Vivaldi (Web Browser)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki  | |
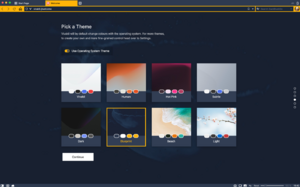 Vivaldi running on macOS | |
| Developer(s) | Vivaldi Technologies |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 27 January 2015[1][2] |
| Stable release(s) [±] | |
5.7 (February 16, 2023[3]) [±]
| |
| Written in | C++[5] |
| Engines | Blink (WebKit on iOS/iPadOS), V8 |
| Operating system |
|
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64, ARM (macOS, Linux & Android only) |
| Available in | 53 languages[7] |
List of languages Albanian, Arabic, Armenian, Basque, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, Frisian, Galician, Georgian, German, Greek, Hungarian, Icelandic, Ido, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Kurdish, Latvian, Lithuanian, Lojban, Macedonian, Norwegian (Bokmal), Norwegian (Nynorsk), Persian, Polish, Portuguese (Brazil), Portuguese (Portugal), Romanian, Russian, Sardinian, Scots Gaelic, Serbian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Spanish (Peru), Swedish, Turkish, Ukrainian, Vietnamese | |
| Type | Web browser |
| License | Proprietary freeware[lower-alpha 1] |
| Website | vivaldi |
Vivaldi (/vɪˈvɑːldi, vəˈv-/)[9][10] is a freeware, cross-platform web browser with a built-in email client developed by Vivaldi Technologies, a company founded by Tatsuki Tomita and Jon Stephenson von Tetzchner, who was the co-founder and CEO of Opera Software. Vivaldi was initially released on 27 January 2015.[11][12]
Although intended for general users, it is first and foremost targeted towards technically-inclined users as well as former Opera users disgruntled by its transition from the Presto layout engine to a Chromium-based browser that resulted in the loss of many of its distinctive features.[11][13] Despite also being Chromium-based, Vivaldi aims to revive the features of the Presto-based Opera with its own proprietary modifications.[14][15]
Vivaldi replaced Firefox as the default browser on the Manjaro Cinnamon Community Edition.[16] (As of April 2023), Vivaldi has more than 2.4 million active users.[17]
History
Vivaldi began as a virtual community website that replaced My Opera, which was shut down by Opera Software in March 2014.[18] Jon Stephenson von Tetzchner was angered by this decision because he believed that this community helped make the Opera web browser what it was. Tetzchner then launched the Vivaldi Community—a virtual community focused on providing registered users with a discussion forum, blogging service, and numerous other practical web services—to make up for My Opera's closure.
Later, on 27 January 2015, Vivaldi Technologies launched the first technical preview of the Vivaldi web browser.[19] In the first 10 days of being available, Vivaldi was downloaded 500,000 times, which, according to Jon von Tetzchner, this was "a very high number, especially if you consider that it's still a technical preview".[20] Its name comes from the Italian composer Antonio Vivaldi, which, according to Tatsuki Tomita, is an easy name to be remembered and understood worldwide.[12]
The first stable release of the browser, version 1.0, was released on 6 April 2016.[21] Initially being available only for Linux, macOS, and Windows, Vivaldi was launched with the intent of giving additional functionality, when other browsers on the market at the time tried "their best at simplifying, and streamlining their products", according to Ars Technica.[22]
In September 2021, Vivaldi replaced Firefox as the default browser on the Manjaro Cinnamon Community Edition to a mixed reception from the Linux community, as Vivaldi is not free and open source software;[16] Manjaro developers cited this decision on Vivaldi's feature-richness and exceptional customisability.[23] In December 2021, Vivaldi became the first web browser to be available for the Android Automotive operating system used in the Swedish electric vehicle manufacturer Polestar's Polestar 2. For safety purposes, the browser can only be used when the car is parked.[24]
Features
Vivaldi has a minimalistic user interface with basic icons and fonts, and, optionally, a colour scheme that changes based on the background and design of the web page being visited.[25] The browser also allows users to customise the appearance of UI elements such as background colour, overall theme, address bar and tab positioning, and start pages.[26] According to CEO Jon von Tetzchner, Vivaldi's unique customisability is how the browser caters to experienced users.[27]
Vivaldi comes with built-in ad blocker, pop up blocker and tracker blocker. These features block intrusive ads, help web pages load faster, and protect against malicious ads and trackers.[28] It comes with built-in e-mail client with IMAP and POP3 support. Some of the Mail features are saved searches and offline message search.[29] The browser can be used as a feed reader to save RSS and Atom feeds.[30] It also comes with built-in Vivaldi Calendar to manage events in the browser.[31] Vivaldi Translate is powered by Lingvanex and can instantly translate websites, without the need for third-party extensions.[32]
Vivaldi features the ability to "stack" and "tile" tabs, annotate web pages, and add notes to bookmarks.[33][34] Furthermore, users can place digital bookmarks on a "speed dial" page for quick access and harness "quick commands" to search bookmarks, browsing history, open tabs, and settings.[35] Vivaldi is built around and based on web technologies such as HTML5, Node.js, React.js, and numerous NPM modules.[36] As of Technical Preview 4, Vivaldi also supports numerous mouse gestures for actions like tab switching and keyboard activation.[27] Vivaldi can also be set to a "Chromeless UI", which gives users more screen real-estate and the ability to focus on a single page without distractions.[37] To accommodate users who prefer to use a large number of tabs at the same time, Vivaldi supports hibernation for both individual tabs and for tab stacks, freeing resources while the user does not actively use those tabs.
Extensions
Vivaldi can use many browser extensions developed for Google Chrome and Firefox (they both use the WebExtensions API[38]), and users can install extensions directly from the Chrome Web Store. Most of these work properly in Vivaldi, with the exception of user interface customisations due to its visual changes to the Chromium source code.[39][40]
Starting with version 2.10, Vivaldi changed its user agent string to mimic a generic build of Chromium, which results in it not being recorded as a unique browser and causing a decrease in its recorded market share.[41]
Reception
Ars Technica reviewer Scott Gilbertson wrote about version 1.0 in April 2016. He praised its innovative features, such as its tab handling, while noting that it will most likely remain a niche browser and not see widespread uptake.[42] In October 2018, Gilbertson gave version 2.0 a very positive review and stated that Vivaldi is now his usual browser and that he would be hard put to go back to a browser without its unique features.[43]
Ghacks editor-in-chief Martin Brinkmann wrote about the privacy of Vivaldi in January 2018. He criticised the lack of an opt-out option for the unique user ID it generates to get general statistics about the browser's userbase, but commented that the unique ID "is easy enough to delete" and "it is different anyway if you use Vivaldi on multiple devices".[44]
TechRadar's managing editor, Desire Athow, published a review of Vivaldi in August 2021. In the review, Athow praised browser's focus on the productivity, highlighting its advanced tab management features such as tab hibernation, multi-tab management, and split-screen view. However, he also pointed out that Vivaldi's extensive feature set and high degree of customizability can also be overwhelming for a casual user, making it clear that browser is not designed for everyone.[45]
Wired's senior writer, Scott Gilbertson, reviewed version 4.0 of the browser in June 2021. He praised the high number of customization options, suggesting it might be the "Emacs of web browsers" for its personalized user experience. Gilbertson highlighted the browser's unique features, including a built-in email client, RSS feed reader, calendar, and translation tools. Additionally, he recommended Vivaldi to users searching for a more tailored and efficient browsing experience, while also praising its performance.[46]
Notes
- ↑ The user interface (UI) layer of the browser is closed-source. The C++ backend and the open-source Chromium codebase used in the browser is released under BSD-3.[8]
References
- ↑ "Vivaldi Tech Preview 1 Just Arrived". Vivaldi Technologies. 27 January 2015. https://vivaldi.com/blog/vivaldi-tech-preview-1-just-arrived/.
- ↑ Paul, Ian (27 January 2015). "New Vivaldi browser aims to win over power users". PCWorld. https://www.pcworld.com/article/431512/new-vivaldi-browser-aims-to-win-over-power-users.html.
- ↑ "Changelog – Vivaldi on Desktop". 2023-02-16. https://vivaldi.com/changelog-vivaldi-browser-5-7/.
- ↑ "Changelog – Vivaldi on Android". 2023-02-23. https://vivaldi.com/blog/vivaldi-on-android-5-7/.
- ↑ "Vivaldi browser: Interview with Jon Stephenson von Tetzchner". utappia.org. September 21, 2016. https://utappia.org/2016/09/21/vivaldi-browser-interview-with-jon-stephenson-von-tetzchner/.
- ↑ "Download Vivaldi". Vivaldi Technologies. https://vivaldi.com/download/.
- ↑ "Vivaldi version 1.13.1008.32 for Windows (7+)". Vivaldi Technologies. November 25, 2017. https://downloads.vivaldi.com/stable/Vivaldi.1.13.1008.32.exe.
- ↑ Picalausa, Julien (2021-07-09). "Why isn't Vivaldi browser open-source?". https://vivaldi.com/blog/technology/why-isnt-vivaldi-browser-open-source. "Vivaldi is built in roughly three layers: 1. Chromium, the foundation for our browser. 2. A lot of backend C++ code to support unique features like Ad blocker and Notes. 3. Our UI for desktop (HTML+CSS+JS) and Android [...] Roughly 92% of the browser’s code is open source coming from Chromium, 3% is open source coming from us, which leaves only 5% for our UI closed-source code."
- ↑ Vivaldi 5.3: Tweak and tune your browser with the new Editable Toolbars. Vivaldi. 1 June 2022. Retrieved 2 October 2022 – via YouTube.
- ↑ What's New in Vivaldi | April 2022. Vivaldi. 2022-04-06. Retrieved 2022-10-03 – via YouTube.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Shankland, Stephen (January 27, 2015). "Ex-Opera CEO composes Vivaldi, a new Web browser". CNET. CBS Interactive. https://www.cnet.com/news/ex-opera-ceo-launches-new-browser-vivaldi/.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Vivaldi: testamos o navegador de internet que tem personalização completa" (in pt). Grupo NZN. 4 November 2015. https://www.tecmundo.com.br/navegador/88912-vivaldi-testamos-navegador-internet-tem-personalizacao-completa.htm.
- ↑ Minic, Ivan (February 10, 2015). "Jon S. von Tetzchner: We will (re)create a browser you love.". Medium. https://medium.com/@burek/jon-s-von-tetzchner-we-will-re-create-a-browser-you-love-123f766386c4.
- ↑ Gilbertson, Scott (March 6, 2015). "Hands-on with Vivaldi, the new Web browser for power users". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2015/03/hands-on-with-vivaldi-the-new-web-browser-for-power-users/.
- ↑ "Vivaldi is building "Opera as it should've been"". Ars Technica. January 16, 2017. https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2017/01/vivaldi-opera-one-million-users/.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Borisov, Bobby (9 September 2021). "Manjaro Cinnamon Edition Decided to Switch from Firefox to Vivaldi". Linuxiac. https://linuxiac.com/manjaro-cinnamon-edition-switched-from-firefox-to-vivaldi/.
- ↑ "We're in Control" (in en). https://vivaldi.com/company/#WeAreInControl.
- ↑ Shankland, Stephen (23 January 2014). "Ex-CEO picks up where Opera left off, launching Vivaldi site". CNET. CBS Interactive. https://www.cnet.com/news/ex-ceo-picks-up-where-opera-left-off-launching-vivaldi-site/.
- ↑ Shankland, Stephen (2015-01-27). "Ex-Opera CEO composes Vivaldi, a new Web browser" (in en). https://www.cnet.com/tech/services-and-software/ex-opera-ceo-launches-new-browser-vivaldi/.
- ↑ Dagenborg, Joachim (6 February 2015). "Vivaldi browser hits 500,000 downloads in first 10 days". Reuters. Oslo, Norway. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-internet-vivaldi-idUSKBN0LA1JH20150206.
- ↑ "Vivaldi 1.0: Not for everybody, just you". Vivaldi Technologies. 6 April 2016. https://vivaldi.com/blog/vivaldi-finale-1-0/.
- ↑ Andrii, Degeler (6 April 2016). "Vivaldi 1.0 tries to reverse web browser simplification trend". Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2016/04/vivaldi-browser-version-1-0-released/.
- ↑ "Vivaldi Replaces Firefox as the Default Browser on Manjaro Linux Cinnamon". betanews. 9 September 2021. https://betanews.com/2021/09/09/manjaro-linux-cinnamon-vivaldi-web/.
- ↑ "Vivaldi in Polestar: The first browser for Android Automotive OS". Vivaldi Browser. 22 December 2021. https://vivaldi.com/blog/a-browser-first-vivaldi-now-in-polestar-2/.
- ↑ Lardinois, Frederic (March 8, 2015). "Vivaldi Is Quickly Becoming The Alternative Browser To Beat". TechCrunch. https://techcrunch.com/2015/03/08/vivaldi-chrome-alternative-tech-preview-2/.
- ↑ Brinkmann, Martin (June 2, 2015). "Latest Vivaldi snapshot introduces interface scaling". Ghacks. https://www.ghacks.net/2015/06/02/latest-vivaldi-snapshot-introduces-interface-scaling/.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Frederic, Lardinois (July 16, 2015). "Vivaldi Browser Gets New Customization Options, Mouse Gestures And Experimental Chrome Extension Support". TechCrunch. AOL Inc.. https://techcrunch.com/2015/07/15/vivaldi-browser-gets-new-customization-options-mouse-gestures-and-experimental-chrome-extension-support/.
- ↑ "Ad Blocker – fast and free, no extensions needed". https://vivaldi.com/features/ad-blocker/.
- ↑ "Mail | an email client built into your browser | Vivaldi". https://vivaldi.com/features/mail/.
- ↑ "Feed Reader | Read feeds from the sources you choose | Vivaldi". https://vivaldi.com/features/feed-reader/.
- ↑ "Calendar | Manage private and shared calendars | Vivaldi". https://vivaldi.com/features/calendar/.
- ↑ "Translate | Private translation on desktop and Android | Vivaldi". https://vivaldi.com/features/translate/.
- ↑ Williams, Owen (April 28, 2015). "Latest Vivaldi browser preview brings useful tab stacking feature and more". The Next Web. https://thenextweb.com/apps/2015/04/28/latest-vivaldi-browser-preview-brings-useful-tab-stacking-feature-mouse-gestures-and-more/.
- ↑ Paul, Ian (April 28, 2015). "This is neat: You can stack and tile browser tabs in the Vivaldi beta browser for power users". PCWorld. https://www.pcworld.com/article/2915914/this-is-neat-you-can-stack-and-tile-browser-tabs-in-the-vivaldi-beta-browser-for-power-users.html.
- ↑ Clarke, Victor (January 27, 2015). "Vivaldi Browser: a Quick Look at the Opera Successor". LifeHacker. https://hackerspace.kinja.com/vivaldi-browser-a-quick-look-at-the-opera-successor-1681989432.
- ↑ Williams, Owen (January 27, 2015). "Meet Vivaldi, a new browser from the former CEO of Opera". The Next Web. https://thenextweb.com/apps/2015/01/27/meet-vivaldi-new-browser-former-ceo-opera/.
- ↑ Ødegaard, Ruarí (July 17, 2015). "Snapshot 1.0.228.3 – With Chromeless UI". Vivaldi Technologies. https://vivaldi.net/en-US/blogs/teamblog/item/41-snapshot-1-0-228-3-with-chromeless-ui.
- ↑ "MDN: Browser Extensions". June 8, 2023. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Add-ons/WebExtensions. "Extensions, or add-ons, can modify and enhance the capability of a browser. Extensions for Firefox are built using the WebExtensions API cross-browser technology. The technology for extensions in Firefox is, to a large extent, compatible with the extension API supported by Chromium-based browsers such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Opera. In most cases, extensions written for Chromium-based browsers run in Firefox with just a few changes."
- ↑ Williams, Owen (July 16, 2015). "Sick of Chrome? Vivaldi can now run your favorite extensions". The Next Web. https://thenextweb.com/insider/2015/07/16/sick-of-chrome-vivaldi-can-now-run-your-favorite-extensions/.
- ↑ "Using Extensions in Vivaldi". Vivaldi Browser Help. January 29, 2016. https://help.vivaldi.com/article/extensions/.
- ↑ "Vivaldi 2.10: No strings attached". Vivaldi Technologies. December 19, 2019. https://vivaldi.com/blog/vivaldi-2-10-no-strings-attached-2/.
- ↑ Gilbertson, Scott (April 28, 2016). "Even at 1.0, Vivaldi closes in on the cure for the common browser". Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2016/04/even-at-1-0-vivaldi-closes-in-on-the-cure-for-the-common-browser/.
- ↑ Gilbertson, Scott (October 19, 2018). "Vivaldi 2.0 review: The modern Web browser does not have to be so bland". Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2018/10/vivaldi-2-0-review-meet-your-ideal-browser-if-youre-willing-to-invest-time/.
- ↑ Brinkmann, Martin (January 30, 2018). "Vivaldi browser and privacy". Ghacks. https://www.ghacks.net/2018/01/30/vivaldi-browser-privacy/.
- ↑ Athow, Desire (2021-08-29). "Vivaldi browser review" (in en). https://www.techradar.com/reviews/vivaldi.
- ↑ Gilbertson, Scott. "You're Probably Not Using the Web's Best Browser" (in en-US). Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. https://www.wired.com/story/vivaldi-4-2021/.
External links
 |
Categories: [Android web browsers] [Cross-platform web browsers] [Email client software for Linux] [Linux web browsers] [Windows email clients] [Windows web browsers]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 05/12/2024 16:34:49 | 6 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Software:Vivaldi_(web_browser) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF