nebulae: Unlike emission nebulae, reflection nebulae do not produce significant amounts of visible light on their own. Rather, they contain dust particles that scatter (reflect) the light of nearby stars.[4] Given that light is scattered more readily in the blue region than in the red, reflection nebulae tend to appear bluish.[6]
Dark nebulae are similar to diffuse nebulae, but they are not seen by their emitted or reflected light. Instead, they are observed as dark clouds in front of more distant stars or in front of emission nebulae.[4]
Although these nebulae appear different at optical wavelengths, they all appear to be bright sources of emission at infrared wavelengths. This emission comes primarily from the dust within the nebulae.[4]
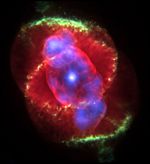
Planetary nebulae
Planetary nebulae are nebulae that form from the gaseous shells ejected from low-mass red giants (toward the end of the star's life) when they transform into white dwarfs.[4] These nebulae are emission nebulae, with spectral emission that is similar to the emission nebulae found in star formation regions.[4] Technically, they are a type of HII region because most of their hydrogen content will be ionized. However, planetary nebulae are denser and more compact than the emission nebulae in star formation regions.[4]
The name "planetary nebulae" was given because the astronomers who first observed these objects thought that they resembled the disks of planets. However, they are not related to planets at all.[7]
Protoplanetary nebula
A protoplanetary nebula (PPN) is an astronomical object that is at the short-lived episode during a star's rapid stellar evolution between the late asymptotic giant branch (LAGB) phase and the subsequent planetary nebula (PN) phase.[8] A PPN emits strong infrared radiation, and it is a kind of reflection nebula. The exact stage when a PPN becomes a planetary nebula (PN) is defined by the temperature of the central star.
Supernova remnants

A supernova is produced when a high-mass star reaches the end of its life. When nuclear fusion ceases in the core of the star, the star collapses inward on itself and forms a neutron core. The gas falling inward either rebounds or gets so strongly heated that it expands outward from the core, thus causing the star to explode.[4] The expanding shell of gas forms what is called a supernova remnant, a special type of diffuse nebula.[4] Although much of the optical and X-ray emission from supernova remnants originates from ionized gas, a substantial amount of the radio emission is a form of nonthermal emission called synchrotron emission.[4] This latter emission originates from near the core of the remnant as high-velocity electrons move within the magnetic field of the neutron star.[9]
Examples of notable named nebulae
- Barnard's Loop
- Cat's Eye Nebula
- Crab Nebula
- Eagle Nebula
- Eta Carinae Nebula
- Horsehead Nebula
- Hourglass Nebula
- Orion Nebula
- Red Square Nebula
- Ring Nebula
- Rosette Nebula
- Tarantula Nebula
Notes
- ↑ Online Etymology Dictionary, Nebula. Retrieved June 23, 2008.
- ↑ fuseweb.llnl.gov, Planetary Nebulae. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ↑ University of Illinois, The Messier Catalog: Diffuse Nebulae. Retrieved September 19, 2007.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 F.H. Shu, The Physical Universe (Mill Valley, CA: University Science Books, 1982, ISBN 0935702059).
- ↑ FusEdWeb Fusion Energy Education, Emission Nebulae. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ↑ Fusion Energy Education, Reflection Nebulae. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ↑ E. Chaisson and S. McMillan, Astronomy: A Beginner's Guide to the Universe (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, ISBN 013733916X).
- ↑ R. Sahai, C. Sánchez Contreras, and M. Morris, A Starfish Preplanetary Nebula: IRAS 19024+0044, Astrophysical Journal 620:948-960. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ↑ Fusion Energy Education, Supernova Remnants. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Coe, Steven R. 2007. Nebulae and How to Observe Them. London: Springer. ISBN 978-1846284823.
- Gurzadyan, Grigor A. 1997. The Physics and Dynamics of Planetary Nebulae. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3540609652.
- Kaufmann, William J. 1978. Stars and Nebulas. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 3540609652.
- O'Dell, C. Robert. 2003. The Orion Nebula: Where Stars Are Born. Cambridge, MA: Belknap. ISBN 067401183X.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/03/2023 22:43:55 | 90 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Nebula | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:






 KSF
KSF