Globe (Human Eye)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Globe | |
|---|---|
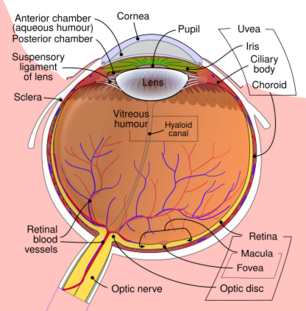 Schematic diagram of the human eye. | |
| Details | |
| Artery | anterior ciliary arteries, long posterior ciliary arteries, short posterior ciliary arteries |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | bulbus oculi |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
The globe of the eye, or bulbus oculi, is the frontmost sensory organ of the human ocular system, going from the cornea at the front, to the anterior part of the optic nerve at the back. More simply, the eyeball itself, as well as the ganglion cells in the retina that eventually transmit visual signals through the optic nerve. [1] A hollow structure, the bulbus oculi is composed of a wall enclosing a cavity filled with fluid with three coats: the sclera, choroid, and the retina.[2] Normally, the bulbus oculi is bulb-like structure.[3] However, the bulbus oculi is not completely spherical. Its anterior surface, transparent and more curved, is known as the cornea of the bulbus oculi.
The main purpose of the bulbus oculi is to refract photons passing through the cornea, pupil, and lens to focus onto the retina, where the photons in the refracted light rays trigger electric and chemical reactions within the layers of the retina, specifically the fovea centralis. These reactions are then passed as electrical signals through the optic nerve into the posterior section of the human ocular system (which takes place in the brain). [4]
See also
- Sclera
- Choroid
- Retina
References
- ↑ "Globe of eye ", Biology Online, 2009-08-20. Retrieved on 2009-08-20.
- ↑ Bailey, Frederick Randolph (1920). Text-book of histology (6 ed.). University of California: W. Wood. https://books.google.com/books?id=XaYLAQAAIAAJ&q=bulbus+oculi.
- ↑ TMB. "Wall of the Bulbus Oculi". Tpub.com. http://www.tpub.com/content/armymedical/md0805/md08050081.htm.
- ↑ "Eye Globe Anatomy ", Medscape, 2017-11-09. Retrieved on 2023-08-01.
 |
Categories: [Human eye anatomy]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/16/2024 10:15:53 | 16 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Medicine:Globe_(human_eye) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0



 KSF
KSF