Chicago
 From Conservapedia
From Conservapedia | Chicago | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Country | United States |
| State | Illinois |
| Settled | 1830 |
| Population | 2,700,000 (2020) |
| Area (sq mi) | 227.3 sq mi |
| Population density (/sq mi) | 11,900/sq mi |
| Current mayor | Lori Lightfoot |
| Demonym | Chicagoan |
| Co-ordinates | 41.8° N., 87.7° W |
Chicago is a city located in the northeastern corner of the state of Illinois on the shore of the southwestern tip of Lake Michigan. Chicago is a relatively young city, first incorporated in 1833 and completely rebuilt after a city-wide fire in 1871. It is located mostly within Cook County, but a corner of its O'Hare Airport is in DuPage County. It is the largest city in Illinois and the third-largest city in the United States, with 2.8 million residents, after New York City and Los Angeles.[1] The Chicago metropolitan area, which extends from southern Wisconsin to northeastern Indiana and is often called "Chicagoland", contains 9.3 million people.[2] It is the dominant city of the Midwest for transportation, trade, finance and high culture, and only reluctantly gave up the "second city" title to Los Angeles in the 1970s.
The name "Chicago" originated in 1630, when the Miami-Illinois Indians arrived in the region, and called it after a type of wild garlic that grew in the area.
Chicago is home to the Willis Tower, which at 1,450 feet is the tallest building in the United States, and was once the tallest building in the world. The building, more commonly known locally and internationally as the "Sears Tower", was originally the headquarters of Sears when constructed. In the late 2000s, London-based Willis Insurance bought the naming rights to the tower upon leasing a significant amount of space.[3] The world-renowned Art Institute of Chicago houses both a museum and a school.[4]
The City of Chicago has high gun violence levels, and the strict gun control laws of the city and of Illinois have not had any effect in reducing violence.[5] Chicago is very liberal, and as of 2019, it has more members of the Democratic Socialists of America in its city council than Republicans.[6] Chicago's last Republican mayor was elected in 1927.
Chicago is projected to fall to the fourth-largest city in 2030, as Houston surpasses its population by then.[7]
Contents
- 1 Demography
- 2 Geography
- 3 History
- 4 Reputation
- 5 See also
- 6 External links
- 7 Bibliography
- 7.1 Current
- 7.2 History
- 7.2.1 Surveys
- 7.2.2 Geography, region, housing
- 7.2.3 Pre 1871
- 7.2.4 Politics
- 7.2.5 Crime, law and disaster
- 7.2.6 Labor
- 7.2.7 Business and economics
- 7.2.8 Environment
- 7.2.9 High culture, architecture, science
- 7.2.10 Black Chicago
- 7.2.11 Social, religious, and ethnic
- 7.2.12 Sports, entertainment, music, newspapers
- 7.2.13 Reputation, images, visions, planning
- 7.2.14 Primary sources
- 7.2.15 Notes
- 8 References
Demography[edit]
Although originally settled by Yankees, the railroads, stockyards, and other heavy industry of the late 19th century attracted a variety of skilled workers from Europe, especially Germans, English, Swedish and Dutch, as well as unskilled Irish Catholics. From 1890 to 1914 migrations swelled, attracting especially unskilled workers from Eastern and Southern Europe, including Poles, Lithuanians, Croatians, Czechs, Greeks, Italians and Jews among others. World War I cut off immigrations from Europe, and restrictions in the 1920s slowed the European influx to a trickle, apart from refugees after World War II. During both world wars poor Americans arrived from the South—whites from Appalachia and blacks from the cotton fields due south. The near south side was the first Black area, and it continued to expand, as did the black neighborhoods on the near west side. These were segregated areas (few blacks were tolerated in white neighborhoods), and after 1950 public housing high rises anchored poor black neighborhoods south and west of the Loop.
Old stock Americans who relocated to Chicago after 1900 preferred the outlying areas and suburbs, making Oak Park and Evanston enclaves of the upper middle class. The lakefront north of the Loop saw construction of high-rise luxury apartments starting in the 1910s, and continuing into the 21st century. The high-rises had wealthy residents but few children, since the city had an abysmal public school system, a large parochial system of middling quality for the Catholics, and few upscale private schools. The northern and western suburbs boasted some of the best public schools in the nation. The suburban trend accelerated after 1945, with middle class Chicagoans headed to the outlying areas of the city, and then pouring into the Cook County and Dupage County suburbs. Jews and Irish in particular rose sharply in status, leaving slums and heading north. Well educated migrants from around the country moved to the far suburbs.
Beginning in the 1940s waves of Latino (or "Hispanic") immigrants began to arrive, with the largest numbers from Mexico and Puerto Rico, as well as Cuba and (by the 1980s), other Hispanic lands. After 1965 large numbers of Asian immigrants came, the largest proportion were well educated Indians and Chinese. By the 1970s gentrification began, turning old inner city slums into upscale neighborhoods, which proved attractive to singles and gays.
Geography[edit]
Loop[edit]
The "Loop" was named in 1901 when the new elevated rail line (the "L") looped around the main downtown business section. It remains a world class locus for banking, finance, law, business and high culture. It has numerous colleges and universities and a large upscale population in condominiums. The main department and specialty stores, however, have moved a mile or two north to the "Miracle Mile" (North Michigan Avenue).
Neighborhoods[edit]
Chicagoans define themselves by neighborhood (or for Catholics, by their parish).
Home ownership[edit]
Concentrating the family resources to achieve home ownerships was a common strategy in the ethnic neighborhoods. It meant sacrificing current consumption, and pulling children out of school as soon as they could earn a wage. By 1900 working-class ethnics immigrants owned homes at higher rates than native-born people. After borrowing from friends and building associations, immigrants kept boarders, grew market gardens, and even opened home-based commercial laundries, eroding home-work distinctions while sending out women and children to work to repay loans. They sought not middle class upward mobility but the security of home ownership. Many social workers wanted them to pursue upward job mobility (which required more education), but realtors asserted that houses were better than a bank for a poor man. With hindsight, and considering uninsured banks' precariousness, this appears to have been true. Chicago's workers made immense sacrifices for home ownership, contributing to Chicago's sprawling suburban geography and to modern myths about the American dream. The Jewish community, by contrast, rented apartments and maximized education and upward mobility for the next generation.[8]
Suburbs[edit]
Keating (2004) studied the origins of 233 settlements that by 1900 had become suburbs or city neighborhoods of Chicago. The settlements began as farm centers (41%), industrial towns (30%), residential railroad suburbs (15%), and recreational/institutional centers (13%).
Environment and planning[edit]
Danish immigrant Jens Jensen arrived in 1886 and soon became a highly successful and celebrated landscape designer. Jensen's work was characterized by a democratic approach to landscaping, informed by his interest in social justice and conservationism and his rejection of antidemocratic formalism. Among Jensen's creations were four Chicago city parks, most famously Columbus Park. His work also included garden design for some of the region's most influential people, including the Ford and Rosenwald families. The Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal was first proposed in 1885 by civil engineer Lyman Edgar Cooley, who envisioned a deep waterway that would dilute and divert the city's sewage by funneling water from Lake Michigan into a canal, which would drain into the Mississippi River via the Illinois River. Beyond presenting a solution for Chicago's sewage problem, Cooley's proposal appealed to the economic need to link the Midwest with America's central waterways to compete with East Coast shipping and railroad industries. Strong regional support for the project led the Illinois legislature to circumvent the federal government and complete the canal with state funding. The opening in January 1900 met with controversy and a lawsuit against Chicago's appropriation of water from Lake Michigan. By the 1920s the lawsuit was divided between the states of the Mississippi River Valley, who supported the development of deep waterways linking the Great Lakes with the Mississippi, and the Great Lakes states, who feared sinking water levels might harm shipping in the lakes. In 1929 the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in support of Chicago's use of the canal to promote commerce, but ordered the city to discontinue its use for sewage disposal.[9]
One of the largest municipal public works projects in US history lies inconspicuously 150 to 300 feet below the streets of Chicago, a city plagued from its inception by pollution and flooding related to Lake Michigan's basin. Engineering techniques pioneered specifically for the project have created mammoth overflow sewers commonly known as the Deep Tunnel and more officially as the Tunnel and Reservoir Plan (TARP). Construction began in 1976 after nearly fifty years of financial, engineering, and political maneuvering by local, state, and federal officials. While the project's long-promised rewards were materializing as of 2001, critics asserted that the city approached the problem of flood overflow in its usual grandiose manner, employing large-scale solutions when simpler, less-costly alternatives to TARP, such as curbing wasteful water use and creating green belts, should have been explored.[10]
Museums[edit]
The Chicago Historical Society has probably the finest local history collection in the world, with an equally strong library to support research.[11] Following his 1924 retirement as chairman of the board of Sears, Roebuck & Company, Julius Rosenwald embarked on a campaign to found a science and industry museum in Chicago similar to the Deutsches Museum in Munich, Germany, which he had visited in 1911. Although a city bond issue provided some funds, Rosenwald and his estate spent over $11 million through the mid-1940s. Portions of the Museum of Science and Industry opened in 1933, one year after Rosenwald's death, and the entire museum opened in 1938.[12]
History[edit]
Chicago's locational advantage is the link between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River system. Its first permanent resident, Jean Baptiste Point du Sable, a Frenchman West Indian and African descent, and operated an fur-trading 1780–1800. The U.S. government erected Fort Dearborn in 1803 three years later. In the War of 1812 it was captured by Indians and the residents massacred. After 1830 the rich farmlands of Northern Illinois attracted Yankee settlers. Yankee real estate operators created a city overnight in the 1830s. Hundreds of wagons a day of farm produce arrived, so the entrepreneurs built grain elevators and docks to load ships bound for points east. By the 1850s the railroads made Chicago a major hub with over 30 lines. The main lines from the East ended in Chicago, and those oriented to the West began in Chicago, so the city became the nation's trans-shipment and warehousing center by 1860. Factories were created, most famously the harvester factory opened in 1847 by Cyrus Hall McCormick. The Wisconsin forests supported the mill-work and lumber business; the Illinois hinterland provided the wheat, as well as hogs and cattle that were slaughtered, preserved in salt and shipped east; by 1870 refrigerated cars allowed fresh meat to ship.
As the city grew large numbers of Irish Catholics and Germans arrived. Their saloons became the focus of attacks by the Know-Nothing Party, which was anti-immigration and anti-liquor, and called for the purification of politics by reducing the power of the saloon-keepers. In 1855, the new party elected Levi Boone mayor and he banned Sunday sales of liquor and beer, angering the Germans who frequented beer gardens, and Irish who frequented saloons. Law enforcement resulted in the Lager Beer Riot of April 1855, which erupted outside a courthouse where eight Germans were being tried for liquor ordinance violations. After the Civil War, saloons became community centers only for local ethnic men, as reformers saw them as places that incited riotous behavior and moral decay.
Newspapers[edit]
Late-19th century big city newspapers such as the Chicago Daily News - founded in 1875 by Melville E. Stone - ushered in an era of news reporting that was, unlike earlier periods, in tune with the particulars of community life in specific cities. Vigorous competition between older and newer-style city papers soon broke out, centered on civic activism and sensationalist reporting of urban political issues and the numerous problems associated with rapid urban growth. In Chicago competition was especially fierce between the Chicago Times (Democratic), the Chicago Tribune, (Republican) and the Daily News (independent), with the latter becoming the city's most popular paper by the 1880s.[13]
1900-1945[edit]
Business[edit]
Samuel Insull (1859 – 1938), born poor in England, built a great electrical empire in the city (notably "Commonwealth Edison", a giant utility formed in 1907[14]) and electrified much of the Midwest, 1910–1929. His empire collapsed in the Great Depression, for which he was blamed and put on trial by the New Deal; he was acquitted.
Chicago, along with New York, was the center of the nation's advertising industry. Albert Lasker (1880-1952), known as the "father of modern advertising" made Chicago his base 1898–1942. As head of Lord and Thomas, Lasker devised a copywriting technique that appealed directly to the psychology of the consumer. Women seldom smoked cigarettes; he told them if they smoked Lucky Strikes they could stay slender. Lasker's use of radio, particularly with his campaigns for Palmolive soap, Pepsodent toothpaste, Kotex products, and Lucky Strike cigarettes, not only revolutionized the advertising industry but also significantly changed popular culture.
Labor[edit]
After 1900 Chicago was a heavily unionized city, apart from the factories (which were non-union until the 1930s). The unionized teamsters in Chicago enjoyed an unusually strong bargaining position when they contended with employers around the city. Their wagons could easily be positioned to disrupt streetcars and block traffic. In addition, their families and neighborhood supporters often surrounded the wagons of nonunion teamsters and made strikebreaking a very unpleasant endeavor. When the teamsters used their clout to engage in sympathy strikes, employers decided to coordinate their antiunion efforts, claiming that the teamsters held tyrannical power over commerce in their control of the streets. The teamsters' strike in 1905 represented a clash both over labor issues and the public nature of the streets. To the employers the streets were arteries for commerce, while to the teamsters they remained public spaces integral to their neighborhoods.[15]
Disasters[edit]
On 7 December 1903 the "absolutely fireproof," five-week-old Iroquois Theater was destroyed by fire in Chicago. The fire lasted less than thirty minutes; however, 602 people died as a result of being burned, asphyxiated, or trampled.[16]
The cruise ship Eastland capsized at its pier on a calm day, July 24, 1915, killing over 800 passengers. It was top-heavy because of new federal laws (passed in response to the Titanic) requiring lifeboats.[17]
A major environmental disaster came in July 1995, with 739 heat-related deaths after one week of record high heat and humidity.[18]
Crime[edit]
By 1900, Progressive Era political and legal reformers initiated far-ranging changes in the American criminal justice system, with Chicago taking the lead. Violent crime rates were high yet law enforcers rarely convicted killers, more than three-fourths of whom went unpunished. Even in homicide cases in which the identity of killers was certain and the police made arrests, jurors typically exonerated or acquitted killers. A blend of gender-, race-, and class-based notions of justice trumped the rule of law, producing low homicide conviction rates during a period of soaring violence.[19]
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, rates of domestic murder tripled in Chicago. Domestic homicide was often a manifestation of strains in gender relations induced by urban and industrial change. At the core of such family murders were male attempts to preserve masculine authority. Yet, there were nuances in the motives for the murder of family members, and study of the patterns of domestic homicide among ethnic groups reveals basic cultural differences. German immigrants tended to murder over declining status and the failure to achieve economic prosperity. In addition, they were likely to kill all members of the family and then commit suicide in the ultimate attempt at maintaining control. Italian men killed family members to save a gender-based ideal of respectability that entailed patriarchal control over women and family reputation. African Americans, like the Germans, often murdered in response to economic conditions but not over desperation about the future. Like the Italians, the killers tended to be young, but family honor was not usually at stake. Instead, black men murdered to regain control of wives and lovers who resisted their patriarchal "rights."[20]
Progressive reformers in the business community created the Chicago Crime Commission (CCC) in 1919 after an investigation into the robbery at a factory showed the city's criminal justice system was deficient. The CCC initially served as a watchdog of the justice system. However, after a suggestion that the justice system begin collecting criminal records was rejected, the CCC assumed a more active role in fighting crime. The commission's role expanded even further after Frank J. Loesch became president in 1928. Loesch recognized the need to eliminate the glamour that Chicago's media typically attributed to criminals. Determined to expose the horrors and violence of the crime world, Loesch drafted a list of public enemies and turned Al Capone into a scapegoat for society's evils.[21]
Black migration[edit]
Chicago's black population swelled dramatically during World War I as immigration from Europe was impossible and factories demanded more and more war workers. Whites got the factory jobs, but many opportunities opened for black men and women. Economic conditions for the city's blacks during the 1920s were much better than in the South, but were also characterized by chronic unemployment and low wage rates. Many families living below the poverty line. These conditions were caused primarily by employers' discriminatory hiring and promotion policies, a surplus of labor at a time of continued black migration from the South, and residential segregation in the African American neighborhoods of Chicago. Consequently, the economic conditions that brought about political radicalization and realignment of African Americans during the 1930s, and which are associated primarily with the Great Depression, were in evidence throughout much of the 1920s. Accordingly, the Great Migration of the 1910s and 1920s, rather than being seen largely as a phenomenon associated with World War I, takes on greater significance in terms of its economic and political repercussions in black Chicago in the years before the depression.[22]
Polonia[edit]
Chicago's Polonia sustained diverse political cultures, each with its own newspaper. In 1920 the community had a choice of five daily papers - from the Socialist Dziennik Ludowy [People's daily] (1907–25) to the Polish Roman Catholic Union's Dziennik Zjednoczenia [Union daily] (1921–39) - all of which supported workers' struggles for better working conditions and were part of a broader program of cultural and educational activities. The decision to subscribe to a particular paper reaffirmed a particular ideology or institutional network based on ethnicity and class, which lent itself to different alliances and different strategies.[23]
Great Depression[edit]
Since 1940[edit]
Politics[edit]
Many recent mayors of Chicago belonged to the Democratic Party. The current mayor of Chicago is Lori Elaine Lightfoot. She is preceded by Rahm Emanuel. Before him, Richard M. Daley (b. 1942), who was elected in 1989, was mayor until 2011. His father, Richard J. Daley (1902-1976), was mayor from 1955 to 1976, and controlled the powerful Cook County Democratic organization, called "the machine." [24] Current President Barack Obama spent his politically formative years as a city planner "foot soldier" for the Democratic machine, an experience that deeply affected his political methods and radical beliefs later in life.
The city hosted the 1968 Democratic National Convention when Richard J. Daley was mayor. The convention was disrupted by radicals such as Abbie Hoffman.
Holli (1999) argues that the political regime of Chicago Mayor Richard J. Daley during 1955-76 was unusually stable during an era of national instability because Daley kept firm control of the governmental machinery, which slowed change to a manageable pace and had a deep and profound appeal to Chicagoans. Ethnic and racial squabbling erupted after Daley's death in 1976 and continued through the tenures of four mayors, even as the rest of the nation entered a period of greater political stability. After the transitory tenure of interim mayor Eugene Sawyer, the years of political instability ended with the 1989 election of the former boss's son, Richard M. Daley. Young Daley's election marked a return to political calm seen, in the light of equilibrium theory, as inevitable after the tumultuous years that preceded it.[25]
Public housing[edit]
The Robert Taylor Homes (RTH), part of Chicago's public housing projects financed by the federal government, opened in 1962. As the largest US public housing project, RTH consisted of 28 high-rises of 16 floors each, providing homes for 27,000 people. By 1965, RTH was already substandard and crime-ridden. Through the 1970s, RTH became predominantly single-mother welfare households. During site selection, the size of the project kept increasing. Federal cost worries forced the use of the high-rise design. Minors so outnumbered adults at RTH from the beginning that gangs, vandalism, and other crimes quickly became endemic. RTH was too large to administer effectively. Substandard systems, including elevators, plumbing, and heating, insufficient police protection, and the demographic burden on local schools were instrumental in RTH's failure.[26]
Japanese[edit]
In 1942-43 60,000 Nisei (born in U.S. of Japanese parents) were removed from the West Coast relocation camps and resettled in distant cities. 20,000 came to Chicago. In contrast to their self-contained, West-coast lifestyle, the Nisei in Chicago attempted to more fully integrate themselves in the community. This permitted many to take advantage of their racial "inbetweenness" to fill labor shortages caused by the war. Nisei used this "twilight zone" status between blacks and whites to distance themselves from blacks, frequently adopting the language of racial prejudice to heighten distinctions. Most Nisei successfully shed their ethnic identity in Chicago, amalgamated into the white community and stayed in the city.[27]
Hispanic immigrants[edit]
Fernandez (2005) documents the history of Mexican and Puerto Rican immigration and community formation in Chicago after World War II. Beginning with World War II, Mexican and Puerto Rican workers traveled to the Midwest through varying migrant streams to perform unskilled labor. They settled in separate areas of Chicago. These parallel migrations created historically unique communities where both groups encountered one another in the mid-twentieth century. By the 1950s and 1960s, both groups experienced repeated displacements and dislocations from the Near West Side, the Near North Side and the Lincoln Park neighborhood. At the macro level, Mexican and Puerto Rican workers' life chances were shaped by federal policies regarding immigration, labor, and citizenship. At the local level, they felt the impact of municipal government policies, which had specific racial dimensions. As these populations relocated from one neighborhood to the next, they made efforts to shape their own communities and their futures. During the period of the Civil Rights Movement, Mexicans and Puerto Ricans engaged in social struggles, both in coalition with one another but also as separate, distinct, national minorities. They created organizations and institutions such as Casa Aztlán, the Young Lords Organization, Mujeres Latinas en Acción, the Latin American Defense Organization, and El Centro de la Causa. These organizations drew upon differing strategies based on notions of nation, gender, and class, and at times produced inter-ethnic and inter-racial coalitions.[28]
2020 Antifa riots[edit]

- See also: 2020 Antifa riots
In 2018, Chicago recorded 561 murders, more than the two biggest US cities - New York and Los Angeles - combined.
On May 31, 2020, Chicago saw its deadliest day in at least 60 years (records only go back to 1961), with 18 killings in a 24-hour period. Over the Memorial Day holiday - 85 people were shot and 24 killed, according to the University of Chicago Crime Lab.[30] Mayor Lori Lightfoot said that day the city's 911 emergency call centre received 65,000 calls - 50,000 more than on an average day. White rioters assaulted a police woman.[31] Mayor Lori Lightfoot acknowledged “an organized effort”. Chicago Business reported Lightfoot as saying,
| “There is no doubt. This was an organized effort last night,” she said. “There were clearly efforts to subvert the peaceful process and make it into something violent.”[32] |
A racist black woman objected to Arabs defending their property with AK-47s "if we decided to loot it".[33] An Alderman asked Lightfoot, “Once they’re done looting and rioting, and whatever’s going to happen tonight, God help us, what happens when they start going after residents? Going into the neighborhoods? Once they start trying to break down people’s doors if they think they’ve got something," noting that there were “gang-bangers with AK-47s walking around right now, just waiting to settle some scores." When Lightfoot did not respond the Alderman added, “It’s not something you ignore. This is a question that I have.” The mayor responded, “I think you’re 100% full of sh**, is what I think.” The Alderman shot back, “No offense — F*** you, then. Who are you to tell me I’m full of sh**? Maybe you should come out and see what’s going on.”[34] The call was recorded. One alderman could be heard weeping while others angrily decried what was going on in the city. “My ward is a sh** show,” one alderman says. “They are shooting at the police.”[35] President Trump offered assistance to Gov. Pritzker and Mayor Lightfoot in dealing with the systemic racism that has plagued Democrat-run Chicago for decades:
"I recently read an article from the Chicago Sun-Times on June 8, 2020, “18 murders in 24 hours: Inside the most violent day in 60 years in Chicago,” which discussed the severe crime and lack of law and order in our Nation’s third largest city. The article details how “85 people were shot and 24 killed the previous weekend, the most in modern history in Chicago.” Your lack of leadership on this important issue continues to fail the people you have sworn to protect. I am concerned it is another example of your lack of commitment to the vulnerable citizens who are victims of this violence and a lack of respect for the men and women in law enforcement. ...Violence and death, which are disproportionately harming young African Americans, are tragic and unacceptable, particularly on such a shocking scale. According to the Chicago Sun Times, “shootings across the City increased by 71 percent last month,” and just this past weekend 102 people were shot in the city’s most violent weekend of the year. A 3-year old toddler was killed. More Americans have been killed in Chicago than in combat zones of Afghanistan and Iraq combined since September 11, 2001, a deadly trend that has continued under your tenure....
Unlike previous Administrations of both parties, I am willing to tackle unsolved challenges. If you are willing to put partisanship aside, we can revitalize distressed neighborhoods in Chicago, together. But to succeed, you must establish law and order. The combination of crime, high State and local taxes, and onerous State and local government regulations have caused thousands of Illinoisans to flee to other States. Between 2010 and 2019, Illinois lost more of its population than any other state in the Nation. If you are interested, I am willing to ask members of my Cabinet to meet with you and help devise a plan to make Chicago safe, since a successful formula has escaped both you and your predecessors. My Administration would also welcome the opportunity to engage with you and your colleagues as you develop bipartisan policy recommendations to improve policing and make our great cities safer for all."[36]
On July 17, 2020, BLM and Antifa rioters assaulted police with bricks, rocks, sticks, bottles, and fireworks. The police, most of whom had no helmets, were defending a monument.[37]
Dozens of Antifa and Black Lives Matter rioters attempted to pull down a statue of Christopher Columbus at Grant Park in Chicago and viciously attacked police officers who attempted to defend the statue by using various projectiles and fireworks against the officers, but the rioters soon paid for their criminal actions when police reinforcements arrived and, with that backup, the police turned the tables and beat down the punks with batons and pepper-sprayed them.[38] Several of the hoodlums were arrested while the other punks, showing themselves as the cowardly crybullies they are, ran away when the tide turned against them.
In the month of July 2020 alone there were 105 homicides in Chicago compared to 44 the previous July.[39]
Lightfoot era[edit]
In May 2021 Chicago NBC5 reported mayor Lori Lightfoot refused to do interviews with white people.[40] The report was confirmed by Chicago PBS station WTTW.[41] The formal announcement said Lightfoot would only grant interviews to "Black and brown" reports. Lightfoot complained bitterly about the "whiteness and maleness" of Chicago's liberal media which had only aided in her election.[42] Chicago Tribune reporter Gregory Pratt, a Latino was granted an interview and asked the mayor's office to lift its exclusion others. When the mayor's office refused, Pratt protested the racist policy and canceled the interview. A Chicago WGN anchor and a Washington Post reporter supported the Tribune's action and called on all reporters to boycott the mayor's office racist policies.[43] The National Association of Black Journalists issued a statement: "that NABJ’s history of advocacy does not support excluding any bona fide journalists from one-on-one interviews with newsmakers, even if it is for one day and in support of activism...We have members from all races and backgrounds and diversity, equity and inclusion must be universal."[44] Former Rep. Tulsi Gabbard who excoriated Hillary Clinton as "the personification of the rot that has sickened the Democratic party", called upon Lightfoot to resign. "I call upon President Biden, Kamala Harris, and other leaders of our county—of all races—to join me in calling for Mayor Lightfoot's resignation.[45]
With the Defund the Police movement, black people have been the victims of roughly 81 percent of the 317 murders in the first six months of 2021, virtually all black-on-black crime. They were the victims of about 70 percent of the 295 murders committed in the first six months of 2020.[46]
Billionaire hedge fund manager Ken Griffin of Citidel LLC said "Chicago is like Afghanistan on a good day."[47]
Biden Putsch[edit]
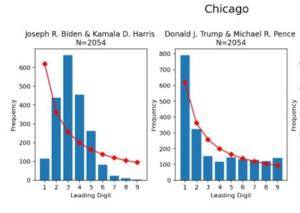
- See also: Democrat voter fraud and Biden Putsch
Former Illinois governor Rod Blagojevich explained that there is no question that voter fraud was happening in Chicago, Philadelphia, Milwaukee, Detroit, and other cities.
| “In big cities where they control the political apparatus and they control the apparatus that counts the votes, and they control the polling places and the ones who count the votes, it’s widespread and it’s deep.”[49] |
Schools[edit]
Benjamin C. Willis was superintendent of the Chicago Public Schools (1953 - 1966). During his tenure, the public schools in Chicago, as in many large cities, declined in terms of both the quality of the education they provided and the quantity of resources they received. Willis saw educational leadership as the work of professionals, not of community activists or political leaders. This outlook isolated his administration and undermined his influence. In the 1970s, efforts to desegregate schools through busing led to an exodus of whites from the city.[50]
As a politician and as Chicago's black mayor (1983–87), Harold Washington maintained a distinctive strategy toward reform of public schools.[51] Rather than focus on integration (bringing whites and minorities into the same schools), Washington favored measures to strengthen local schools, especially in minority neighborhoods. He called for more state support to urban schools in place of property taxes and more power to local groups to influence curriculum and the quality of teaching. In 1987 the teacher strike transformed educational problems into a crisis. Washington created the Parent Community Council from local groups and arranged for a summit with their representatives and those of business, school administration, and teachers. His death in 1987 unraveled the deliberations for change that had been taking place. The schoold were so beset by violence, teacher shortages and inadequate financing that few Few disagreed with the brutal verdict of U.S. Secretary of Education William Bennett in 1987, "Chicago's public schools are the worst in the nation." In the late 1990s, the realization that busing had become unrealistic caused Chicago's political leaders and community activists to join together in focusing attention and resources on improving neighborhood schools. Mayor Richard M. Daley seized control of the school system in 1995 and promised drastic reforms. However, the legislature largely left in place elected councils made up of parents and community members at each of the district's nearly 600 schools. At struggling schools on probation, Daley has stripped councils of power, but at others the councils hire principals and oversee a significant portion of each school's budget. Paul G. Vallas, a blunt-talking, bottom-line-driven manager led the system from 1995 to 2001. Vallas presided over a $3 billion construction effort that built 71 schools and renovated 500. He cut 2,000 nonteaching positions and stabilized the district's finances. Given broad executive authority, Vallas ended automatic promotion from grade to grade and greatly expanded summer school, policies that have been copied across the country. Math and reading scores improved, with about 40% of students at grade level in 2001, up from 30% in 1995.[52] In 2001 Daley appointed Arne Duncan, 36, to preside over a school system with 435,000 students, 45,900 employees and a $3.5-billion annual budget. In 2009 Duncan, hailed for his work in Chicago, became Secretary of Education for the Obama Administration.
Reputation[edit]
Journalists, novelists and poets shaped Chicago's national and international reputation. Images and representations are important means by which the city is known and negotiated. During the years of rapid urbanization 1890-1930 the numerous daily newspapers presented the most important and pervasive word versions of the city. Among the significant innovations of Chicago's newspapers in these years that shaped the idea of the city was the emergence of the local color columnist. Groeninger (2005) examines the role of columnists in Chicago newspapers in creating a "city of the mind." After a review of the literature on images of cities, the relationship of newspapers to modern city life in the thought of Robert Park, and the world of Chicago's newspapers at the turn-of-the-century, detailed studies of a number of the most important columnists of the era follow. George Ade's column of the 1890s in the Daily News, "Stories of the Streets and of the Town," presented a view of Chicago from the perspective of migrants from the small towns of the Midwest. In the same decade Finley Peter Dunne's column in the Evening Post, featuring the fictional Irish barkeeper, Mr. Dooley, offered readers a literary version of the Irish working-class neighborhood of Bridgeport. Ring Lardner's Tribune sports column of the teens, "In the Wake of the News," satirized not only Chicagoans obsession with sports, but also the middle-class culture of opera, musical theater, and the newspaper itself. Several columns in the black newspaper, The Whip, offered images of Bronzeville in the 1920s that both reflected and helped shape the experience of African-Americans on the South Side of Chicago. Ben Hecht's "1001 Afternoons in Chicago" column in the Daily News expressed a new, anti-Victorian sensibility in the post-war era, but his most enduring contributions to the image of Chicago were on the stage and in the new medium of film. The columnists who wrote about everyday life in the city were the most distinctive and powerful newspaper voices in shaping the idea of Chicago and the civic personality of the city itself.[53] Often referred to as the "Windy City", many people mistake that saying for the weather. It actually refers to the chatter of deal-making among Chicago politicians, the wind being talk. Chicago was the United States' bid city for the 2016 Olympics, which ultimately were awarded to Rio de Janeiro.
The city was also rather notorious for several dirty elements in politics, including a quote attributed to Richard J. Daley called "Vote early, vote often", alluding to stuffing the ballot box to ensure a win in an election cycle, as well as a joke on how Chicago was the place where "people come back from the grave to vote", in reference to ghost voters, which is a variant of ballot box stuffing which included names of people who had in fact died before the election.
See also[edit]
- Art cities
- Chicago School of Economics
- Hull House
- Jane Addams
- Gun control—Chicago, along with San Francisco, Washington D.C., New York City and Los Angeles, is known to be one of the 5 top American cities with the most left-wing Anti-Second Amendment laws. See "Vote with your feet" strategic relocation to free states with low population density
External links[edit]
- The Field Museum
- National Museum of Mexican Art
- City of Chicago - Tourism
- summary of 2000 census for city
- Kenneth M. Johnson, "Demographic Trends in the Chicago Metropolitan Area" (2006)
Bibliography[edit]
the best source to study all aspects of Chicago is James R. Grossman, Ann Durkin Keating, and Janice L. Reiff, eds.. The Encyclopedia of Chicago University of Chicago Press, (2005) ISBN 0-226-31015-9; (online version)
- Szucs, Loretto Dennis. Chicago and Cook County: A Guide to Research (1996), 517pp; bibliographies for genealogy and local history excerpt and text search
Current[edit]
- Frommer's Chicago 2007 (2006) excerpt and text search
History[edit]
- The Encyclopedia of Chicago (2005) (online version), the place to start
Surveys[edit]
- Longstreet, Stephen. Chicago: An Intimate Portrait of People, Pleasures, and Power, 1860-1919. (1973). 547 pp. popular
- Miller, Donald L. City of the Century: The Epic of Chicago and the Making of America (1997), popular epic; excerpt and text search
- Pierce, Bessie Louise. A History of Chicago, Volume I: The Beginning of a City 1673-1848 (1937; reprint 2007); Volume II: From Town to City 1848-1871 (reprint 2007); Volume III: The Rise of a Modern City, 1871-1893 (reprint 2007)
- Spinney, Robert G. City of Big Shoulders: A History of Chicago (2000), popular epic; excerpt and text search
Geography, region, housing[edit]
- Barrett, Paul. The Automobile and Urban Transit: The Formation of Public Policy in Chicago, 1900-1930. (1983). 295 pp.
- Betancur, John J. "The Settlement Experience of Latinos in Chicago: Segregation, Speculation, and the Ecology Model." Social Forces 1996 74(4): 1299–1324. Issn: 0037-7732 Fulltext: Jstor
- Bigott, Joseph C. From Cottage to Bungalow: Houses and the Working Classes in Metropolitan Chicago, 1869-1929 (2001) excerpt and text search
- Bronsky, Eric, Neal Samors and Jennifer Samors. Downtown Chicago in Transition (2007) excerpt and text search
- Cronon, William. Nature's Metropolis: Chicago and the Great West. (1991). 530 pp. excerpt and text search
- Garb, Margaret. City of American Dreams: A History of Home Ownership and Housing Reform in Chicago, 1871-1919. (2005). 261 pp.
- Keating, Ann Durkin. Building Chicago: Suburban Developers and the Creation of a Divided Metropolis. (1988). 230 pp.
- Keating, Ann Durkin. "Chicagoland: More than the Sum of its Parts." Journal of Urban History 2004 30(2): 213–230. Issn: 0096-1442 Fulltext: Ebsco
- Mayer, Harold M., and Richard C. Wade. Chicago: Growth of a Metropolis (1969) 510pp
- Pacyga, Dominic A. and Skerrett, Ellen. Chicago: City of Neighborhoods. Histories and Tours. (1986). 582 pp.
- Randall, Gregory C. America's Original G.I. Town: Park Forest, Illinois. 2000. 236 pp.
- Venkatesh, Sudhir Alladi. American Project: The Rise and Fall of a Modern Ghetto, (2002), 360pp, on Robert Taylor Homes, a high rise public housing project with a negative reputation excerpt and text search
- WPA. Illinois: A Descriptive and Historical Guide (1939)
Pre 1871[edit]
- Fehrenbacher, Don E. Chicago Giant: A Biography of "Long John" Wentworth. (1957). 278 pp. online edition
- Karamanski, Theodore J. Rally 'Round the Flag: Chicago and the Civil War. (1993). 292 pp.
- Pierce, Bessie Louise. A History of Chicago, Volume I: The Beginning of a City 1673-1848 (1937; reprint 2007); Volume II: From Town to City 1848-1871 (reprint 2007)
- Quaife, Milo Milton. Chicago and the Old Northwest, 1673-1835. (1913, reprint 2001). 480 pp.
Politics[edit]
- Allswang, John. A House For All Peoples: Ethnic Politics In Chicago, 1890-1936. (1973). 213 pp.
- Barnard, Harry. "Eagle Forgotten": The Life of John Peter Altgeld (1938)
- Beito, David T. Taxpayers in Revolt: Tax Resistance during the Great Depression. (1989). 216 pp.
- Biles, Roger. Richard J. Daley: Politics, Race, and the Governing of Chicago. (1995). 292 pp.
- Biles, Roger. Big City Boss in Depression and War: Mayor Edward J. Kelly of Chicago. (1984). 219 pp.
- Bukowski, Douglas. Big Bill Thompson, Chicago, and the Politics of Image. (1998). 273 pp. excerpt and text search
- Cohen, Adam, and Elizabeth Taylor. American Pharaoh: Mayor Richard J. Daley - His Battle for Chicago and the Nation. (2001). 614pp ISBN 0-316-83489-0 excerpt and text search
- Flanagan, Maureen A. Charter Reform in Chicago. (1987). 207 pp.
- Fuchs, Ester R. Mayors and Money: Fiscal Policy in New York and Chicago. (1992). 361 pp.
- Green, Paul M. and Holli, Melvin G., eds. The Mayors: The Chicago Political Tradition (1995) online edition
- Green, Paul M. and Holli, Melvin G., eds. Restoration 1989: Chicago Elects a New Daley. (1991). 212 pp.
- Gosnell, Harold F. Machine Politics: Chicago Model (1937), classic statistical study online edition
- Guterbock, Thomas M. Machine Politics in Transition: Party and Community in Chicago. (1980). 324 pp.
- Hartley, Robert E. Big Jim Thompson of Illinois (1979), governor 1980s
- Hogan, David John. Class and Reform: School and Society in Chicago, 1880-1930. (1985). 328 pp.
- Kantowicz, Edward R. Polish-American Politics in Chicago, 1888-1940. (1975). 260 pp.
- Kleppner, Paul. Chicago Divided: The Making of a Black Mayor. (1985). 313 pp.
- Littlewood, Thomas B. Horner of Illinois (1969), governor 1933-40
- Merriam, Charles Edward. Chicago: A More Intimate View of Urban Politics (1929) online edition
- Miller, Kristie. Ruth Hanna Mccormick: A Life in Politics, 1880-1944 (1992)
- Morton, Richard Allen. Justice and Humanity: Edward F. Dunne, Illinois Progressive (1997), 174pp Democrfatic mayor 1905-7 and governor 1913–17.
- Peterson, Paul E. The Politics of School Reform, 1870-1940. (1985). 241 pp.
- Pinderhughes, Dianne M. Race and Ethnicity in Chicago Politics: A Reexamination of Pluralist Theory. (1987). 318 pp.
- Rivlin, Gary. Fire on the Prairie: Chicago's Harold Washington and the Politics of Race. (1992). 426 pp.
- Schmidt, John R. "The Mayor Who Cleaned Up Chicago": A Political Biography of William E. Dever. (1989). 239 pp.
- Schneirov, Richard. Labor and Urban Politics: Class Conflict and the Origins of Modern Liberalism in Chicago, 1864-97. (1998). 390 pp. excerpt and text search
- Simpson, Dick. Rogues, Rebels, and Rubber Stamps: The Politics of the Chicago City Council from 1863 to the Present (2001) 356pp online edition
- Smith, Joan K. Ella Flagg Young: Portrait of a Leader. (1979). 272 pp.
- Tarr, Joel Arthur. A Study in Boss Politics: William Lorimer of Chicago. (1971). 376 pp. online edition
- Wendt, Lloyd, Herman Kogan, and Bette Jore. Big Bill of Chicago. (2005) ISBN 0-8101-2319-3, popular vio of mayor in 1920s
Crime, law and disaster[edit]
- Adler, Jeffrey S. First in Violence, Deepest in Dirt: Homicide in Chicago, 1875-1920. (2006). 357 pp. excerpt and text search
- Adler, Jeffrey S. "'We've Got a Right to Fight; We're Married': Domestic Homicide in Chicago, 1875-1920." Journal of Interdisciplinary History 2003 34(1): 27–48. Issn: 0022-1953 Fulltext: Project Muse
- Avrich, Paul. The Haymarket Tragedy (1984) excerpt and text search
- Bales, Richard F. The Great Chicago Fire and the Myth of Mrs. O'Leary's Cow. (2002). 338 pp.
- Hilton, George W. Eastland: Legacy of the Titanic. (1995). 364 pp. The cruise ship capsized at its pier on a calm day in 1915, killing over 800 passengers. It was topheavy because of new federal laws (passed in response to the Titanic) requiring lifboats.
- Brandt, Nat. Chicago Death Trap: The Iroquois Theatre Fire of 1903. (2003). 180 pp.
- Bruno, Robert. Reforming the Chicago Teamsters: The Story of Local 705. (2003). 203 pp.
- Cahan, Richard. A Court that Shaped America: Chicago's Federal District Court from Abe Lincoln to Abbie Hoffman. (2002). 273 pp.
- Chicago Commission on Race Relations. The Negro in Chicago: A Study of Race Relations and a Race Riot (1922) - 672 pages; full text online
- Cohen, Andrew Wender. The Racketeer's Progress: Chicago and the Struggle for the Modern American Economy, 1900-1940. (2004). 333 pp.
- Getis, Victoria. The Juvenile Court and the Progressives. (2000). 216 pp.
- Farber, David. Chicago '68. (1988). 304 pp.
- Heinz, John P. and Laumann, Edward O. Chicago Lawyers: The Social Structure of the Bar. (1983). 496 pp.
- Higdon, Hal. Leopold and Loeb: The Crime of the Century. (1975). 380 pp.
- Hoffman, Dennis E. Scarface Al and the Crime Crusaders: Chicago's Private War against Capone. (1993). 192 pp.
- Lindberg, Richard Carl. To Serve and Collect: Chicago Politics and Police Corruption from the Lager Beer Riot to the Summerdale Scandal: 1855-1960. 1991. ISBN 0-275-93415-2 online edition
- Merriner, James L. Grafters and Goo Goos: Corruption and Reform in Chicago, 1833-(2003). (2004). 302 pp. online edition
- Miller, Ross. The Great Chicago Fire (2000); 1st ed was American Apocalypse: The Great Chicago Fire and the Myth of Chicago 287 pp.
- Mumford, Kevin J. Interzones: Black/White Sex Districts in Chicago and New York in the Early Twentieth Century. (1997). 238 pp.
- Sawislak, Karen. Smoldering City: Chicagoans and the Great Fire, 1871-1874. (1995). 408 pp.
- Tuttle, William M., Jr. Race Riot: Chicago in the Red Summer of 1919. (1970). 305 pp.
- Wendt, Lloyd, and Herman Kogan. Lords of the Levee. (1967), popular stories from early 20th century.
- Willrich, Michael. City of Courts: Socializing Justice in Progressive Era Chicago. (2003). 332 pp. excerpt and text search
- Wolcott, David B. Cops and Kids: Policing Juvenile Delinquency in Urban America, 1890-1940. (2005). 264 pp.
Labor[edit]
- Bae, Youngsoo. Labor in Retreat: Class and Community among Men's Clothing Workers of Chicago, 1871-1929. (2001). 295 pp.
- Barrett, James. Work and Community in the Jungle: Chicago's Packinghouse Workers, 1894--1922 (1987), excerpt and text search
- Cohen, Lizabeth. Making a New Deal: Industrial Workers in Chicago, 1919-1939. (1990). 526 pp.
- Cummings, John. "The Chicago Teamsters’ Strike: A study in industrial democracy." Journal of Political Economy (1905) 13: 536–73. in jstor
- Fine, Lisa M. The Souls of the Skyscraper: Female Clerical Workers in Chicago, 1870-1930. (1990). 249 pp.
- Green, James. Death in the Haymarket: A Story of Chicago, the First Labor Movement and the Bombing that Divided Gilded Age America. (2006). 383 pp.
- Halpern, Rick. Down on the Killing Floor: Black and White Workers in Chicago's Packinghouses, 1904-1954. (1997). 309 pp.
- Meyerowitz, Joanne J. Women Adrift: Independent Wage Earners in Chicago, 1880-1930. (1988). 224 pp.
- Newell, Barbara Wayne. Chicago and the Labor Movement: Metropolitan Unionism in the 1930s (1961)
- Papke, David Ray. The Pullman Case: The Clash of Labor and Capital in Industrial America. (1999). 118 pp. legal aspects
- Schneirov, Richard; Stromquist, Shelton; and Salvatore, Nick, eds. The Pullman Strike and the Crisis of the 1890s: Essays on Labor and Politics. (1999). 258 pp.
- Schneirov, Richard and Suhrbur, Thomas J. Union Brotherhood, Union Town: A History of the Carpenters' Union of Chicago, 1863-1987. (1988). 211 pp.
Business and economics[edit]
- Ascoli, Peter Max. Julius Rosenwald: The Man Who Built Sears, Roebuck and Advanced the Cause of Black Education in the American South (2006) excerpt and text search
- Emmet, Boris, and John E. Jeuck. Catalogues and Counters: A History of Sears, Roebuck & Company (1965), the standard corporate history
- Ferris, William G. The Grain Traders: The Story of the Chicago Board of Trade. (1988). 221 pp.
- Franch, John. Robber Baron: The Life of Charles Tyson Yerkes. (2006). 374 pp.
- McDonald, Forrest. Insull: The Rise and Fall of a Billionaire Utility Tycoon (2004)
- Rast, Joel. Remaking Chicago: The Political Origins of Urban Industrial Change. (1999). 220 pp. redevelopment of area near downtown
- Smith, Raymond D., and William P. Darrow. "Strategic Management and Entrepreneurial Opportunity: The Rise of Sears, Inc.," Journal of Business & Entrepreneurship (1999) 11#1
- Young, David M. The Iron Horse and the Windy City: How Railroads Shaped Chicago. (2005). 270 pp. popular
- Young, David M. Chicago Aviation: An Illustrated History. (2003). 254 pp. popular
- Young, David M. Chicago Transit: An Illustrated History. (1998). 213 pp. popular
Environment[edit]
- Cain, Louis P. Sanitation Strategy for a Lakefront Metropolis: The Case of Chicago. (1978). 141 pp.
- Capano, Daniel E. "Chicago's War with Water." American Heritage of Invention & Technology 2003 18(4): 50–58. Issn: 8756-7296 full text online
- O'Connell, James C. Chicago's Quest for Pure Water. (1976).
- Pellow, David Naguib. Garbage Wars: The Struggle for Environmental Justice in Chicago. (2002). 234 pp.
- Platt, Harold L. Shock Cities: The Environmental Transformation and Reform of Manchester and Chicago. (2005). 628 pp.
- Platt, Harold L. The Electric City: Energy and the Growth of the Chicago Area, 1880-1930. (1991). 318 pp. excerpt and text search
High culture, architecture, science[edit]
- Bolotin, Norman and Laing, Christine. The World's Columbian Exposition: The Chicago World's Fair of 1893. (1992). 166 pp.
- Bonner, Thomas Neville. Medicine in Chicago, 1850-1950: A Chapter in the Social and Scientific Development of a City. ( 1957, 2d ed. 1991). 335 pp.
- Bruegmann, Robert. The Architects and the City: Holabird & Roche of Chicago, 1880-1918. (1997). 544 pp.
- Cappetti, Carla. Writing Chicago: Modernism, Ethnography, and the Novel. (1993). 274 pp.
- Christiansen, Richard. A Theater of Our Own: A History and a Memoir of 1,001 Nights in Chicago. (2004). 317 pp.
- Clarke, Jane H.; Saliga, Pauline A.; and Zukowsky, John. The Sky's the Limit: A Century of Chicago Skyscrapers. (1990). 304 pp.
- Condit, Carl W. Chicago, 1910-29: Building, Planning, and Urban Technology. (1973). 354 pp.
- Condit, Carl W. Chicago, 1930-70: Building, Planning, and Urban Technology. (1974). 351 pp.
- Garvey, Timothy J. Public Sculptor: Lorado Taft and the Beautification of Chicago. (1988). 222 pp.
- Gray, Mary Lackritz. A Guide to Chicago's Murals. (2001). 488 pp.
- Greenhouse, Wendy and Weininger, Susan. Chicago Painting 1895-1945: The Bridges Collection. (2004). 251 pp.
- Hallwas, John E. ed., Illinois Literature: The Nineteenth Century (1986)
- Harris, Neil. Chicago Apartments: A Century of Lakefront Luxury. (2004). 352 pp.
- Hines, Thomas S. Burnham of Chicago: Architect and Planner. (1974). 445 pp.
- Longstreth, Richard, ed. The Charnley House: Louis Sullivan, Frank Lloyd Wright, and the Making of Chicago's Gold Coast. (2004). 249 pp.
- Lowe, David Garrard. Lost Chicago (2000), architectural landmarks that were torn down. excerpt and text search
- McCarthy, Kathleen D. Noblesse Oblige: Charity and Cultural Philanthropy in Chicago, 1849-1929. (1982). 230 pp.
- Moudry, Roberta, ed. The American Skyscraper: Cultural Histories. (2005). 281 pp.
- Saum, Lewis O. Eugene Field and His Age. (2001). 324 pp.
- Schaffer, Kristen. Daniel H. Burnham: Visionary Architect and Planner. (2003). 223 pp.
- Siry, Joseph M. The Chicago Auditorium Building: Adler and Sullivan's Architecture and the City. (2002). 550 pp.
- Siry, Joseph. Carson Pirie Scott: Louis Sullivan and the Chicago Department Store. (1989). 290 pp.
- Waldheim, Charles and Ray, Katerina Rüedi, eds. Chicago Architecture: Histories, Revisions, Alternatives. (2005). 488 pp.
- Wright, Gwendolyn. Moralism and the Model Home: Domestic Architecture and Cultural Conflict in Chicago, 1873-1913. (1980). 382 pp.
- Zukowsky, John, ed. Chicago Architecture and Design, 1923-1993: Reconfiguration of an American Metropolis. (1993). 479 pp.
Black Chicago[edit]
- Best, Wallace D. Passionately Human, No Less Divine: Religion and Culture in Black Chicago, 1915-1952. (2005). 251 pp.
- Black, Timuel D., Jr. Bridges of Memory: Chicago's First Wave of Black Migration. (2003). 600 pp.
- Blakely, Robert J. Earl B. Dickerson: A Voice for Freedom and Equality. (2006). 270 pp.
- Chicago Commission on Race Relations. The Negro in Chicago: A Study of Race Relations and a Race Riot (1922) - 672 pages; full text online
- Drake, St. Clair, and Horace R. Cayton. Black Metropolis: A Study of Negro Life in a Northern City (4th ed. 1945), classic sociological study
- Grimshaw, William J. Bitter Fruit: Black Politics and the Chicago Machine, 1931-1991. (1992). 248 pp.
- Grossman, James R. Land of Hope: Chicago, Black Southerners, and the Great Migration. (1989). 384 pp.
- Hirsch, Arnold R. Making the Second Ghetto: Race and Housing in Chicago, 1940-60. (1983). 362 pp.
- Knupfer, Anne Meis. The Chicago Black Renaissance and Women's Activism. (2006). 244 pp.
- Lemann, Nicholas. The Promised Land: The Great Black Migration and How It Changed America. (1991). 401 pp.
- Philpott, Thomas Lee. The Slum and the Ghetto: Immigrants, Blacks, and Reformers in Chicago, 1880-1930. (1978). 437 pp.
- Pinderhughes, Dianne M. Race and Ethnicity in Chicago Politics: A Reexamination of Pluralist Theory. (1987). 318 pp.
- Reed, Christopher Robert. Black Chicago's First Century. Vol. 1: 1833-1900. (2005). 582 pp.
- Reed, Christopher Robert. The Chicago NAACP and the Rise of Black Professional Leadership, 1910-1966. (1997). 257 pp. online edition
- Rivlin, Gary. Fire on the Prairie: Chicago's Harold Washington and the Politics of Race. (1992). 426 pp.
- Spear, Allan. Black Chicago: The Making of a Negro Ghetto, 1890--1920 (1967),
- Strickland, Arvarh E. History of the Chicago Urban League. 1966, 2nd ed. (2001). 286 pp.
- Tuttle, William M., Jr. Race Riot: Chicago in the Red Summer of 1919. (1970). 305 pp.
- Venkatesh, Sudhir Alladi. American Project: The Rise and Fall of a Modern Ghetto, (2002), 360pp, on Robert Taylor Homes, a high rise public housing project with a negative reputation excerpt and text search
- Wellman, James K., Jr. The Gold Coast Church and the Ghetto: Christ and Culture in Mainline Protestantism. (1999). 241 pp.
Social, religious, and ethnic[edit]
- Anderson, Philip J. and Blanck, Dag, eds. Swedish-American Life in Chicago: Cultural and Urban Aspects of an Immigrant People, 1850-1930. (1992). 394 pp.
- Avella, Steven M. This Confident Church: Catholic Leadership and Life in Chicago, 1940-1965. (1992). 410 pp.
- Barrett, James. Work and Community in the Jungle: Chicago's Packinghouse Workers, 1894--1922 (1987), excerpt and text search
- Beijbom, Ulf. Swedes in Chicago: A Demographic and Social Study of the 1846-1880 Immigration. (1971). 381 pp
- Betancur, John J. "The Settlement Experience of Latinos in Chicago: Segregation, Speculation, and the Ecology Model." Social Forces 1996 74(4): 1299–1324. Issn: 0037-7732 Fulltext: Jstor
- Bowly Jr., Devereux The Poorhouse: Subsidized Housing in Chicago, 1895-1976 (1978) Bowly Jr.&dcontributors=Devereux+Bowly+Jr. online edition
- Candeloro, Dominic. Italians in Chicago. (1999). 128 pp.
- Cutler, Irving. The Jews of Chicago: From Shtetl to Suburb. (1996). 316 pp.
- Dahm, Charles and Ghelardi, Robert. Power and Authority in the Catholic Church: Cardinal Cody in Chicago. (1982). 334 pp.
- DeGenova, Nicholas. Working the Boundaries: Race, Space, and "Illegality" in Mexican Chicago. (2005). 329 pp.
- Duis, Perry R. Challenging Chicago: Coping with Everyday Life, 1837-1920. (1998). 430 pp. online review
- Duis, Perry R. The Saloon: Public Drinking in Chicago and Boston, 1880-1920 (1983).
- Erdmans, Mary Patrice. Opposite Poles: Immigrants and Ethnics in Polish Chicago, 1976-1990. (1998). 267 pp.
- Fuerst, J. S. and Hunt, D. Bradford, eds. When Public Housing Was Paradise: Building Community in Chicago. (2003) 228 pp.
- Green, Paul M., and Melvin G. Holli. Chicago, World War II (2003) excerpt and text search
- Greene, Victor. For God and Country: The Rise of Polish and Lithuanian Ethnic Consciousness in America, 1860-1910. (1975). 202 pp.
- Guglielmo, Thomas A. White on Arrival: Italians, Race, Color, and Power in Chicago, 1890-1945. (2003). 296 pp. online edition
- Harden, Jacalyn D. Double Cross: Japanese Americans in Black and White Chicago. (2003). 232 pp.
- Holli, Melvin G. and Jones, Peter d'A., eds. Ethnic Chicago: A Multicultural Portrait. (4th ed. 1995). 648 pp. essays by scholars on each major ethnic group
- Hoy, Suellen. Good Hearts: Catholic Sisters in Chicago's Past. (2006). 242 pp.
- Jaher, Frederic Cople. The Urban Establishment: Upper Strata in Boston, New York, Charleston, Chicago, and Los Angeles. (1982). 777 pp.
- Kantowicz, Edward R. Corporation Sole: Cardinal Mundelein and Chicago Catholicism. (1983). 295 pp.
- Keil, Hartmut, ed. German Workers' Culture in the United States, 1850 to 1920. (1988). 330 pp.
- Keil, Hartmut and Jentz, John B., eds. German Workers in Industrial Chicago, 1850-1910: A Comparative Perspective. (1983). 252 pp.
- Lovoll, Odd S. A Century of Urban Life: The Norwegians in Chicago before 1930. (1988). 367 pp.
- McCaffrey, Lawrence J.; Skerrett, Ellen; Funchion, Michael F.; and Fanning, Charles. The Irish in Chicago. (1987). 171 pp.
- Nelli, Humbert S. The Italians in Chicago: A Study in Ethnic Mobility, 1880–1930. (1970). 300 pp.
- Pacyga, Dominic A. Polish Immigrants and Industrial Chicago: Workers on the South Side, 1880–1920. (1991). 322 pp. excerpt and text search
- Padilla, Felix M. Puerto Rican Chicago. (1987). 277 pp.
- Parot, Joseph John. Polish Catholics in Chicago, 1850-1920: A Religious History. (1982) 298 pp.
- Philpott, Thomas Lee. The Slum and the Ghetto: Immigrants, Blacks, and Reformers in Chicago, 1880–1930. (1978). 437 pp.
- Posadas, Barbara M. "Crossed Boundaries in Interracial Chicago: Filipino American Families since 1925," in Unequal Sisters: A Multi-Cultural Reader in U.S. Women's History, ed. Vicki L. Ruiz and Ellen Carol DuBois (1994), 319+.
- Rangaswamy, Padma. Namasté America: Indian Immigrants in an American Metropolis. 2000. 366 pp.
- Robertson, Darrel M. The Chicago Revival, 1876: Society and Revivalism in a Nineteenth century City. (1989). 225 pp.
- Sanders, James W. The Education of an Urban Minority: Catholics in Chicago, 1833–1965. (1977). 278 pp.
- Shanabruch, Charles. Chicago's Catholics: The Evolution of an American Identity. (1981). 296 pp.
- Shaw, Stephen J. The Catholic Parish as a Way-Station of Ethnicity and Americanization: Chicago's Germans and Italians, 1903–1939.(1991). 206 pp.
- Swierenga, Robert P. Dutch Chicago: A History of the Hollanders in the Windy City. (2002). 825 pp. excerpt and text search
- Tischauser, Leslie V. The Burden of Ethnicity: The German Question in Chicago, 1914–1941. (1990). 282 pp.
- Tuttle, William M., Jr. Race Riot: Chicago in the Red Summer of 1919. (1970). 305 pp.
- Wade, Louise Carroll. Chicago's Pride: The Stockyards, Packingtown, and Environs in the Nineteenth Century. (1987). 423 pp.
- Walch, Timothy. The Diverse Origins of American Catholic Education: Chicago, Milwaukee, and the Nation. (1988). 235 pp.
- Wellman, James K., Jr. The Gold Coast Church and the Ghetto: Christ and Culture in Mainline Protestantism. (1999). 241 pp.
Sports, entertainment, music, newspapers[edit]
- Kenney, William Howland. Chicago Jazz: A Cultural History, 1904–1930. (1993). 233 pp.
- Kinsley, Philip. The Chicago Tribune: Its First Hundred Years (1943) online edition
- Sengstock, Charles A., Jr. That Toddlin' Town: Chicago's White Dance Bands and Orchestras, 1900–1950. (2004). 244 pp.
- Smith, Richard Norton. The Colonel: The Life and Legend of Robert R. McCormick, 1880–1955. (1997). 597 pp.
- Spirou, Costas and Bennett, Larry. It's Hardly Sportin': Stadiums, Neighborhoods, and the New Chicago. (2003). 212 pp.
- Vaillant, Derek. Sounds of Reform: Progressivism & Music in Chicago, 1873–1935. (2003). 401 pp.
- Ziemba, Joe. When Football Was Football: The Chicago Cardinals and the Birth of the NFL. (1999). 408 pp.
Reputation, images, visions, planning[edit]
- Fairfield, John D. The Mysteries of the Great City: The Politics of Urban Design, 1877–1937. (1993). 320 pp.
- Flanagan, Maureen A. Seeing with Their Hearts: Chicago Women and the Vision of the Good City, 1871–1933. (2002). 319 pp. excerpt and text search
- Hines, Thomas S. Burnham of Chicago: Architect and Planner. (1974). 445 pp.
- Miller, Ross. American Apocalypse: The Great Fire and the Myth of Chicago. 1990. 287 pp.
- Ciccone, F. Richard Royko: A Life in Print (2001) online edition
- Smith, Carl S. Chicago and the American Literary Imagination, 1880–1920. (1984). 232 pp.
- Spears, Timothy B. Chicago Dreaming: Midwesterners and the city, 1871–1919. (2005). 322 pp.
- Williams, Kenny J. A Storyteller and a City: Sherwood Anderson's Chicago. (1988). 314 pp.
- Williams, Kenny J. and Duffy, Bernard, eds. Chicago's Public Wits: A Chapter in the American Comic Spirit. (1983). 289 pp.
- Williams, Kenny J. Prairie Voices: A Literary History of Chicago from the Frontier to 1893. (1980). 529 pp.
Primary sources[edit]
- Byrne, Jane. My Chicago. (1992), mayor in 1980s
- Despres, Leon M. and Heise, Kenan. Challenging the Daley Machine: A Chicago Alderman's Memoir. (2005). 168 pp.
- Fanning, Charles, ed. Mr. Dooley and the Chicago Irish: An Anthology. (1976).
- Keil, Hartmut and Jentz, John B., eds. German Workers in Chicago: A Documentary History of Working-Class Culture from 1850 to World War I. (1988). 427 pp.
- Pierce, Bessue Louise, ed. As Others See Chicago: Impressions of Visitors, 1673–1933. (1937, reprinted 2004). 548 pp
- Royko, Mike. For the Love of Mike: More of the Best of Mike Royko. (2001). 270 pp.
- Sandburg, Carl. Chicago Poems (1916) online edition
- Thomas, William, and Florian Znaniecki. The Polish Peasant in Europe and America. 2 vol 1920, ISBN 0252010922 (1984 printing). ; famous classic online edition
Notes[edit]
- ↑ http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/17/1714000.html
- ↑ https://www.census.gov/population/estimates/metro_general/2006/CSA-EST2006-alldata.csv
- ↑ http://www.thesearstower.com/buildinginfo.axis?type=n&name=Property Profile
- ↑ The Art Institute of Chicago
- ↑ Schallhorn, Kaitlyn (August 9, 2018). Chicago shootings put spotlight on Illinois gun laws. Fox News. Retrieved August 9, 2018.
- ↑ Richardson, Valerie (April 5, 2019). Left-wing wave: More socialists than Republicans to hold seats on Chicago City Council. The Washington Times. Retrieved April 5, 2019.
- ↑ https://www.click2houston.com/features/2020/01/24/ask-2-when-will-houston-overtake-chicago-as-the-third-most-populous-city/
- ↑ Elaine Lewinnek, "Better than a Bank for a Poor Man? Home Financing Strategies in Early Chicago." Journal of Urban History 2006 32(2): 274-301. Issn: 0096-1442 Fulltext: Sage; see also Joseph C. Bigott, From Cottage to Bungalow: Houses and the Working Classes in Metropolitan Chicago, 1869-1929 (2001) excerpt and text search
- ↑ Lorien Foote, "Bring the Sea to Us: the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal and the Industrialization of the Midwest, 1885-1929." Journal of Illinois History 1999 2(1): 39-56. Issn: 1522-0532
- ↑ Timothy B. Neary, "Chicago-style Environmental Politics: Origins of the Deep Tunnel Project." Journal of Illinois History 2001 4(2): 83-102. Issn: 1522-0532
- ↑ See Catherine M. Lewis, The Changing Face of Public History: The Chicago Historical Society and the Transformation of an American Museum. (2005). 172 pp.
- ↑ Ascoli (2006)
- ↑ David Paul Nord, "Read All about It"" Chicago History 2002 31(1): 26-57. Issn: 0272-8540
- ↑ It is now part of Exelon Corporation, and serves 3.8 million customers in Chicago and northern Illinois.
- ↑ David Witwer, "Unionized Teamsters and the Struggle over the Streets of the Early-Twentieth-century City." Social Science History 2000 24(1): 183-222. Issn: 0145-5532 Fulltext: Project Muse
- ↑ Anthony P. Hatch, "Inferno at the Iroquois." Chicago History 2003 32(2): 4-31. Issn: 0272-8540
- ↑ George W. Hilton, Eastland: Legacy of the Titanic. (1995).
- ↑ Christopher R. Browning; Wallace, Danielle; Feinberg, Seth L.; and Cagney, Kathleen A.; Klinenberg, Eric (Reply). "Neighborhood Social Processes, Physical Conditions, and Disaster-related Mortality: the Case of the 1995 Chicago Heat Wave." American Sociological Review 2006 71(4): 661-678. Issn: 0003-1224
- ↑ Jeffrey S. Adler, "'It Is His First Offense. We Might as Well Let Him Go': Homicide and Criminal Justice in Chicago, 1875-1920." Journal of Social History 2006 40(1): 5-24. Issn: 0022-4529 Fulltext: History Cooperative and Project Muse
- ↑ Adler, "'We've Got a Right to Fight; We're Married': Domestic Homicide in Chicago, 1875-1920." 2003
- ↑ Bill Barnhart, "Public Enemies: Chicago Origins of Personalized Anticrime Campaigns." Journal of Illinois History 2001 4(4): 258-270. Issn: 1522-0532
- ↑ Gareth Canaan, "'Part of the Loaf': Economic Conditions of Chicago's African-American Working Class During the 1920's." Journal of Social History 2001 35(1): 147-174. Issn: 0022-4529 Fulltext: Project Muse
- ↑ Jon Bekken, "Negotiating Class and Ethnicity: the Polish-language Press in Chicago." Polish American Studies 2000 57(2): 5-29. Issn: 0032-2806
- ↑ http://www.law.umkc.edu/faculty/projects/ftrials/Chicago7/Daley2.html
- ↑ Melvin G. Holli, "Political Equilibrium and the Daley Eras in Chicago." Continuity 1999 (23): 83-96. Issn: 0277-1446
- ↑ D. Bradford Hunt, "What Went Wrong with Public Housing in Chicago? A History of the Robert Taylor Homes." Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society 2001 94(1): 96-123. Issn: 1522-1067; Sudhir Alladi Venkatesh, American Project: The Rise and Fall of a Modern Ghetto, (2002).
- ↑ Charlotte Brooks, "In the Twilight Zone Between Black and White: Japanese American Resettlement and Community in Chicago, 1942-1945." Journal of American History 2000 86(4): 1655-1687. Issn: 0021-8723 Fulltext: History Cooperative and Jstor
- ↑ Lilia Fernández, "Latina/o Migration and Community Formation in Postwar Chicago: Mexicans, Puerto Ricans, Gender, and Politics, 1945-1975." PhD dissertation U. of California, San Diego 2005. 302 pp. DAI 2006 66(10): 3779-A. DA3191767 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses. See also Mérida M. Rúa, "Claims to `the City': Puerto Rican Latinidad amid Labors of Identity, Community, and Belonging in Chicago." PhD dissertation U. of Michigan 2004. 219 pp. DAI 2005 65(10): 3877-A. DA3150079 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- ↑ https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-8546473/Almost-50-Chicago-cops-injured-protesters-throw-fireworks-frozen-bottles.html
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-52984535
- ↑ https://twitter.com/silver_report/status/1266551798057316364
- ↑ https://www.chicagobusiness.com/greg-hinz-politics/there-no-doubt-was-organized-effort
- ↑ https://www.redstate.com/elizabeth-vaughn/2020/06/09/chicago-woman-goes-ballistic-because-shop-owners-with-guns-prevent-her-from-looting/
- ↑ https://www.breitbart.com/politics/2020/06/08/chicago-mayor-lori-lightfoot-in-expletive-filled-fight-with-alderman-over-black-lives-matter-riots/
- ↑ https://news.wttw.com/2020/06/05/what-are-we-going-have-left-our-community-aldermen-react-panic-sorrow-unrest
- ↑ https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefings-statements/president-donald-j-trumps-letter-governor-illinois-mayor-chicago/
- ↑ https://www.redstate.com/nick-arama/2020/07/17/dozens-of-blm-and-antifa-full-on-attack-police-in-chicago-police-reinforcements-make-them-regret-it/
- ↑ Dozens of BLM and Antifa Full On Attack Police in Chicago, Police Reinforcements Make Them Regret It at Red State
- ↑ https://apnews.com/5a4b1f1cde30f26bd1a9dcd6f2390d83
- ↑ https://twitter.com/RitaPanahi/status/1394813036741885954
- ↑ https://www.bizpacreview.com/2021/05/19/reporters-say-chicago-mayor-lightfoot-limiting-interviews-to-black-and-brown-journalists-1076308/
- ↑ https://www.bizpacreview.com/2021/05/20/lightfoot-defends-her-bigotry-slams-overwhelming-whiteness-and-maleness-of-chicago-media-outlets-1076689/
- ↑ https://therightscoop.com/cancel-back-after-mayor-lightfoot-cancels-white-reporters-one-hispanic-reporter-cancels-her-in-return/
- ↑ https://www.bizpacreview.com/2021/05/21/black-journalists-group-reluctantly-says-it-cannot-support-chicago-mayors-bigotry-against-white-scribes-1077398/
- ↑ https://townhall.com/tipsheet/katiepavlich/2021/05/21/tulsi-gabbard-calls-on-chicago-mayor-to-resign-over-antiwhite-racism-n2589828
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/mkt_breakingnews/homicides-have-skyrocketed-in-these-six-democratic-cities-black-people-are-disproportionately-the-victims-data-shows_3872643.html
- ↑ https://www.foxbusiness.com/markets/ken-griffin-citadel-bail-chicago
- ↑ https://theredelephants.com/there-is-undeniable-mathematical-evidence-the-election-is-being-stolen/
- ↑ https://theredelephants.com/there-is-undeniable-mathematical-evidence-the-election-is-being-stolen/
- ↑ John L. Rury, "Race, Space, and the Politics of Chicago's Public Schools: Benjamin Willis and the Tragedy of Urban Education." History of Education Quarterly 1999 39(2): 117-142. Issn: 0018-2680 Fulltext: in Jstor
- ↑ Jim Carl, "Harold Washington and Chicago's Schools Between Civil Rights and the Decline of the New Deal Consensus, 1955-1987." History of Education Quarterly 2001 41(3): 311-343. Issn: 0018-2680 Fulltext: in Jstor
- ↑ See Jodi Wilgoren, "Chief Executive of Chicago Schools Resigns," New York Times June 7, 2001
- ↑ David V. Groeninger, "Chicago Imagined: The Role of Newspaper Columnists in Creating a City of the Mind, 1890-1930." PhD dissertation Loyola U., Chicago 2005. 280 pp. DAI 2005 66(5): 1925-A. DA3175764 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses. See also Sarah Susan Marcus, "Up from the Prairie: Depictions of Chicago and the Middle West in Popular Culture, 1865-1983." PhD dissertation U. of Wisconsin, Madison 2001. 445 pp. DAI 2001 62(4): 1554-1555-A. DA3012550 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
| ||||||||||||||||||||
References[edit]
Categories: [Illinois Cities and Towns] [Urban History] [Featured articles] [Anti Second Amendment] [Gun Control] [Most Liberal American Cities]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/15/2023 22:10:55 | 197 views
☰ Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Chicago | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:






 KSF
KSF