Johann Pachelbel
 From Nwe
From Nwe
| Johann Pachelbel | |
|---|---|
| Birth name | Johann Pachelbel |
| Born | September 1, 1653 (Baptized) Nuremberg, Germany[1] |
| Died | March 3, 1706 (age 52) Nuremberg, Germany[1] |
| Genre(s) | Baroque |
| Occupation(s) | Composer Organist |
| Instrument(s) | Organ |
Johann Pachelbel (IPA: [paˈxɛlbəl]) (baptized September 1, 1653 – March 3, 1706) was an acclaimed German Baroque composer, organist and teacher who brought the south German organ tradition to its peak. He composed a large body of sacred and secular music, and his contributions to the development of the chorale prelude and fugue have earned him a place among the most important composers of the middle Baroque. Pachelbel saw in the chorale preludes and fugues a way of imparting certain universal values of spiritual well-being and moral precepts by using compositional techniques to uplift and reform one's spirit.
Pachelbel's music was influenced by south German composers such as Johann Jakob Froberger and Johann Kaspar Kerll, Italians such as Girolamo Frescobaldi and Alessandro Poglietti, French composers and the composers of the Nuremberg tradition. Pachelbel preferred a lucid, uncomplicated contrapuntal style that emphasized melodic and harmonic clarity. His music is less virtuosic and less adventurous harmonically than that of Dieterich Buxtehude, although like Buxtehude, Pachelbel experimented with different ensembles and instrumental combinations in his chamber music and, most importantly, his vocal music, much of which features exceptionally rich instrumentation. Pachelbel explored variation forms and associated techniques, which manifest themselves in many diverse pieces, from sacred concertos to harpsichord suites.
Life
1653–1673: Early youth and education (Nuremberg, Altdorf, Regensburg)
Johann Pachelbel was born in 1653 in Nuremberg into the family of a tinsmith.[2] His exact date of birth is unknown, but since he was baptized on September 1 we can be almost certain that he was born in August. During his early youth, Pachelbel received musical training from Georg Caspar Wecker, organist of the Church of Saint Sebald (Sebalduskirche), and Heinrich Schwemmer, a musician and music teacher who later became the cantor of the same church. Both Wecker and Schwemmer were trained by Johann Erasmus Kindermann, one of the founders of the Nuremberg musical tradition, himself a pupil of Johann Staden.
Johann Mattheson, whose Grundlage einer Ehrenpforte (Hamburg, 1740) is one of the most important sources of information about Pachelbel's life, mentions that the young Pachelbel demonstrated exceptional musical and academic abilities. He received his primary education in local Nuremberg schools and became a student at the University of Altdorf at the age of 15. During his stay in Altdorf, Pachelbel not only studied but also served as organist of one of the churches. Unfortunately, he was forced to leave the university after less than a year because of financial difficulties. In order to complete his studies, Pachelbel in 1670 became a scholarship student at the Gymnasium poeticum at Regensburg.
The school authorities at Regensburg, impressed by Pachelbel's academic qualifications and his advanced standing in music, permitted him to study music outside the gymnasium. His teacher was Kaspar Prentz, a student of Johann Kaspar Kerll. The latter was greatly influenced by Italian composers such as Giacomo Carissimi, so it was probably through Prentz that Pachelbel started developing an interest in Italian music of the early and middle Baroque.
1673–1690: Career (Vienna, Eisenach, Erfurt)
In 1673 Pachelbel moved to Vienna, where he became a deputy organist at the famous Saint Stephen Cathedral (Stephansdom). At the time, Vienna was the center of the vast Habsburg empire and had much cultural importance, its tastes in music predominantly Italian. Several renowned cosmopolitan composers worked there, most of them contributing to the exchange of musical traditions in Europe. In particular, Johann Jakob Froberger served as court organist in Vienna until 1657 and was succeeded by Alessandro Poglietti; Georg Muffat lived in the city for some time, and most importantly, Johann Kaspar Kerll moved to Vienna in 1673 - while there, he may have known or even taught Pachelbel, whose music shows traces of Kerll's style. Pachelbel spent five years in Vienna, absorbing the music of Catholic composers from southern Germany and Italy, whose styles contrasted with the more strict Lutheran tradition he was bred in. In some respects, Pachelbel is similar to Haydn, who too served as professional musician of the Stephansdom in his youth and as such was exposed to music of the leading composers of the time.
In 1677 Pachelbel moved to Eisenach, where he found employment as court organist under Kapellmeister Daniel Eberlin (also a native of Nuremberg), in the employ of Johann Georg I, Duke of Saxe-Eisenach. He met the Bach family in Eisenach (which was the home city of JS Bach's father, Johann Ambrosius Bach), becoming a close friend of Johann Ambrosius and tutoring his children. Pachelbel only spent one year in Eisenach before his patron's brother died—during the period of mourning court musicians were greatly curtailed[3] and Pachelbel was left without employment. He requested a testimonial from Eberlin, who wrote one for him (in the document, Eberlin described Pachelbel as a 'perfect and rare virtuoso'—einen perfecten und raren Virtuosen[3] With this document, Pachelbel left Eisenach on May 18, 1678.
In June 1678, Pachelbel was employed as organist of the Lutheran Preacher's Church (Predigerkirche) in Erfurt, succeeding Johann Bach (1604-1673), the eldest son of Hans Bach. The Bach family was very well known in Erfurt (where virtually all organists would later be called "Bachs"), so Pachelbel's friendship with them continued here: Pachelbel became godfather to Johann Ambrosius' daughter, Johanna Juditha, and taught Johann Christoph Bach. Pachelbel remained in Erfurt for 12 years and established his reputation as one of the leading German organ composers of the time during his stay. Chorale preludes became the most characteristic products of the Erfurt period, since Pachelbel's contract specifically required him to compose the preludes for church services beforehand (as opposed to improvising during the service). His duties also included organ maintenance and, more importantly, composing a large-scale work every year to demonstrate his progress as composer and organist (as every work of that kind had to be better than the one composed the year before).
Pachelbel married twice during his stay in Erfurt. Barbara Gabler became his wife on October 25, 1681, however, she and their only son died in September 1683 during a plague. Pachelbel's first published work, a set of chorale variations called Musicalische Sterbens-Gedancken ("Musical Thoughts on Death," Erfurt, 1683), was probably influenced by this event. Pachelbel married Judith Drommer (Trummert), daughter of a coppersmith,[2] on August 24, 1684. They had five sons and two daughters; two of his sons, Wilhelm Hieronymus Pachelbel and Charles Theodore Pachelbel, also became organ composers; another son, Johann Michael, became an instrument maker. One of his daughters, Amalia, achieved recognition as a painter and engraver.
1690–1706: Final years (Stuttgart, Gotha, Nuremberg)
Even though Pachelbel was outstandingly successful as organist, composer, and teacher at Erfurt, he asked for a permission to leave, apparently seeking a better appointment. He was formally released on August 15, 1690, receiving a testimonial in which his "diligence and faithfulness" were praised.[2] Pachelbel found new employment in less than two weeks: from September 1, 1690 he was musician and organist at the Württemberg court at Stuttgart under the patronage of Duchess Magdalena Sibylla. The position was an improvement, but unfortunately, he only spent two years in Stuttgart before he was forced to flee before a French invasion. His next post was that of town organist in Gotha, which he occupied for two years, starting on November 8, 1692. While in Gotha, Pachelbel published his first and only collection of liturgical music: Acht Chorale zum Praeambulieren (1693).
During his three-year stay in Gotha, Pachelbel received at least two job invitations, one from Stuttgart and one from Oxford, England, but declined both. When Georg Caspar Wecker, Pachelbel's former teacher and organist of the Church of Saint Sebald in Nuremberg, died on April 20, 1695, Nuremberg city authorities were so anxious to appoint Pachelbel—by then a celebrated native of the city—that they have sent Pachelbel an official invitation to take up the post at Saint Sebald (contrary to the usual practice of organizing an examination or inviting prominent organists of lesser churches to apply). Pachelbel accepted the invitation; Gotha authorities released him in 1695 and he arrived in Nuremberg sometime during summer, his road expenses paid by the Nuremberg city council.
Pachelbel remained in Nuremberg for the rest of his life. His late Nuremberg period saw the publication of Musikalische Ergötzung, a collection of chamber music, and, most importantly, Hexachordum Apollinis (Nuremberg, 1699), a set of six keyboard arias with variations. Although Pachelbel was mostly influenced by Italian and southern German composers, he apparently was acquainted with the northern German school, because Hexachordum Apollinis was dedicated to Dieterich Buxtehude. Also composed during these final years were numerous Italian-influenced concertato Vespers pieces and a set of more than ninety Magnificat fugues. Pachelbel died on March 3, 1706, aged 52.
Posthumous influence and the rise of popularity of the Canon in D
One of the last middle Baroque composers, Pachelbel did not have any considerable influence on most of the famous late Baroque composers such as George Frideric Handel, Domenico Scarlatti or Georg Philipp Telemann. He did influence Johann Sebastian Bach (indirectly: the young Johann Sebastian was tutored by Johann Christoph Bach, who studied with Pachelbel), but although JS Bach's early chorales and chorale variations borrow from Pachelbel's music, the style of northern German composers (Georg Böhm, Dieterich Buxtehude, Johann Adam Reincken) played a more important role in the development of Bach's talent.
Pachelbel was the last great composer of the Nuremberg tradition and the last important southern German composer. Pachelbel's influence was mostly limited to his pupils, most notably Johann Christoph Bach, Johann Heinrich Buttstett, Andreas Nicolaus Vetter, and two of Pachelbel's sons, Wilhelm Hieronymus and Charles Theodore. The latter became one of the first European composers to take up residence in the American colonies and so Pachelbel influenced, although indirectly and only to a certain degree, the American church music of the era. Composer, musicologist and writer Johann Gottfried Walther is probably the most famous of the composers influenced by Pachelbel - he is, in fact, referred to as the "second Pachelbel" in Mattheson's Grundlage einer Ehrenpforte, although this is somewhat misleading.
As Baroque style went out of fashion during the eighteenth century, the majority of Baroque and pre-Baroque composers were virtually forgotten. Local organists in Nuremberg and Erfurt knew Pachelbel's music and occasionally performed it, but the public and the majority of composers and performers did not pay much attention to Pachelbel and his contemporaries. In the first half of the nineteenth century some organ works by Pachelbel were published and several musicologists started considering him an important composer (particularly Philipp Spitta, who was one of the first researchers to trace Pachelbel's role in the development of Baroque keyboard music). Much of his work was published in the early twentieth century in the Denkmäler der Tonkunst in Österreich series, but it was not until the rise of interest in early and Baroque music in the middle of the twentieth century and the advent of historically-informed performance practice and associated research that Pachelbel's works began to be studied extensively and performed more frequently.
Pachelbel's Canon in D major is the only exception. A piece of chamber music scored for three violins and basso continuo (and originally paired with a gigue in the same key), it experienced a tremendous surge in popularity during the 1970s, which made the Canon in D a universally recognized cultural item, one of the most famous classical compositions ever. Numerous musical adaptations and arrangements of the canon for diverse ensembles exist and the main theme (or the associated harmonic sequence) is frequently adapted by pop music artists, similarly to the opening of Bach's Toccata and Fugue in D minor, BWV 565. Interestingly, the gigue that originally accompanied the canon never received the same amount of popularity, even though it is a lively energetic dance.
Works
General information
During his lifetime, Pachelbel was best known as an organ composer. He wrote more than two hundred pieces for the instrument, both liturgical and secular, and explored most of the genres that existed at the time. Pachelbel was also a prolific vocal music composer: around a hundred works survive, including some 40 large-scale works. Only a few chamber music pieces by Pachelbel exist, although he might have composed many more, particularly while serving as court musician in Eisenach and Stuttgart.
Several principal sources exist for Pachelbel's music, although none of them as important as, for example, the Oldham manuscript is for Louis Couperin. Among the more significant materials are several manuscripts that were lost before and during World War II but partially available as microfilms of the Winterthur collection, a two-volume manuscript currently in possession of the Oxford Bodleian library which is a major source for Pachelbel's late work, and the first part of the Tabulaturbuch (1692, currently at the Biblioteka Jagiello´nska in Kraków) compiled by Pachelbel's pupil Johann Valentin Eckelt, which includes the only known Pachelbel's autographs. The Neumeister manuscript and the so-called Weimar tablature of 1704 provide valuable information about Pachelbel's school, although they do not contain any pieces that can be confidently ascribed to him.
Currently there is no standard numbering system for Pachelbel's works. Several catalogues are used, by Antoine Bouchard (POP numbers, organ works only), Jean M. Perreault (P numbers, currently the most complete catalogue; organized alphabetically), Hideo Tsukamoto (T numbers, L for lost works; organized thematically) and Kathryn Jane Welter (PC numbers).
Keyboard music
Much of Pachelbel's liturgical organ music, particularly the chorale preludes, is relatively simple and written for manuals only, no pedal is required. This is partly due to Lutheran religious practice where congregants sang the chorales. Household instruments like virginals or clavichords accompanied the singing, so Pachelbel and many of his contemporaries made music playable using these instruments. The quality of the organs Pachelbel used also played a role: south German instruments were not, as a rule, as complex and as versatile as the north German ones, and Pachelbel's organs must have only had around 15-25 stops on two manuals (compare to Buxtehude's Marienkirche instrument with 52 stops, 15 of them in the pedal). Finally, neither the Nuremberg nor the southern German organ tradition endorsed extensive use of pedals seen in the works by composers of the northern German school.
Some pieces (several chorales, all ricercars, some fantasias) are written in white mensural notation. This notation system has hollow note heads and omits bar lines (measure delimiters). It was widely used since the 15th century but was being dropped in favor of modern notation (sometimes called black notation) during the sixteenth-seventeenth centuries]]. In most cases Pachelbel used white notation for pieces composed in old-fashioned styles, to provide artistic integrity, as it were. In chorales, he may have used the notation to make the works more familiar to performers and musicians, most of whom were not used to the modern system.
Chorales
Chorales and chorale preludes constitute almost half of Pachelbel's surviving organ output, in part because of his Erfurt job duties which required him to compose chorale preludes on a regular basis. The models Pachelbel used most frequently are the three-part cantus firmus setting, the chorale fugue and, most importantly, a model he invented which combined the two types. This latter type begins with a brief chorale fugue that is followed by a three- or four-part cantus firmus setting. Chorale phrases are treated one at a time, in the order in which they occur; frequently, the accompanying voices anticipate the next phrase by using bits of the melody in imitative counterpoint. Here's an example from Wenn mein Stündlein vorhanden ist:
The piece begins with a chorale fugue (not shown here) that morphs into a four-part chorale setting which starts at bar 35. The slow-moving chorale (the cantus firmus, i.e., the original hymn tune) is in the soprano, and is highlighted in blue. The lower voices anticipate the shape of the second phrase of the chorale in an imitative fashion (notice the distinctive pattern of two repeated notes). Pachelbel wrote numerous chorales using this model (Auf meinen lieben Gott, Ach wie elend ist unsre Zeit, Wenn mein Stündlein vorhanden ist, etc.), which soon became a standard form.
A distinctive feature of almost all of Pachelbel's chorale preludes is his treatment of the melody: the cantus firmus features virtually no figuration or ornamentation of any kind, always presented in the plainest possible way in one of the outer voices. Pachelbel's knowledge of both ancient and contemporary chorale techniques is reflected in Acht Chorale zum Praeambulieren, a collection of eight chorales he published in 1693. It included, among other types, several chorales written using outdated models. Of these, Nun lob, mein Seel, den Herren (Psalm 103) is based on the German polyphonic song; it is one the very few Pachelbel chorales with cantus firmus in the tenor. Wir glauben all' an einen Gott is a three-part setting with melodic ornamentation of the chorale melody, which Pachelbel employed very rarely. Finally, Jesus Christus, unser Heiland der von uns is a typical bicinium chorale with one of the hands playing the unadorned chorale while the other provides constant fast-paced accompaniment written mostly in 16th notes. Pachelbel only used the bicinium form in two other pieces.
Fugues and ricercars
Pachelbel wrote more than a hundred fugues on free themes. These fall into two categories: some 30 free fugues and around 90 of the so-called Magnificat Fugues. Pachelbel's fugal writing is, without exceptions, very plain: the episodes are usually based on non-thematic material and rather short compared to the later model (of which JS Bach's works are now considered the prime example), and neither stretto nor the usual contrapuntal devices such as diminution or inversion are employed in any fugue. Nevertheless, Pachelbel's fugues display a tendency towards a more unified, subject-dependent structure which was to become the key element of late Baroque fugues; given the amount of fugues he composed and the extraordinary variety of subjects he used, Pachelbel is regarded as one of the key composers in the evolution of the form. He was also the first major composer to pair a fugue with a preludial movement (a toccata or a prelude) - this technique was adopted by later composers and was extensively used by JS Bach.
The Magnificat Fugues were all composed during Pachelbel's final years in Nuremberg. The singing of the Magnificat at Vespers was usually accompanied by the organist, and earlier composers provided examples of Magnificat settings for organ, based on themes from the chant. Pachelbel's fugues, however, are almost all based on free themes and it is not yet understood exactly where did they fit during the service. It could be that they served to help singers establish pitch, or simply act as introductory pieces played before the beginning of the service. There are 95 pieces extant, covering all eight Church Modes: 23 in primi toni, 10 in secundi toni, 11 in tertii toni, 8 in quarti toni, 12 in quinti toni, 10 in sexti toni, 8 in septimi toni and 13 in octavi toni. Although a few two- and four-voice works are present, most employ three voices (sometimes expanding to four-voice polyphony for a bar or two). With the exception of the three double fugues (primi toni No. 12, sexti toni No. 1 and octavi toni No. 8), all are straightforward pieces, frequently in common time and all comparatively short - at an average tempo, most take around a minute and a half to play.
Although most of them are brief, the subjects are extremely varied (see Example 1). Frequently some form of note repetition is used to emphasize a rhythmic (rather than melodic) contour. Many feature a dramatic leap (up to an octave), which may or may not be mirrored in one of the voices sometime during an episode - a characteristic Pachelbel technique, although it was also employed by earlier composers, albeit less pronounced. Minor alterations to the subject between the entries are observed in some of the fugues, and simple countersubjects occur several times. An interesting technique employed in many of the pieces is an occasional resort to style brisé for a few bars, both during episodes and in codas. The double fugues exhibit a typical three-section structure: fugue on subject 1, fugue on subject 2, counterpoint with simultaneous use of both subjects.
Most of Pachelbel's free fugues are in three or four voices, with the notable exception of two bicinia pieces that were probably intended for teaching purposes. Pachelbel frequently used repercussion subjects of different kinds, with note repetition sometimes extended to span a whole measure (like in the subject of a G minor fugue, see illustration). Some of the fugues employ textures more suited for the harpsichord, particularly those with broken chord figuration. The three ricercars Pachelbel composed, that are more akin to his fugues than to ricercars by Frescobaldi's or Froberger, are perhaps more technically interesting. In the original sources, all three use white notation and are marked alla breve. The polythematic C minor ricercar is the most popular and frequently performed and recorded. It is built on two contrasting themes (a slow chromatic pattern and a lively simplistic motif) which appear in their normal and inverted forms and concludes with both themes appearing simultaneously. The F-sharp minor ricercar uses the same concept and is slightly more interesting musically: the key of F-sharp minor requires a more flexible tuning than the standard meantone temperament of the Baroque era and was therefore rarely used by contemporary composers. This means that Pachelbel may have used his own tuning system, of which little is known. Ricercare in C major is probably an early work, mostly in three voices and employing the same kind of writing with consecutive thirds as seen in Pachelbel's toccatas (see below).
Pachelbel's use of repercussion subjects and extensive repeated note passages may be regarded as another characteristic feature of his organ writing. Extreme examples of note repetition in the subject are found in magnificat fugues: quarti toni No. 4 has eight repeated notes, octavi toni No. 6 has twelve.[4] Also, even a fugue with an ordinary subject can rely on strings of repeated notes, as it happens, for example, in magnificat fugue octavi toni No. 12:
Chaconnes and variations
Pachelbel's apparent affinity for variation form is evident from his organ works that explore the genre: chaconnes, chorale variations and several sets of arias with variations. The six chaconnes, together with Buxtehude's ostinato organ works, represent a shift from the older chaconne style: they completely abandon the dance idiom, introduce contrapuntal density, employ miscellaneous chorale improvisation techniques, and, most importantly, give the bass line much thematic significance for the development of the piece. Pachelbel's chaconnes are distinctly south German in style; the duple meter C major chaconne (possibly at early work) is reminiscent of Kerll's D minor passacaglia. The remaining five works are all in triple meter and display a wide variety of moods and techniques, concentrating on melodic content (as opposed to the emphasis on harmonic complexity and virtuosity in Buxtehude's chaconnes). The ostinato bass is not necessarily repeated unaltered throughout the piece and is sometimes subjected to minor alterations and ornamentation. The D major, D minor and F minor chaconnes are among Pachelbel's most well-known organ pieces, and the latter is often cited as his best organ work.
In 1699 Pachelbel published Hexachordum Apollinis (the title is a reference to Apollo's lyre), a collection of six variations sets in different keys. It is dedicated to composers Ferdinand Tobias Richter (a friend from the Vienna years) and Dieterich Buxtehude. Each set follows the "aria and variations" model, arias numbered Aria prima through Aria sexta ("first" through "sixth"). The final piece, which is also the most known today, is subtitled Aria Sebaldina, a reference to the Church of Saint Sebald where Pachelbel worked at the time and where he received his first music lessons. Most of the variations are in common time, with Aria Sebaldina and its variations being the only notable exceptions–they are in 3/4 time. The pieces explore a wide range of variation techniques.
Pachelbel's other variation sets include a few arias and an arietta (a short aria) with variations and a few pieces designated as chorale variations. Four works of the latter type were published in Erfurt in 1683 under the title Musicalische Sterbens-Gedancken ("Musical Thoughts on Death"), which might refer to Pachelbel's first wife's death in the same year. This was Pachelbel's first published work and it is now partially lost. These pieces, along with Georg Böhm's works, may or may not have influenced Johann Sebastian Bach's early organ partitas.
Toccatas
About 20 toccatas by Pachelbel survive, including several brief pieces referred to as toccatinas in the Perreault catalogue. They are characterized by consistent use of pedal point: for the most part, Pachelbel's toccatas consist of relatively fast passagework in both hands over sustained pedal notes. Although similar technique is employed in toccatas by Froberger and Frescobaldi's pedal toccatas, Pachelbel distinguishes himself from these composers by having no sections with imitative counterpoint–in fact, unlike most toccatas from the early and middle Baroque periods, Pachelbel's contributions to the genre are not sectional, unless rhapsodic introductory passages in a few pieces (most notably the E minor toccata) are counted as separate sections. Furthermore, no other Baroque composer used pedal point with such consistency in toccatas.
Many of Pachelbel's toccatas explore a single melodic motif, and later works are written in a simple style in which two voices interact over sustained pedal notes, and said interaction—already much simpler than the virtuosic passages in earlier works—sometimes resorts to consecutive thirds, sixths or tenths. Compare the earlier D major toccata, with passages in the typical middle Baroque style, with one of the late C major toccatas:
Sometimes a bar or two of consecutive thirds embellish the otherwise more complex toccata, occasionally there is a whole section written in that manner, and a few toccatas (particularly one of the D minor and one of the G minor pieces) are composed using only this technique, with almost no variation. Partly due to their simplicity, the toccatas are very accessible works; however, the E minor and C minor ones which receive more attention than the rest are in fact slightly more complex.
Fantasias
Pachelbel composed six fantasias. Three of them (the A minor, C major and one of the two D Dorian pieces) are sectional compositions in 3/2 time, the sections are never connected thematically; the other D Dorian piece's structure is reminiscent of Pachelbel's magnificat fugues, with the main theme accompanied by two simple countersubjects
The E-flat major and G minor fantasias are variations on the Italian toccata di durezze e ligature genre. Both are gentle free-flowing pieces featuring intricate passages in both hands with many accidentals, close to similar pieces by Girolamo Frescobaldi or Giovanni de Macque.
Preludes
Almost all pieces designated as preludes resemble Pachelbel's toccatas closely, since they too feature virtuosic passagework in one or both hands over sustained notes. However, most of the preludes are much shorter than the toccatas: the A minor prelude (pictured below) only has 9 bars, the G major piece has 10. The only exception is one of the two D minor pieces, which is very similar to Pachelbel's late simplistic toccatas, and considerably longer than any other prelude. The toccata idiom is completely absent, however, in the short Prelude in A minor:
A texture of similar density is also found in the ending of the shorter D minor piece, where three voices engage in imitative counterpoint. In pairs of preludes and fugues Pachelbel aimed to separate homophonic, improvisatory texture of the prelude from the strict counterpoint of the fugue.
Other keyboard music
There are 21 dance suites, apparently composed around 1683, usually attributed to Pachelbel, although this attribution is questionable for all but three suites. The pieces are French influenced and indicate Pachelbel may have studied Froberger's keyboard suites. Harmonically, the suites are quite varied: 17 keys are in these pieces, including F-sharp minor, which was seldom used in baroque music. (It was difficult to use because of meantone temperament. Pachelbel's other pieces in the same key include an organ ricercare and a chamber suite).
All suites follow the classical model (Allemande, Courante, Sarabande, Gigue), but are sometimes updated with an extra movement between the courante and the sarabande, usually a gavotte or a ballet. Generally, these additional movements are uncomplicated and less developed than main movements, but offer catchy and memorable melodies. All movements are in binary form, except for two arias.
Chamber music
Pachelbel's chamber music is much less virtuosic than Biber's Mystery Sonatas or Buxtehude's Opus 1 and Opus 2 chamber sonatas. The famous Canon in D belongs to this genre, as it was originally scored for three violins and a basso continuo, and paired with a gigue in the same key. The canon is actually more of a chaconne or a passacaglia: it consists of a ground bass over which the violins play a three-voice canon based on a simple theme, the violins' parts form 28 variations of the melody. The gigue which originally accompanied the canon is a simplistic piece that uses strict fugal writing.
Musikalische Ergötzung ("Musical Delight") is a set of six chamber suites for two scordatura violins and basso continuo published sometime after 1695. At the time, scordatura tuning was used to produce special effects and execute tricky passages. However, Pachelbel's collection was intended for amateur violinists, and scordatura tuning is used here as basic introduction to the technique. Scrodatura only involves the tonic, dominant and sometimes the subdominant notes.
Each suite of Musikalische Ergötzung begins with an introductory Sonata or Sonatina in one movement. In suites 1 and 3 these introductory movements are Allegro three-voice fughettas and stretti. The other four sonatas are reminiscent of French overtures. They have two Adagio sections which juxtapose slower and faster rhythms: the first section uses patterns of dotted quarter and eighth notes in a non-imitative manner. The second employs the violins in an imitative, sometimes homophonic structure, that uses shorter note values. The dance movements of the suites show traces of Italian (in the gigues of suites 2 and 6) and German (allemande appears in suites 1 and 2) influence, but the majority of the movements are clearly influenced by the French style. The suites do not adhere to a fixed structure: the allemande is only present in two suites, the gigues in four, two suites end with a chaconne, and the fourth suite contains two arias.
Pachelbel's other chamber music includes an aria and variations (Aria con variazioni in A major) and four standalone suites scored for a string quartet or a typical French five-part string ensemble with 2 violins, 2 violas and a violone (the latter reinforces the basso continuo). Of these, the five-part suite in G major (Partie a 5 in G major) is a variation suite, where each movement begins with a theme from the opening sonatina; like its four-part cousin (Partie a 4 in G major) and the third standalone suite (Partie a 4 in F-sharp minor) it updates the German suite model by using the latest French dances such as the gavotte or the ballet. The three pieces mentioned all end with a Finale movement. Interestingly, Partie a 4 in G major features no figuration for the lower part, which means that it wasn't a basso continuo and that, as Jean M. Perreault writes, "this work may well count as the first true string quartet, at least within the Germanophone domain."[5]
Vocal music
Johann Gottfried Walther famously described Pachelbel's vocal works as "more perfectly executed than anything before them."[6] Already the earliest examples of Pachelbel's vocal writing, two arias So ist denn dies der Tag and So ist denn nur die Treu composed in Erfurt in 1679 (which are also Pachelbel's earliest datable pieces[7]), display impressive mastery of large-scale composition (So ist denn dies der Tag is scored for soprano, SATB choir, 2 violins, 3 violas, 4 trumpets, timpani and basso continuo) and exceptional knowledge of contemporary techniques.
These latter features are also found in Pachelbel's Vespers pieces and sacred concertos, large-scale compositions which are probably his most important vocal works. Almost all of them adopt the modern concertato idiom and many are scored for unusually large groups of instruments (Jauchzet dem Herrn, alle Welt (in C) uses four trumpets, timpani, two violins, three violas, violone and basso continuo; Lobet den Herrn in seinem Heiligtum is scored for a five-part chorus, two flutes, bassoon, five trumpets, trombone, drums, cymbals, harp, two violins, basso continuo and organ). Pachelbel explores a very wide range of styles: psalm settings (Gott ist unser Zuversicht), chorale concertos (Christ lag in Todesbanden), sets of chorale variations (Was Gott tut, das ist wohlgetan), concerted motets, etc. The ensembles for which these works are scored are equally diverse: from the famous D major Magnificat setting written for a 4-part choir, four violas and basso continuo, to the Magnificat in C major scored for a five-part chorus, four trumpets, timpani, two violins, a single viola and two violas da gamba, bassoon, basso continuo and organ.
Pachelbel's large-scale vocal works are mostly written in modern style influenced by Italian Catholic music, with only a few non-concerted pieces and old plainchant cantus firmus techniques employed very infrequently. The string ensemble is typical for the time, three viols and two violins. The former are either used to provide harmonic content in instrumental sections or to double the vocal lines in tutti sections; the violins either engage in contrapuntal textures of varying density or are employed for ornamentation. Distinct features of Pachelbel's vocal writing in these pieces, aside from the fact that it is almost always very strongly tonal, include frequent use of permutation fugues and writing for paired voices. The Magnificat settings, most composed during Pachelbel's late Nuremberg years, are influenced by the Italian-Viennese style and distinguish themselves from their antecedents by treating the canticle in a variety of ways and stepping away from text-dependent composition.
Other vocal music includes motets, arias and two masses. Of the eleven extant motets, ten are scored for two four-part choruses. Most of this music is harmonically simple and make little use of complex polyphony (indeed, the polyphonic passages frequently feature reduction of parts). The texts are taken from the psalms, except in Nun danket alle Gott which uses a short passage from the Ecclesiastes. The motets are structured according to the text they use. One important feature found in Gott ist unser Zuversicht and Nun danket alle Gott is that their endings are four-part chorale settings reminiscent of Pachelbel's organ chorale model: the chorale, presented in long note values, is sung by the sopranos, while the six lower parts accompany with passages in shorter note values:
The arias, aside from the two 1679 works discussed above, are usually scored for solo voice accompanied by several instruments; most were written for occasions such as weddings, birthdays, funerals and baptisms. They include both simple strophic and complex sectional pieces of varying degrees of complexity, some include sections for chorus. The concerted Mass in C major is probably an early work; the D major Missa brevis is a small mass for a SATB choir in three movements (Kyrie, Gloria, Credo). It is simple, unadorned and somewhat reminiscent of his motets.
Legacy
Pachelbel's work enjoyed massive popularity during his lifetime; he had a large number of pupils and his music became a model for the composers of south and central Germany. However, he did not have much influence on the most important composers of the late Baroque such as Johann Sebastian Bach. Today Pachelbel is best known for his Canon in D; it is the only canon he wrote, and is somewhat unrepresentative of the rest of his oeuvre. In addition to the canon, his most well-known works include the Chaconne in F minor, the Toccata in C minor for organ, and the Hexachordum Apollinis, a set of keyboard variations.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wendy Thompson and Basil Smallman, "Pachelbel, Johann" The Oxford Companion to Music, Alison Latham (ed.), (Oxford University Press, 2002).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Walter E. Buszin, Johann Pachelbel's Contribution to Pre-Bach Organ Literature The Good Shepherd Institute. Retrieved May 19, 2018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ewald V. Nolte and John Butt, "Johann Pachelbel," New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, L. Macy (ed.) Oxford University Press.
- ↑ The most extraordinary example of note repetition, however, is not found in Pachelbel's fugues but in his first setting of the Vom Himmel hoch chorale, where a string of 30 repeated 16th-notes occurs in bars 15 and 16.
- ↑ Jean M. Perreault, The thematic catalogue of the musical works of Johann Pachelbel (Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press, 2004, ISBN 0810849704), 224.
- ↑ Translation from: Peter Wollny, liner notes to CD "Pachelbel; Johann Christoph & Johann Michael Bach: Motetten/Motets," DHM 77305
- ↑ Kathryn Jane Welter, "So ist denn dies der Tag: The Erbhuidigung of Prince Elector Carl Heinrich of Mainz" (lecture at the Eighth Annual Meeting of The Society for Seventeenth-Century Music, April 27-30, 2000)
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Nolte, Ewald V., and John Butt. "Johann Pachelbel," New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians L. Macy (ed.) (subscription access). Retrieved May 19, 2018.
- Pachelbel, Johann, and Max Seiffert. Organ works. reprint ed. New York: Dover, 1994. ISBN 0486278581.
- Perreault, Jean M., The thematic catalogue of the musical works of Johann Pachelbel. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press, 2004. ISBN 0810849704.: A complete index of Pachelbel's compositions, the manuscripts in which they survive, and publications in which they can be found today. Includes an exhaustive bibliography.
- Thompson, Wendy, and Basil Smallman, "Pachelbel, Johann" The Oxford Companion to Music, Alison Latham (ed.). Oxford University Press, 2002.
- Welter, Kathryn Jane. Johann Pachelbel: organist, teacher, composer : a critical reexamination of his life, works, and historical significance. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University, 1998, dissertation. Available through UMI Dissertation Services, 2001. OCLC 42665284. As described by Perreault: The only really general book on Pachelbel in English; richly informative, especially on biography and transmission of MS sources.
External links
All links retrieved August 1, 2022.
- Johann Pachelbel's biography at HOASM.org
- Johann Pachelbel at Allmusic.com
- FindAGrave Profile
- Free Public Domain Scores by Pachelbel at IMSLP
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/04/2023 00:19:13 | 8 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Johann_Pachelbel | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:




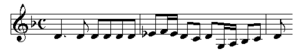






 KSF
KSF