Dissection (Medical)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Dissection (medical) | |
|---|---|
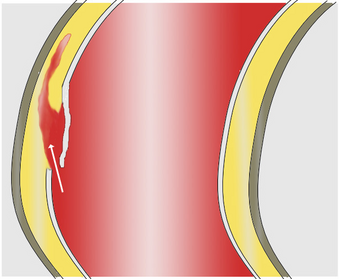 | |
| Aortic dissection | |
| Specialty | Vascular surgery |
A dissection is a tear within the wall of a blood vessel, which allows blood to separate the wall layers. Usually, a dissection is an arterial wall dissection, but rarely it may be a vein wall dissection (VWD).[1]
By separating a portion of the wall of the artery (a layer of the tunica intima or tunica media), a dissection creates two lumens or passages within the vessel, the native or true lumen, and the "false lumen" created by the new space within the wall of the artery.
Description
Dissections become threatening to the health of the organism when growth of the false lumen prevents perfusion of the true lumen and the end organs perfused by the true lumen. For example, in an aortic dissection, if the left subclavian artery orifice were distal to the origin of the dissection, then the left subclavian would be said to be perfused by the false lumen, while the left common carotid (and its end organ, the left hemisphere of the brain) if proximal to the dissection, would be perfused by the true lumen proximal to the dissection.
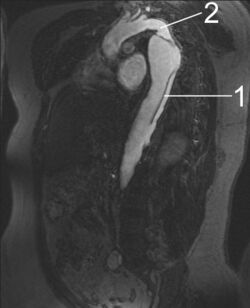
1 Aorta descendens with dissection
2 Aorta isthmus
Vessels and organs that are perfused from a false lumen may be well-perfused to varying degrees, from normal perfusion to no perfusion. In some cases, little to no end-organ damage or failure may be seen. Similarly, vessels and organs perfused from the true lumen but distal to the dissection may be perfused to varying degrees. In the above example, if the aortic dissection extended from proximal to the left subclavian artery takeoff to the mid descending aorta, the common iliac arteries would be perfused from the true lumen distal to the dissection but would be at risk for malperfusion due to occlusion of the true lumen of the aorta by the false lumen.
Types
Examples include:
- Aortic dissection (aorta)
- Coronary artery dissection (coronary artery)
- Carotid artery dissection (carotid artery)
- Vertebral artery dissection (vertebral artery)
Carotid and vertebral artery dissection are grouped together as "cervical artery dissection".
References
- ↑ "Vein wall dissection: a rare puncture-related complication of brachiocephalic fistula. Gray-scale and color Doppler sonographic findings.". J Clin Ultrasound 33 (9): 464-7. 2005. doi:10.1002/jcu.20171. PMID 16281272. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16281272.
External links
| Classification | D
|
|---|
Categories: [Angiology]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/04/2024 19:21:50 | 6 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Medicine:Dissection_(medical) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF